Connect to Azure SQL resource with Microsoft Entra authentication
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
Azure SQL Managed Instance
Azure Synapse Analytics
This article shows you how to use Microsoft Entra authentication to connect to Azure SQL Database, Azure SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics.
Prerequisites
To connect to your Azure SQL resource, you need to have configured Microsoft Entra authentication for your resource.
To confirm the Microsoft Entra administrator is properly set up, connect to the master database using the Microsoft Entra administrator account.
To create a Microsoft Entra-based contained database user, connect to the database with a Microsoft Entra identity with access to the database and at least the ALTER ANY USER permission.
Connect with SSMS or SSDT
The following procedures show you how to connect to SQL Database with a Microsoft Entra identity using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or SQL Server Database Tools (SSDT).
Microsoft Entra Integrated
Use this method when you want to log in using your Windows credentials that are federated into Microsoft Entra ID. For more information, see Microsoft Entra seamless single sign-on.
Start SSMS or SSDT and in the Login tab of the Connect to Server (or Connect to Database Engine) dialog box:
- Provide the Server name in the format
<server-name>.database.windows.net. - For Authentication, select Microsoft Entra Integrated. No need to enter a password because your existing credentials are presented for the connection.
- For Encryption, select Strict (SQL Server 2022 and Azure SQL), which should be used to connect to Azure SQL resources.
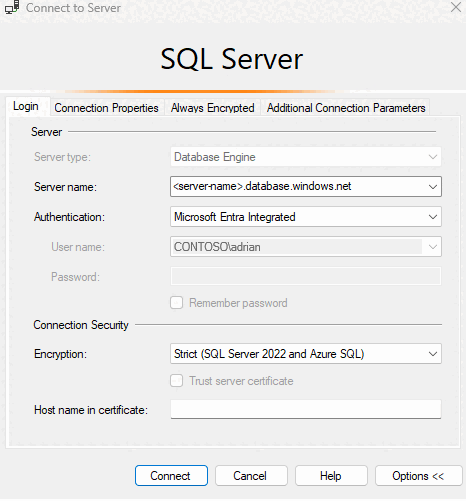
- Provide the Server name in the format
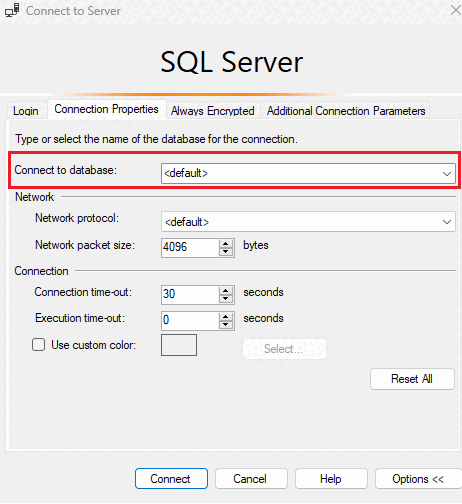
On the Connection properties tab, in the Connect to database field, type the name of the user database you want to connect to.
Microsoft Entra Password
Use this method when connecting with a Microsoft Entra principal name using the Microsoft Entra managed domain. You can also use it for federated accounts without access to the domain when, for example, working remotely.
Use this method to authenticate to the database in SQL Database or SQL Managed Instance with Microsoft Entra cloud-only identity users, or those who use Microsoft Entra hybrid identities. This method supports users who want to use their Windows credential, but their local machine isn't joined with the domain (for example, using remote access). In this case, a Windows user can indicate their domain account and password, and can authenticate to the database in SQL Database, the SQL Managed Instance, or Azure Synapse.
Start SSMS or SSDT and on the Login tab of the Connect to Server (or Connect to Database Engine) dialog box:
- Provide the Server name in the format
<server-name>.database.windows.net. - For Authentication, select Microsoft Entra Password.
- In the User name box, type your Microsoft Entra user name in the format
username@domain.com. User names must be an account from Microsoft Entra ID or an account from a managed or federated domain with Microsoft Entra ID. - In the Password box, type your user password for the Microsoft Entra account or managed/federated domain account.
- For Encryption, select Strict (SQL Server 2022 and Azure SQL), which should be used to connect to Azure SQL resources.
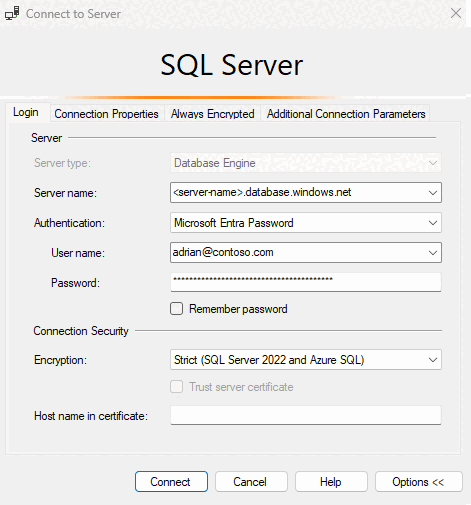
- Provide the Server name in the format
On the Connection properties tab, in the Connect to database field, type the name of the user database you want to connect to.

Microsoft Entra MFA
Use this method for interactive authentication with multifactor authentication (MFA), with the password being requested interactively. This method can be used to authenticate to databases in SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics for Microsoft Entra cloud-only identity users, or those who use Microsoft Entra hybrid identities.
The following steps show how to connect using multifactor authentication in the latest version of SSMS.
To connect using MFA, on the Connect to Server dialog box in SSMS select Microsoft Entra MFA.
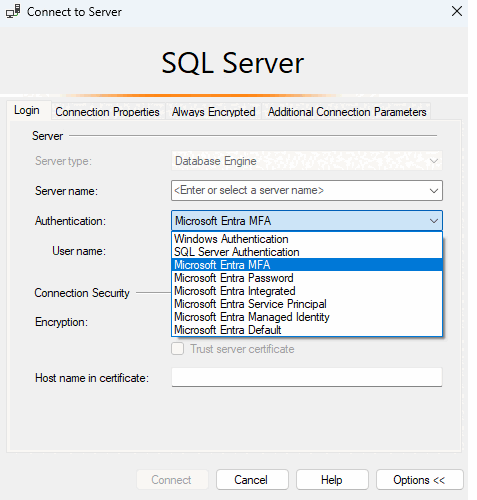
Fill the Server name box with your server's name. Fill the User name box with your Microsoft Entra credentials, in the format
user_name@domain.com.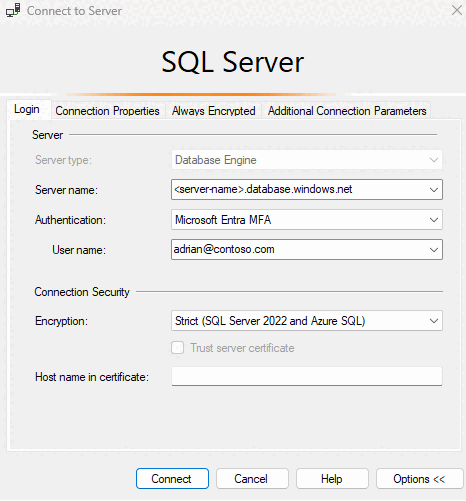
Select Connect.
When the Sign in to your account dialog box appears, it should be prepopulated with the User name you provided in step 2. No password is required if a user is part of a domain federated with Microsoft Entra ID.
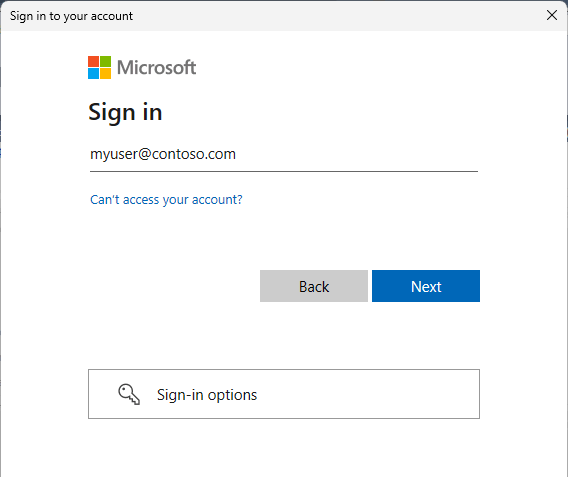
You'll be prompted to authenticate using one of the methods configured based on the MFA administrator setting.
When verification is complete, SSMS connects normally, presuming valid credentials and firewall access.
Microsoft Entra Service Principal
Use this method to authenticate to the database in SQL Database or SQL Managed Instance with Microsoft Entra service principals (Microsoft Entra applications). For more information, see Microsoft Entra service principal with Azure SQL.
Microsoft Entra Managed Identity
Use this method to authenticate to the database in SQL Database or SQL Managed Instance with Microsoft Entra managed identities. For more information, see Managed identities in Microsoft Entra for Azure SQL.
Microsoft Entra Default
The Default authentication option with Microsoft Entra ID enables authentication that's performed through password-less and non-interactive mechanisms including managed identities.
Connect from a client application
The following procedures show you how to connect to a SQL Database with a Microsoft Entra identity from a client application. This isn't a comprehensive list of authentication methods when using a Microsoft Entra identity. For more information, see Connect to Azure SQL with Microsoft Entra authentication and SqlClient.
Configure your client applications
Note
System.Data.SqlClient uses the Azure Active Directory Authentication Library (ADAL), which is deprecated. If you're using the System.Data.SqlClient namespace for Microsoft Entra authentication, migrate applications to Microsoft.Data.SqlClient and the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL). To understand the connection methods available in .NET, see Connect to Azure SQL with Microsoft Entra authentication and SqlClient.
If you must continue using ADAL.DLL in your applications, you can use the links in this section to install the latest ODBC or OLE DB driver, which contain the latest ADAL.DLL library.
On all client machines from which your applications or users connect to SQL Database or Azure Synapse Analytics using Microsoft Entra identities, you must install the following software:
- .NET Framework 4.6 or later.
- Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL) or Microsoft Authentication Library for SQL Server (ADAL.DLL). Links to install the latest SSMS, ODBC, and OLE DB driver that contains the ADAL.DLL library are available here:
You can meet these requirements by:
- Installing the latest version of SQL Server Management Studio or SQL Server Data Tools to meet the .NET Framework 4.6 requirement.
- SSMS installs the x86 version of ADAL.DLL.
- SSDT installs the amd64 version of ADAL.DLL.
- The latest Visual Studio from Visual Studio Downloads meets the .NET Framework 4.6 requirement but doesn't install the required amd64 version of ADAL.DLL.
Microsoft Entra integrated authentication
To use integrated Windows authentication, your domain's Active Directory must be federated with Microsoft Entra ID, or should be a managed domain that is configured for seamless single sign-on for pass-through or password hash authentication. For more information, see Microsoft Entra seamless single sign-on.
Your client application (or a service) connecting to the database must be running on a domain-joined machine under a user's domain credentials.
To connect to a database using integrated authentication and a Microsoft Entra identity, the Authentication keyword in the database connection string must be set to Active Directory Integrated. Replace <server_name> with your logical server name. The following C# code sample uses ADO .NET.
string ConnectionString = @"Data Source=<server-name>.database.windows.net; Authentication=Active Directory Integrated; Initial Catalog=testdb;";
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
conn.Open();
The connection string keyword Integrated Security=True isn't supported for connecting to Azure SQL Database. When making an ODBC connection, you need to remove spaces and set authentication to ActiveDirectoryIntegrated.
Microsoft Entra password authentication
To connect to a database using Microsoft Entra cloud-only identity user accounts, or those who use Microsoft Entra hybrid identities, the Authentication keyword must be set to Active Directory Password. The connection string must contain User ID/UID and Password/PWD keywords and values. Replace <server_name>, <email_address>, and <password> with the appropriate values. The following C# code sample uses ADO .NET.
string ConnectionString =
@"Data Source=<server-name>.database.windows.net; Authentication=Active Directory Password; Initial Catalog=testdb; UID=<email_address>; PWD=<password>";
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
conn.Open();
Learn more about Microsoft Entra authentication methods using the demo code samples available at Microsoft Entra authentication GitHub Demo.
Microsoft Entra ID access token
This authentication method allows middle-tier services to obtain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) to connect to the database in SQL Database, the SQL Managed Instance, or Azure Synapse by obtaining a token from Microsoft Entra ID. This method enables various application scenarios including service identities, service principals, and applications using certificate-based authentication. You must complete four basic steps to use Microsoft Entra token authentication:
- Register your application with Microsoft Entra ID and get the client ID for your code.
- Create a database user representing the application (as described in the Create contained users mapped to Microsoft Entra identities section.)
- Create a certificate on the client computer runs the application.
- Add the certificate as a key for your application.
Sample connection string. Replace <server-name> with your logical server name:
string ConnectionString = @"Data Source=<server-name>.database.windows.net; Initial Catalog=testdb;";
SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(ConnectionString);
conn.AccessToken = "Your JWT token";
conn.Open();
For more information, see SQL Server Security Blog. For information about adding a certificate, see Get started with certificate-based authentication in Microsoft Entra ID.
Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication
Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication is a supported authentication method for all SQL tools. For information on programmatically authenticating with Microsoft Entra ID, see the Overview of the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL).
sqlcmd
The following statements connect using version 13.1 of sqlcmd. Download Microsoft Command Line Utilities 14.0 for SQL Server.
Note
sqlcmd with the -G command does not work with system identities, and requires a user principal login.
sqlcmd -S <database or datawarehouse name>.<server-name>.database.windows.net -G
sqlcmd -S <database or datawarehouse name>.<server-name>.database.windows.net -U adrian@contoso.com -P <password> -G -l 30
Connect in Azure portal Query editor (Azure SQL Database)
For more information on the Azure portal Query editor for Azure SQL Database, see Quickstart: Use the Azure portal query editor to query Azure SQL Database.
Navigate to your SQL database in the Azure portal. For example, visit your Azure SQL dashboard.
On your SQL database Overview page in the Azure portal, select Query editor from the left menu.
On the sign-in screen under Welcome to SQL Database Query Editor, select Continue as <your user or group ID>.
Related content
- Authorize database access to SQL Database, SQL Managed Instance, and Azure Synapse Analytics
- Principals
- Database roles
- Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse IP firewall rules
- Create Microsoft Entra guest users and set them as a Microsoft Entra admin
- Tutorial: Create Microsoft Entra users using Microsoft Entra applications