Merk
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å logge på eller endre kataloger.
Tilgang til denne siden krever autorisasjon. Du kan prøve å endre kataloger.
Scope
Note
This article applies to new Surface Hub 3 devices, Surface Hub 2S devices upgraded with the Surface Hub 3 Compute Cartridge and Surface Hub 2S devices software-migrated to the Teams Rooms on Windows platform.
Introduction
Depending on your organization's security posture, you might wish to take other security measures, as described in this article. At a minimum, we recommended the following measures:
Tip
Before you begin, review the guidance for Microsoft Teams Rooms security, which primarily focuses on security for tabletop conference devices: Teams Rooms certified systems. The Windows 11 IoT Enterprise operating system provides IT admins with a range of centralized configuration and management options.
Change default local admin password
The default local admin account is a well-known entry point for malicious actors. If the default admin password remains unchanged after first-time setup, the device might be vulnerable to data breaches, system manipulation, or other unauthorized access.
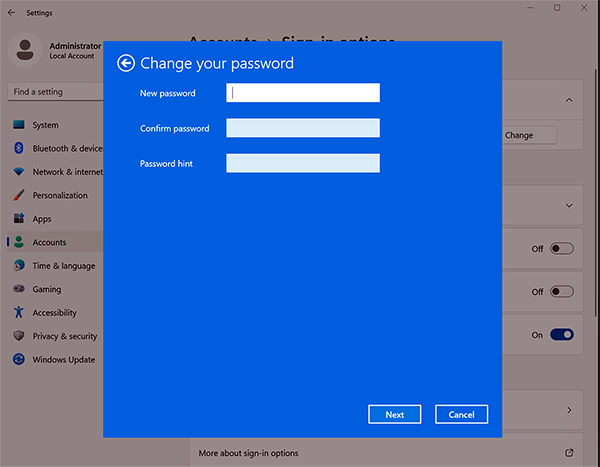
To change the local admin password on Surface Hub
- Sign in with admin credentials and go to Settings > Accounts > Sign-in options > Password > Change.
- Enter the current default password:sfb.
- Create a new password, confirm the password, and add a hint. To learn more, see Change or reset your Windows password.
Tip
When joined to Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD), you can utilize Windows LAPS (Local Administrator Password Solution). Although LAPS doesn't remove local admin accounts, it automatically manages local admin passwords, ensuring they're randomized and securely stored in AD. This reduces the risk associated with stale or widely known admin passwords. To learn more, see Microsoft Intune support for Windows LAPS.
Set a UEFI password
The Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is an advanced firmware interface designed to replace the traditional BIOS (Basic Input/Output System), providing enhanced features like improved security, faster boot times, and support for larger hard drives in modern Windows operating systems. By setting a UEFI password, you add an extra layer of security, preventing unauthorized users from changing the device's firmware settings. Set a strong UEFI password and store it in a secure location.
Use the Surface IT Toolkit to set a UEFI password with Surface Enterprise Management Mode (SEMM).
Enroll Surface Hub in SEMM
You need a dedicated USB drive with at least 50 MB of storage space.
Open the IT Toolkit, select UEFI Configurator > Configure devices.
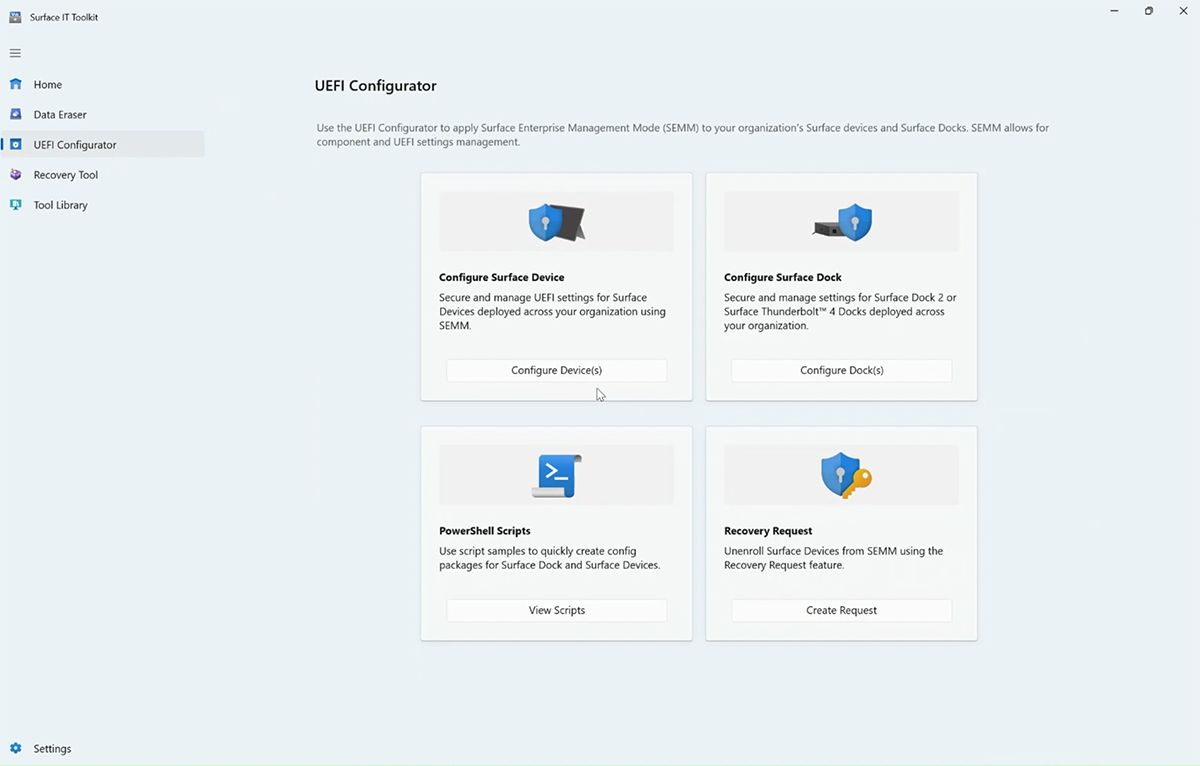
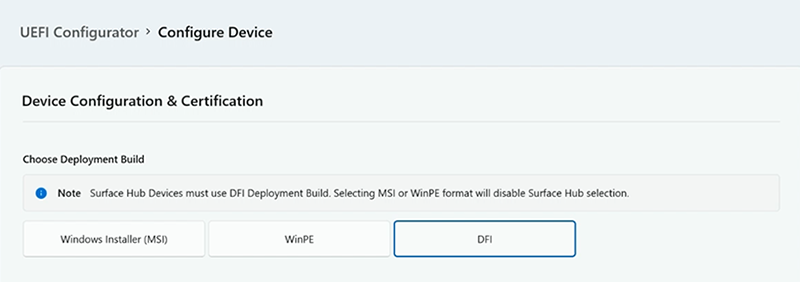
Under Choose Deployment Build, select DFI.
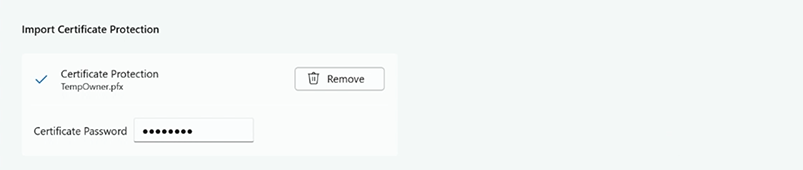
Under Import Certificate Protection, add your organizational Personal Information Exchange (PFE) certificate.
Note
This article assumes that you either obtain certificates from a third-party provider or already have expertise in PKI certificate services and know how to create your own. To learn more, see SEMM certificate requirements and Certificate Services Architecture documentation.
Under DFI Package Type, select Configuration Package. For Device, select Surface Hub > Surface Hub 3 and select Next.
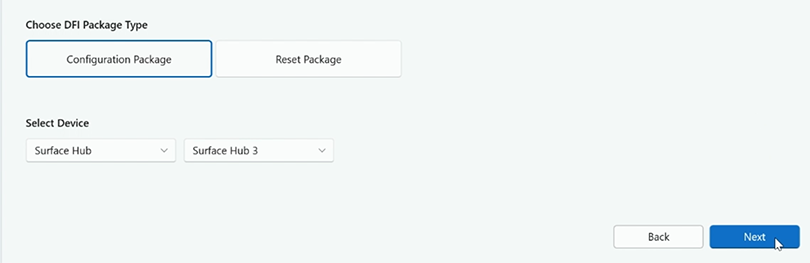
Under UEFI Password select Set or Modify Password and then enter and confirm your password. Select Next.
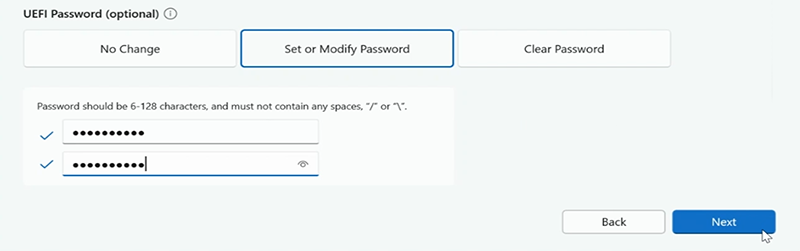
Optionally, you can configure components and advanced settings, as described in the section Manage UEFI settings with SEMM, on this page. Otherwise, select Next.
Select your USB drive and choose Create.
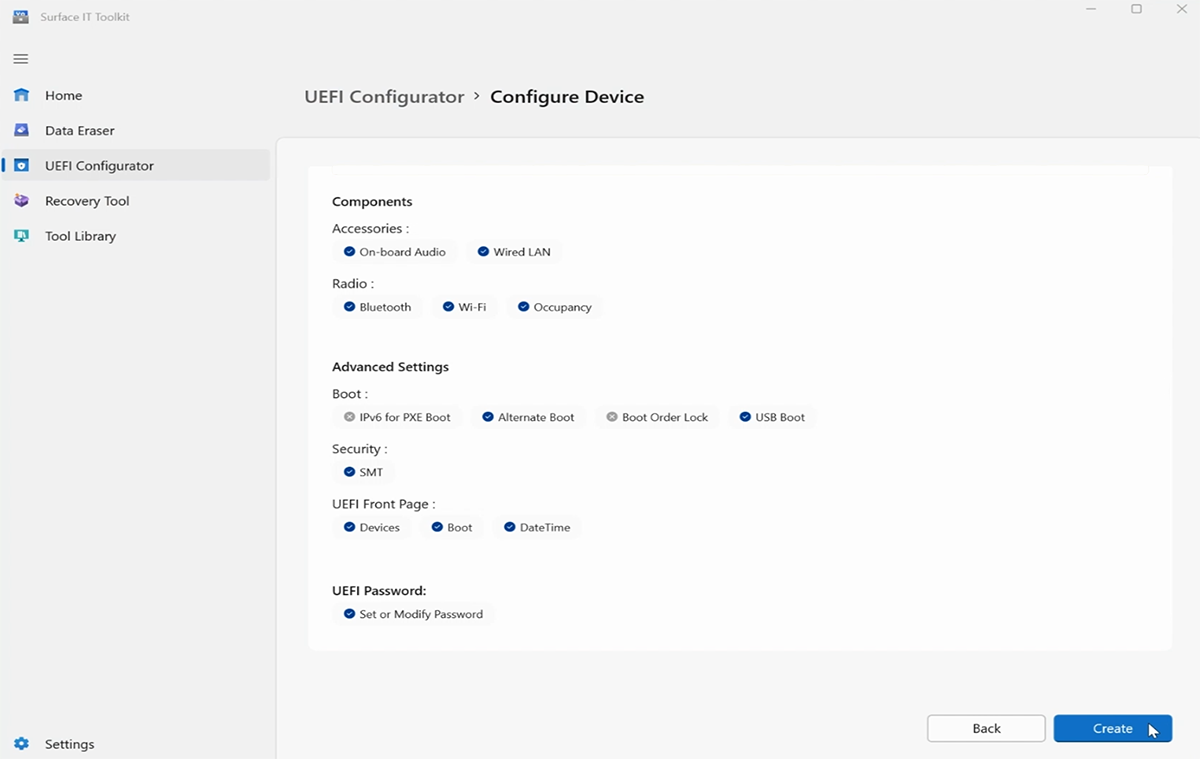
Upon successful creation of the package, the Configurator displays the last two characters of your certificate's thumbprint. You need these characters when you import the configuration to Surface Hub.
Physically secure Surface Hub
Physical security is as crucial a tool as digital security. Devices like the Surface Hub in public conference rooms can be susceptible to physical damage or tampering. To protect Surface Hub, consider the following steps:
- Tamper-evident seals: Use tamper-evident seals on the device. If someone attempts to open the device, the seal shows signs of tampering.
- Security cables and locks: Use security cables and locks to secure the device to a heavy or immovable object, making it difficult for someone to walk away with it.
- Surveillance: Depending on the workplace environment, you might opt to install surveillance cameras in the conference room. The mere presence of cameras can deter potential wrongdoers.
Differences with Windows 10 Team on Surface Hub & Surface Hub 2S
The following security features are no longer enabled by default on Surface Hub running Teams Rooms on Windows:
BitLocker
You can enable BitLocker via Intune when joined to Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD). See Encrypt Windows devices with BitLocker in Intune to learn more.
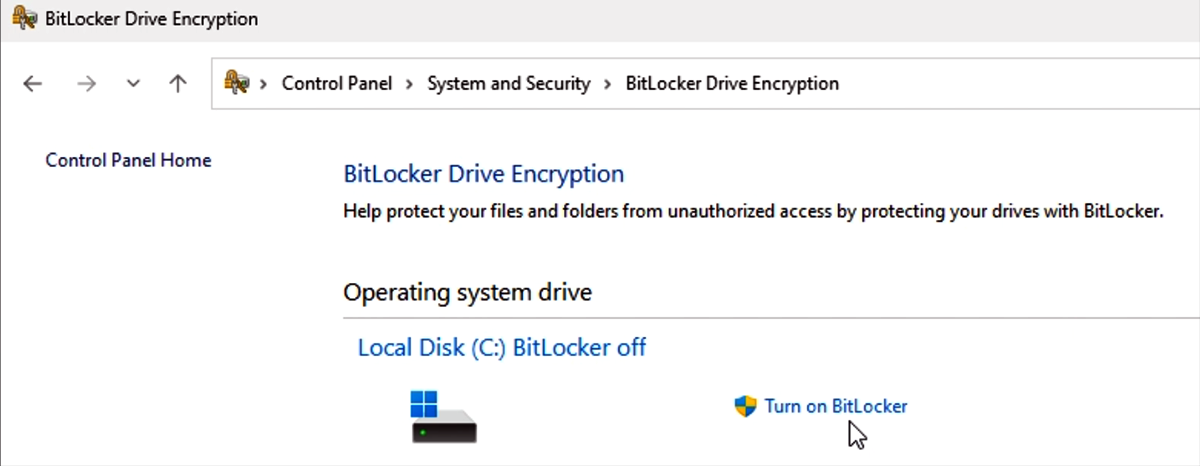
To enable BitLocker on a stand-alone Surface Hub running Teams Rooms on Windows
Sign in to Surface Hub with admin credentials.
Select Start, enter **Control, and open Control Panel.
Select System & Security > BitLocker Drive Encryption > Turn on BitLocker.
User Mode Code Integrity (UMCI)
UMCI enforces code integrity policies and ensures that only trusted code runs in user mode, helping to prevent the execution of malicious or untrusted code. You can configure UMCI via Group Policy when Hub 3 is joined to a Microsoft Entra domain or by using PowerShell cmdlets. UMCI is part of a set of features that you can manage with the Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC), which also includes configurable code integrity policies. To learn more, see Understand Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC) policy rules and file rules.
Microsoft Teams Rooms Pro Management
We highly recommend utilizing the Microsoft Teams Rooms Pro Management portal license. This cloud-based management platform is designed to elevate the meeting room experience by offering proactive monitoring and updates for Microsoft Teams Rooms devices and their peripherals. Intended for organizations looking to optimize their meeting environments, this service ensures real-time oversight and management of Microsoft Teams Rooms devices, including Surface Hub. By adopting this solution, organizations can significantly enhance usability and reliability for end users, ensuring seamless meeting experiences.
- Intelligent operations: Utilizes software and machine learning to automate updates, detect problems, and resolve issues for Microsoft Teams Rooms.
- Timely security updates: Automated update management ensures that security patches are applied promptly as they become available, minimizing the window of vulnerability and protecting devices from known security threats.
- Update management: Automates the orchestration of meeting application and Windows updates based on customer-configurable deployment rings.
To learn more, see Microsoft Teams Rooms Pro Management.
Enterprise Management of Surface Hub running Teams Rooms on Windows
We recommend you join Surface Hub to Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD) and manage the device using Microsoft Intune or equivalent mobile device management (MDM) solution. The following table describes configuration management options for Intune.
| Feature | Description | Learn More |
|---|---|---|
| Device configuration profiles | Use Intune's endpoint protection settings to configure Windows Defender, firewall settings, and other security features to protect the device from potential threats. | Create device profiles in Microsoft Intune |
| Device compliance policies | Ensure the device complies with your organization's security standards. If a device falls out of compliance (for example, if a required update isn't installed), you can configure automated remediation actions or notifications. | Create device compliance policies in Microsoft Intune |
| Update management | Use default update management settings to automatically install updates during a nightly maintenance window. Intune provides more options to customize if needed. | Windows Update settings you can manage with Intune Update Ring policies for Windows 10/11 devices. |
| App management | Use Intune to manage the apps installed on Surface Hub on Teams Rooms on Windows. Ensure only necessary apps related to Teams Rooms functionality are installed and regularly updated. | Manage and secure apps in Intune |
| BitLocker encryption | Ensure that the device's storage is encrypted using BitLocker. This protects data against unauthorized access or device theft. Unlike Surface Hub 2S, BitLocker isn't installed by default. | Encrypt Windows devices with BitLocker in Intune |
| WindowsLocal Administrator Password Solution | Windows LAPS automatically manages local admin passwords, ensuring they're randomized and securely stored in Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD). This reduces the risk associated with stale or widely known admin passwords. | Microsoft Intune support for Windows LAPS |
| Conditional access | Set up conditional access policies to ensure the device can access corporate resources only when it meets specific conditions, such as compliance with security policies. | Use Conditional Access with Microsoft Intune compliance policies |
| Network security | Ensure the device is connected to a secure network segment. Use Intune to configure Wi-Fi settings, VPNs, or other network configurations to protect data in transit. | Create a Wi-Fi profile for devices in Microsoft Intune Network endpoints for Microsoft Intune |
| Remote Wipe and Lock | In the event of a security incident, ensure you can remotely lock or wipe the device using Intune. | Retire or wipe devices using Microsoft Intune |
| Audit and monitoring | Regularly review audit logs and set up alerts for suspicious activities. Intune integrates with other Microsoft security solutions, providing a holistic view of device security. | Audit changes and events in Microsoft Intune |
| User training | Educate users about not leaving sensitive information visible on the screen. If your organization has Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention (DLP), you can define policies that prevent people from sharing sensitive information in a Microsoft Teams channel or chat session. |
Data loss prevention and Microsoft Teams |
Manage Group Policy settings in domain-joined scenarios
When integrating Teams Rooms with a domain, it's imperative to establish a separate, dedicated Organizational Unit (OU) specifically for Teams Rooms. This approach enables the application of Group Policy Object (GPO) exclusions directly to this OU, ensuring that only relevant policies affect Teams Rooms objects.
Disable GPO inheritance. It's crucial to disable all GPO inheritance within this OU to prevent the application of unsupported or irrelevant Group Policy settings to Teams Rooms.
Apply GPOs to OU before joining domain. Ensure that machine objects for Teams Rooms are created within this specific OU before the domain join. This step is essential to avoid the inadvertent application of default computer OU policies to Teams Rooms and maintain the intended configuration and security posture.
To learn more about configuring Group Policy in domain-joined scenarios, see the following resources:
Manage UEFI settings with SEMM
SEMM enables IT admins to lock down features at the firmware level that you might wish to implement depending on the security posture of your environment. Open Surface UEFI Configurator, as explained earlier, and go to the following screens:
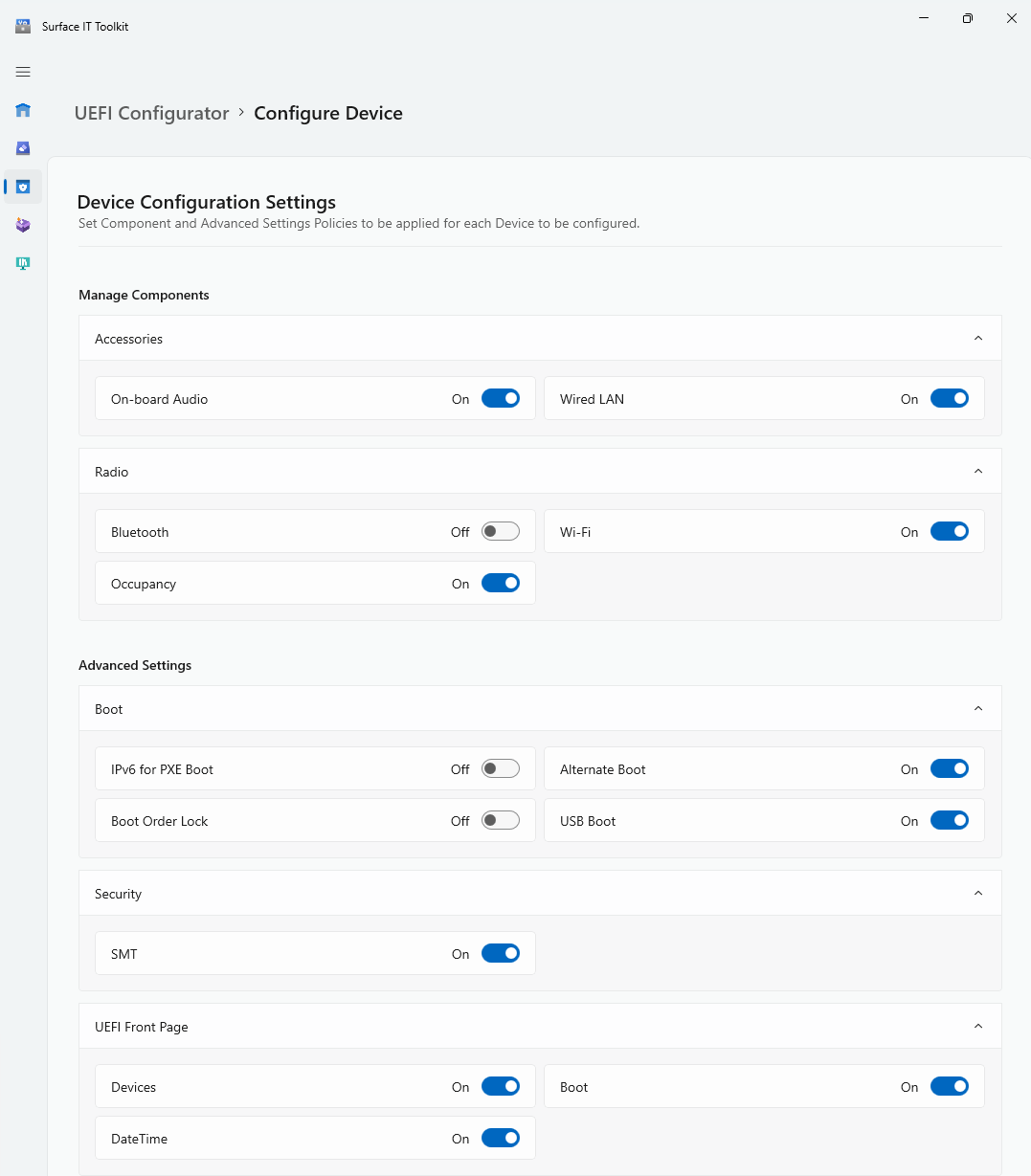
For settings descriptions, see SEMM UEFI settings reference.
Simultaneous Multi-Threading (SMT)
Commonly known as hyperthreading in Intel processors, SMT allows a single physical CPU core to run multiple threads concurrently. This can improve performance in multi-threaded applications. However, there are specific scenarios where you might want to control the SMT setting. Some vulnerabilities, like speculative execution side-channel attacks (for example, L1 Terminal Fault, MDS vulnerabilities), can potentially exploit SMT to access sensitive data. Disabling SMT can mitigate the risk associated with these vulnerabilities, although at the cost of some performance. SMT is enabled by default.
IPv6 for PXE Boot
If your network infrastructure and security controls are primarily designed around IPv4 and still need to be fully equipped to handle IPv6 traffic securely, enabling IPv6 for PXE boot could introduce vulnerabilities. This is because IPv6 might bypass some of the existing security controls for IPv4.
While enabling IPv6 for PXE boot aligns with the broader industry move towards IPv6 adoption, it's essential to ensure that the network infrastructure, security controls, and operational practices are all equipped to handle IPv6 securely. If not, it might be safer to keep IPv6 for PXE boot disabled until those measures are in place.
Alternate Boot & USB Boot
The ability to boot from another source, such as a USB or Ethernet device, provides flexibility for system recovery but can also introduce vulnerabilities:
- Unauthorized Operating Systems: If Alternate boot is enabled, an attacker with physical access to the device could boot the system using an unauthorized operating system from a USB drive. This could bypass the security controls of the primary OS.
- Data Extraction: An attacker could boot from an external device to a system that allows direct access to the internal storage, potentially extracting sensitive data.
- Malware Installation: Booting from an untrusted source could introduce malware, rootkits, or other malicious software at the system level.
Given these implications, organizations in highly secure workplace environments might choose to disable Alternate Boot and USB Boot to reduce the risk of unauthorized access or tampering.
Boot Order Lock
Enabling the "Boot Order Lock" enhances the security posture by ensuring it only boots from authorized sources. Boot Order Lock is turned off by default.