Create and use the paginated report visual
APPLIES TO:
Power BI Report Builder
Power BI service
Power BI Desktop
In this article, you learn how to use the paginated report visual for Power BI reports. This native Power BI visual allows you to render any paginated report you’ve uploaded to the service in a Power BI report.
This visual brings the power of paginated reports to your Power BI reports. You can map fields from your Power BI semantic model to be used as parameter values for your paginated report visual. The ability to map fields provides a fully interactive experience like any other visual.
The paginated report visual is designed to integrate a paginated report with other visuals in a Power BI report. It enables large data exports, detail drills, and generating documents. If you are migrating paginated report content from on premises, or find that the paginated report visual is the only element on a page, consider using the paginated report directly.
Create a paginated report visual
Open your Power BI report in Power BI Desktop or in the Power BI service. If in the Power BI service, select Edit.

Select Paginated Report from the Visualizations pane.

Select Connect to report.

Search for and select an existing paginated report saved to the Power BI service.
Select Set Parameters.
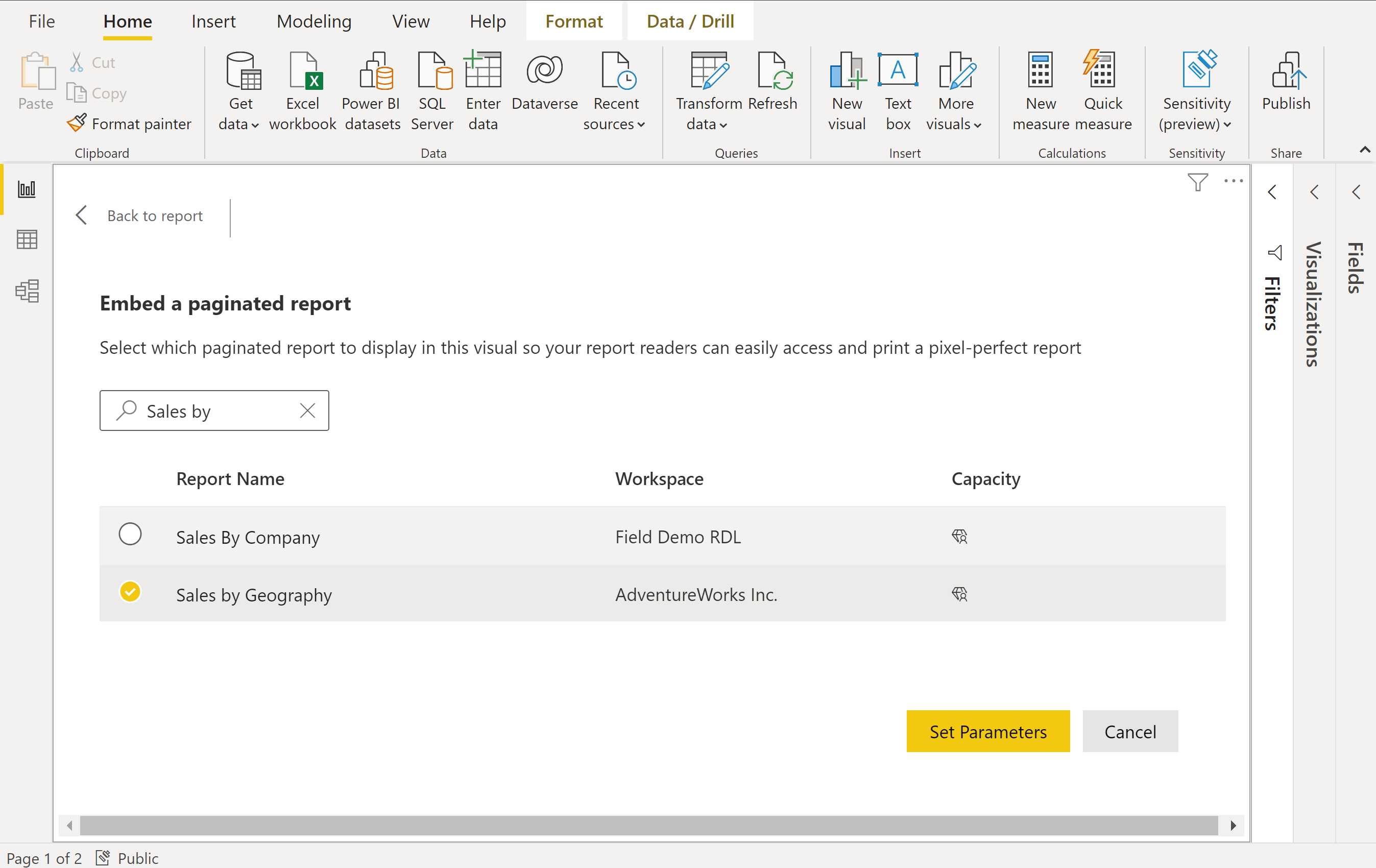
You have two options for mapping paginated report parameters:
You can bind the paginated report parameter to Power BI fields:
a. Drag your Power BI field into the Parameters field in the Visualizations pane.
b. Select this field from the dropdown menu. Select See report.
Or choose to use the default parameter for the paginated report, if the report author specified any.

Now your paginated report will render within your Power BI report.

If making edits in the Power BI service, select Save to save your changes. If making edits in Power BI Desktop, select Publish, then choose a workspace in a Premium capacity to publish your Power BI report to the Power BI service.
Note
We recommend saving the Power BI report with the paginated report visual to the same workspace as the paginated report. This ensures that readers with access to the Power BI report also have access to the paginated report, which is required for the paginated report visual to render.

Cross-filtering
You can enable cross-filtering between your paginated report visual and other visuals in your Power BI report: Map your paginated report parameters to fields in the Power BI report. If you have other visuals that affect the Power BI field you’ve selected for the parameter values, the paginated report visual updates as you interact with those visuals.
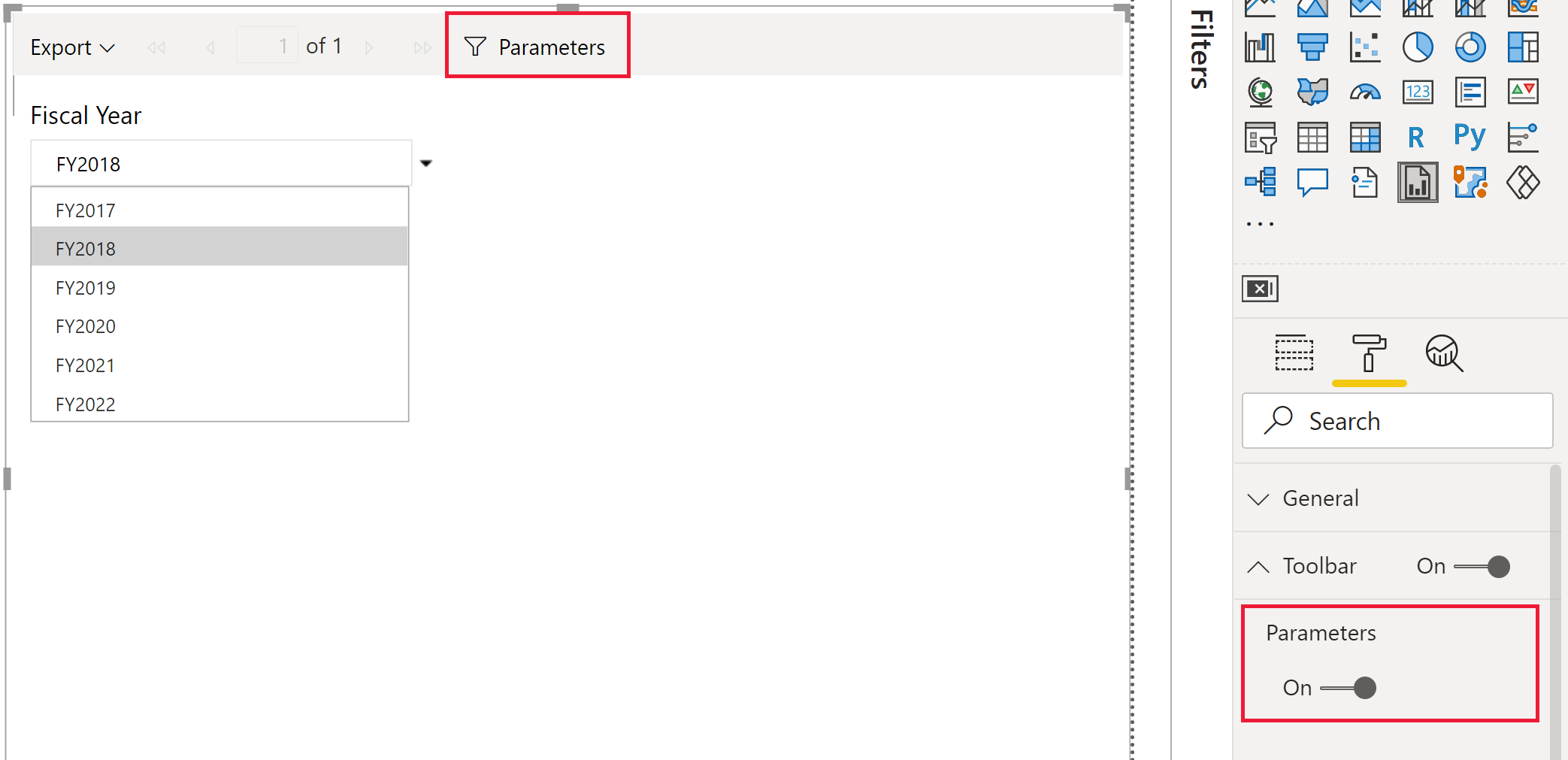
For example, if you select Fiscal Year FY2018 in the slicer visual, the paginated report visual automatically updates to show sales for FY2018, because the Power BI field for Fiscal Year is mapped to the paginated report parameter for Fiscal Year.

Turn on the toolbar
From the Format pane, you can show or hide the Toolbar in your paginated report visual. With the toolbar visible, report readers can easily export the paginated report from within the Power BI report using the paginated report Export toolbar button. Paginated reports support exporting to the following formats: Excel, PDF, Accessible PDF, CSV, PowerPoint, Word, MHTML, and XML. Standard Power BI report visuals impose a 150,000 row limitation when using the Export data option. In contrast, with the paginated report visual, you can export up to 1,000,000 rows to Excel using the Export button in the toolbar, and retain all the formatting in the paginated report.

You can also show parameters in the toolbar. In the Format pane, turn Parameters on. With this option enabled, you can select and apply parameters from the paginated report visual toolbar.
Auto-apply filters
You can decide whether report filters are automatically applied to the paginated report visual, or not. By default, the Auto-apply filters option is turned off. With the option turned off, your paginated report visual remains unchanged as you adjust filters in your Power BI report. If you turn on Auto-apply filters, your paginated report visual automatically updates as you apply filters or update other visuals that affect the field you’ve selected for the parameter value.
- Select your paginated report visual. From the Format pane, turn Auto-apply filters on.
Considerations and limitations
- When connecting fields to a paginated report parameter, double-check whether the field values are used as is, in other words, Don't summarize, or as aggregates (for example, Sum, Average, and so on). You can use the Show as a table option from the context menu of the paginated report visual to see the actual values being passed to paginated reports during runtime.
- You can map an aggregate field in Power BI such as Sum, Average, Minimum, or Maximum to a paginated report parameter. If you do, consider whether your paginated report parameter is a single-value or multi-value parameter. If mapping to a single-value parameter, the aggregate value is used. If mapping to a multi-value parameter, the per-row aggregate values are mapped to the parameter.
- When embedding a Power BI report that contains a paginated report visual, using the embed for your customers method, you need a service principal and a multi-resource embed token as explained in How to embed a Power BI report that contains a paginated report visual.
- When you add a Power BI report that contains a paginated report visual to a Power BI app, make sure to include the paginated report in the app, as well as all subreports and drillthrough target reports that the report visual depends on. If your app doesn't have audiences or if the paginated report referenced by the visual is in another workspace, your app users must have at least Viewer role access to the paginated report workspace in order to view the paginated report in the visual. If you want to keep paginated report hidden from Power BI app navigation menu, refer to Allow access to hidden content.
- The paginated report visual isn't supported for Power BI report subscription or export. You can open the underlying paginated report itself and create a subscription to it, as explained in Subscribe to paginated reports.
- The paginated report visual has a built-in 30,000-value data reduction limit due to the Power BI visual maximum of 30,000. If any field used in the visual contains more than 30,000 values, a data reduction algorithm kicks in and drops the rows that are above the limit. As a result, the paginated report may show incorrect results due to missing data from report parameters. To work around this, try to use filters to filter out unnecessary values, or map the report parameters to fields with fewer values.
- The duration of the paginated report session is capped by the expiration time of your access token. Currently there's no support to automatically refresh the token. After the session expires, a dialog prompts you to refresh the visual and start a new rendering session.
- Paginated report visual does not get updated as part of Deployment Pipelines. As a workaround here, please edit the Power BI report in destination to update the paginated report visual to use the paginated report in destination workspace.
Using a Power BI semantic model with a date parameter
Note
Versions of Power BI Report Builder 15.7.01704.0001 and above allow you to use date parameters with the paginated report visual without having to follow these next steps. Download the newest version of Power BI Report Builder.
When you use a Power BI semantic model as the data source for your paginated report and set up a date parameter in your query that then automatically generates the parameter table and parameter, using that parameter in a paginated report parameter will fail. The paginated report visually treats the parameter as a text field and fails to match the Power BI date field. You have three work-around options:
- From the same Power BI data source, create a new dataset with only the date values. Use this dataset as the available values for your parameter, setting the data type of the parameter as Date/Time.
- Manually change the DAX query text in the auto-generated dataset to remove the part that sets the parameter to be a text value.
- Change the Power BI semantic model using Power Query to add a column that formats the date field as a text field.
Related content
- What are paginated reports in Power BI?
- Tutorial: Create a paginated report and upload it to the Power BI service
- Power BI Paginated Reports in a Day course
More questions? Try the Power BI Community