How to configure content filters with Azure OpenAI Service
The content filtering system integrated into Azure OpenAI Service runs alongside the core models, including DALL-E image generation models. It uses an ensemble of multi-class classification models to detect four categories of harmful content (violence, hate, sexual, and self-harm) at four severity levels respectively (safe, low, medium, and high), and optional binary classifiers for detecting jailbreak risk, existing text, and code in public repositories. The default content filtering configuration is set to filter at the medium severity threshold for all four content harms categories for both prompts and completions. That means that content that is detected at severity level medium or high is filtered, while content detected at severity level low or safe is not filtered by the content filters. Learn more about content categories, severity levels, and the behavior of the content filtering system here. Jailbreak risk detection and protected text and code models are optional and off by default. For jailbreak and protected material text and code models, the configurability feature allows all customers to turn the models on and off. The models are by default off and can be turned on per your scenario. Some models are required to be on for certain scenarios to retain coverage under the Customer Copyright Commitment.
Note
All customers have the ability to modify the content filters and configure the severity thresholds (low, medium, high). Approval is required for turning the content filters partially or fully off. Managed customers only may apply for full content filtering control via this form: Azure OpenAI Limited Access Review: Modified Content Filters. At this time, it is not possible to become a managed customer.
Content filters can be configured at the resource level. Once a new configuration is created, it can be associated with one or more deployments. For more information about model deployment, see the resource deployment guide.
Prerequisites
- You must have an Azure OpenAI resource and a large language model (LLM) deployment to configure content filters. Follow a quickstart to get started.
Understand content filter configurability
Azure OpenAI Service includes default safety settings applied to all models, excluding Azure OpenAI Whisper. These configurations provide you with a responsible experience by default, including content filtering models, blocklists, prompt transformation, content credentials, and others. Read more about it here.
All customers can also configure content filters and create custom safety policies that are tailored to their use case requirements. The configurability feature allows customers to adjust the settings, separately for prompts and completions, to filter content for each content category at different severity levels as described in the table below. Content detected at the 'safe' severity level is labeled in annotations but is not subject to filtering and isn't configurable.
| Severity filtered | Configurable for prompts | Configurable for completions | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low, medium, high | Yes | Yes | Strictest filtering configuration. Content detected at severity levels low, medium, and high is filtered. |
| Medium, high | Yes | Yes | Content detected at severity level low isn't filtered, content at medium and high is filtered. |
| High | Yes | Yes | Content detected at severity levels low and medium isn't filtered. Only content at severity level high is filtered. |
| No filters | If approved1 | If approved1 | No content is filtered regardless of severity level detected. Requires approval1. |
| Annotate only | If approved1 | If approved1 | Disables the filter functionality, so content will not be blocked, but annotations are returned via API response. Requires approval1. |
1 For Azure OpenAI models, only customers who have been approved for modified content filtering have full content filtering control and can turn off content filters. Apply for modified content filters via this form: Azure OpenAI Limited Access Review: Modified Content Filters. For Azure Government customers, apply for modified content filters via this form: Azure Government - Request Modified Content Filtering for Azure OpenAI Service.
Configurable content filters for inputs (prompts) and outputs (completions) are available for the following Azure OpenAI models:
- GPT model series
- GPT-4 Turbo Vision GA* (
turbo-2024-04-09) - GPT-4o
- GPT-4o mini
- DALL-E 2 and 3
Configurable content filters are not available for
- o1-preview
- o1-mini
*Only available for GPT-4 Turbo Vision GA, does not apply to GPT-4 Turbo Vision preview
Content filtering configurations are created within a Resource in Azure AI Studio, and can be associated with Deployments. Learn more about configurability here.
Customers are responsible for ensuring that applications integrating Azure OpenAI comply with the Code of Conduct.
Understand other filters
You can configure the following filter categories in addition to the default harm category filters.
| Filter category | Status | Default setting | Applied to prompt or completion? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt Shields for direct attacks (jailbreak) | GA | On | User prompt | Filters / annotates user prompts that might present a Jailbreak Risk. For more information about annotations, visit Azure OpenAI Service content filtering. |
| Prompt Shields for indirect attacks | GA | On | User prompt | Filter / annotate Indirect Attacks, also referred to as Indirect Prompt Attacks or Cross-Domain Prompt Injection Attacks, a potential vulnerability where third parties place malicious instructions inside of documents that the generative AI system can access and process. Required: Document formatting. |
| Protected material - code | GA | On | Completion | Filters protected code or gets the example citation and license information in annotations for code snippets that match any public code sources, powered by GitHub Copilot. For more information about consuming annotations, see the content filtering concepts guide |
| Protected material - text | GA | On | Completion | Identifies and blocks known text content from being displayed in the model output (for example, song lyrics, recipes, and selected web content). |
Configure content filters via Azure AI Studio
The following steps show how to set up a customized content filtering configuration for your resource.
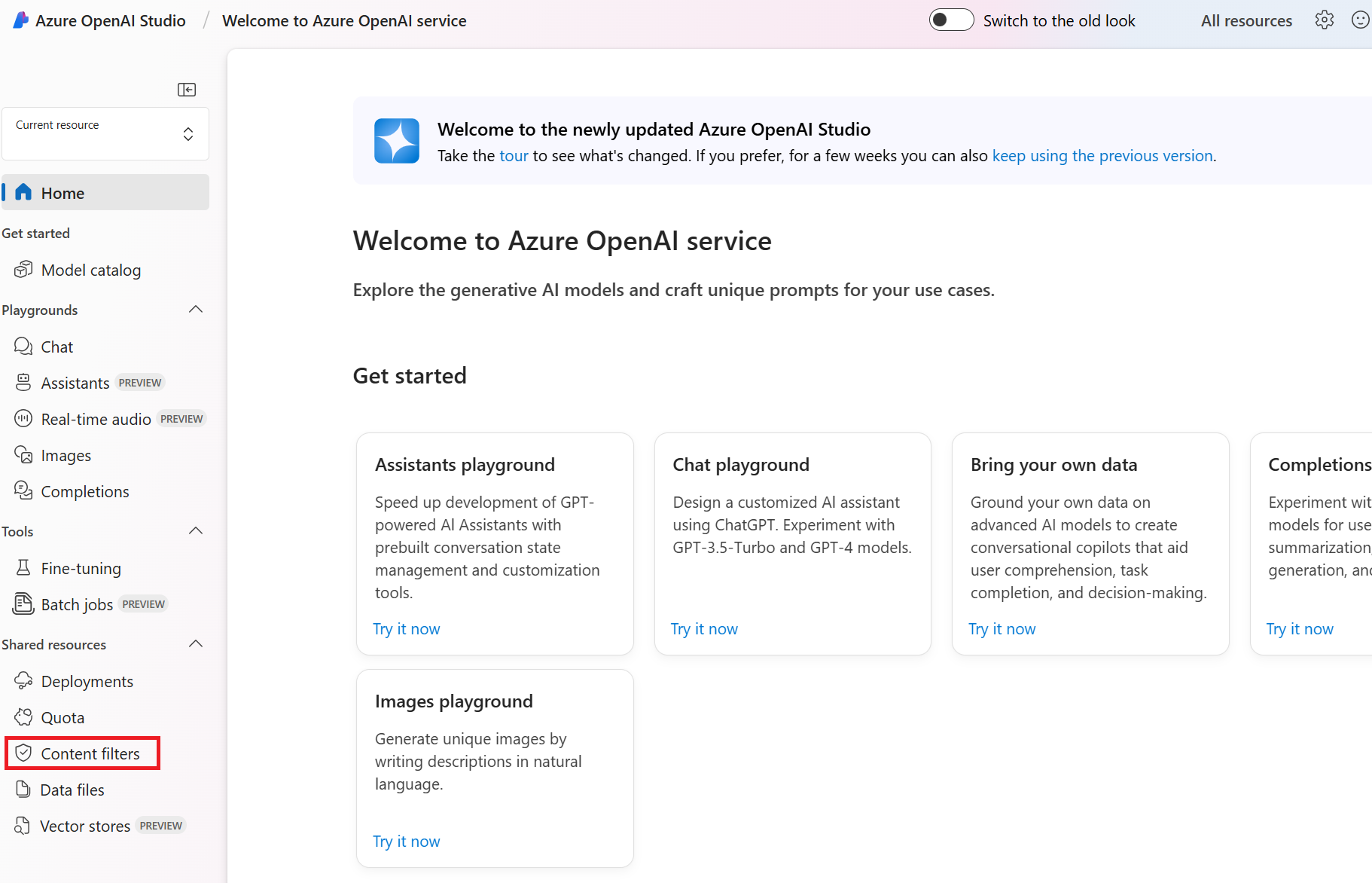
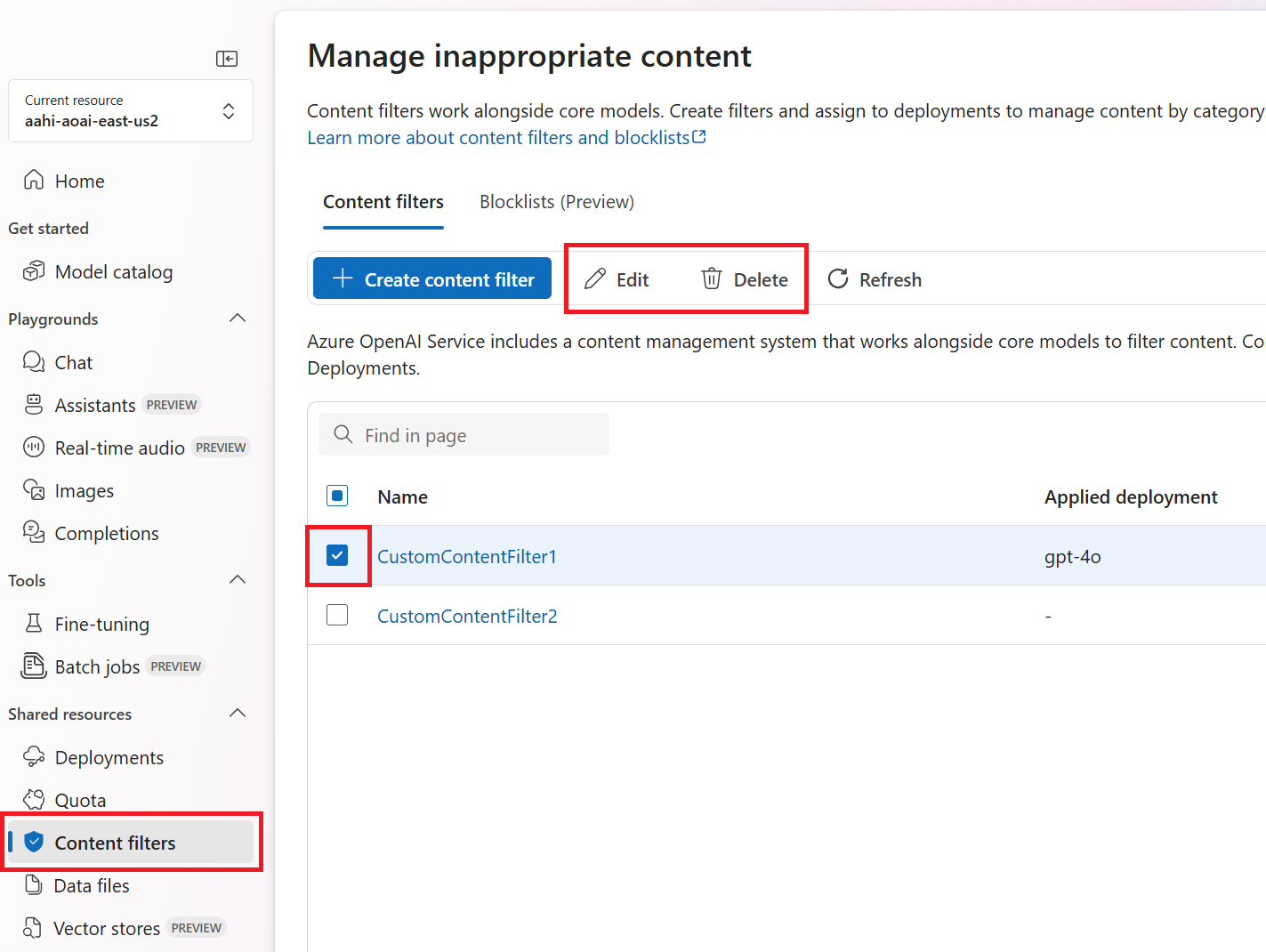
Go to Azure AI Studio and navigate to the Content Filters tab (in the bottom left navigation, as designated by the red box below).
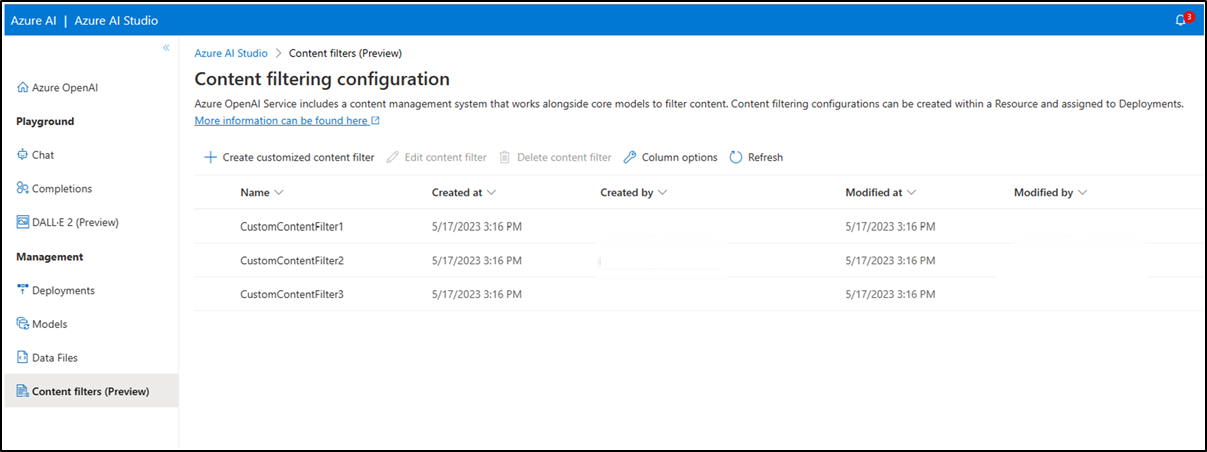
Create a new customized content filtering configuration.
This leads to the following configuration view, where you can choose a name for the custom content filtering configuration. After entering a name, you can configure the input filters (user prompts) and output filters (model response). For the first four content categories there are three severity levels that are configurable: Low, medium, and high. You can use the sliders to set the severity threshold if you determine that your application or usage scenario requires different filtering than the default values. Some filters enable you to determine if the model should annotate and/or block. Selecting Annotate runs the respective model and return annotations via API response, but it will not filter content. In addition to annotations, you can also choose to filter content by switching the Filter toggle to on.
If your use case was approved for modified content filters as outlined above, you receive full control over content filtering configurations and can choose to turn filtering partially or fully off.
You can create multiple content filtering configurations as per your requirements.
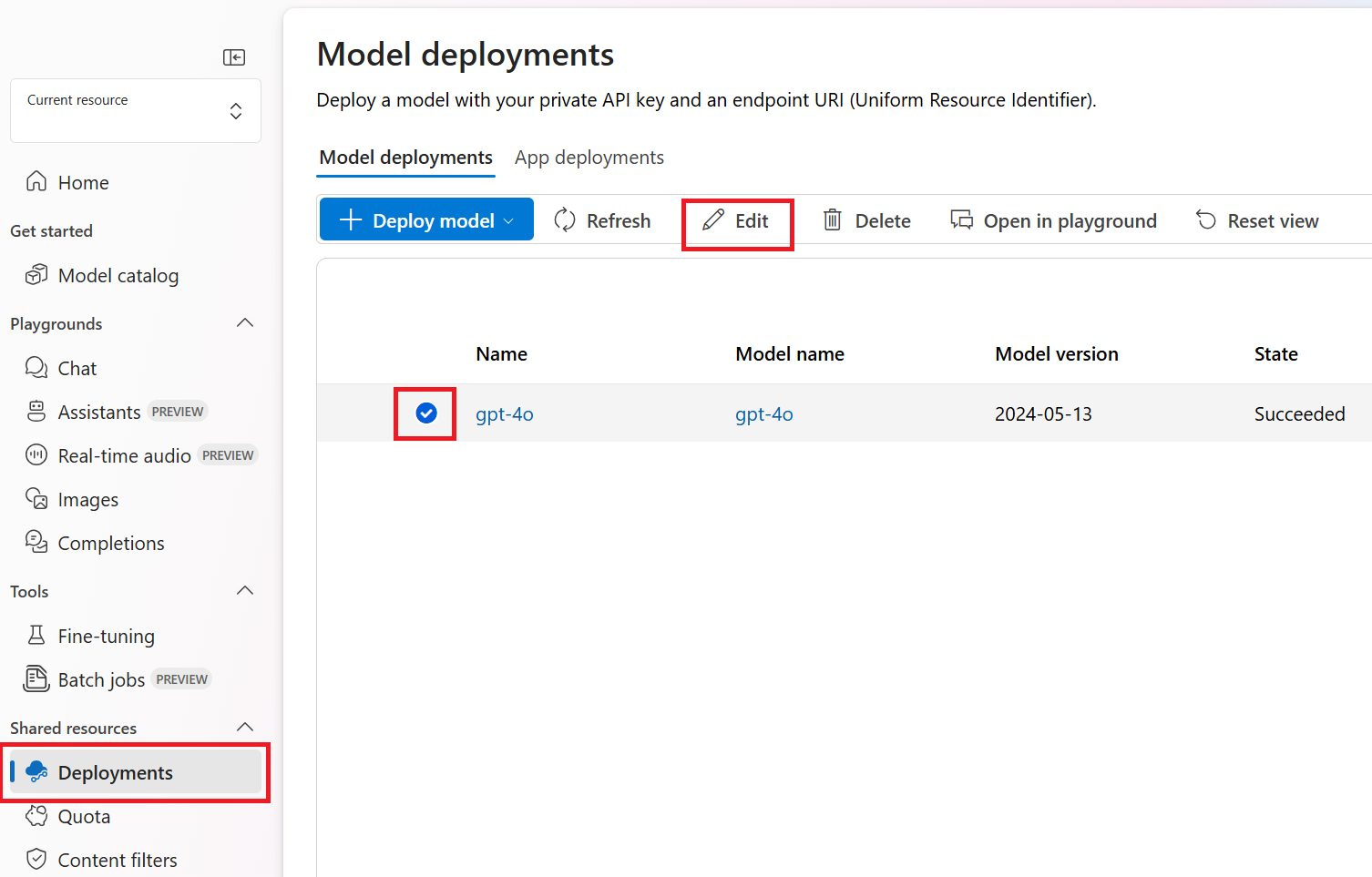
Next, to make a custom content filtering configuration operational, assign a configuration to one or more deployments in your resource. To do this, go to the Deployments tab and select your deployment. Then select Edit.
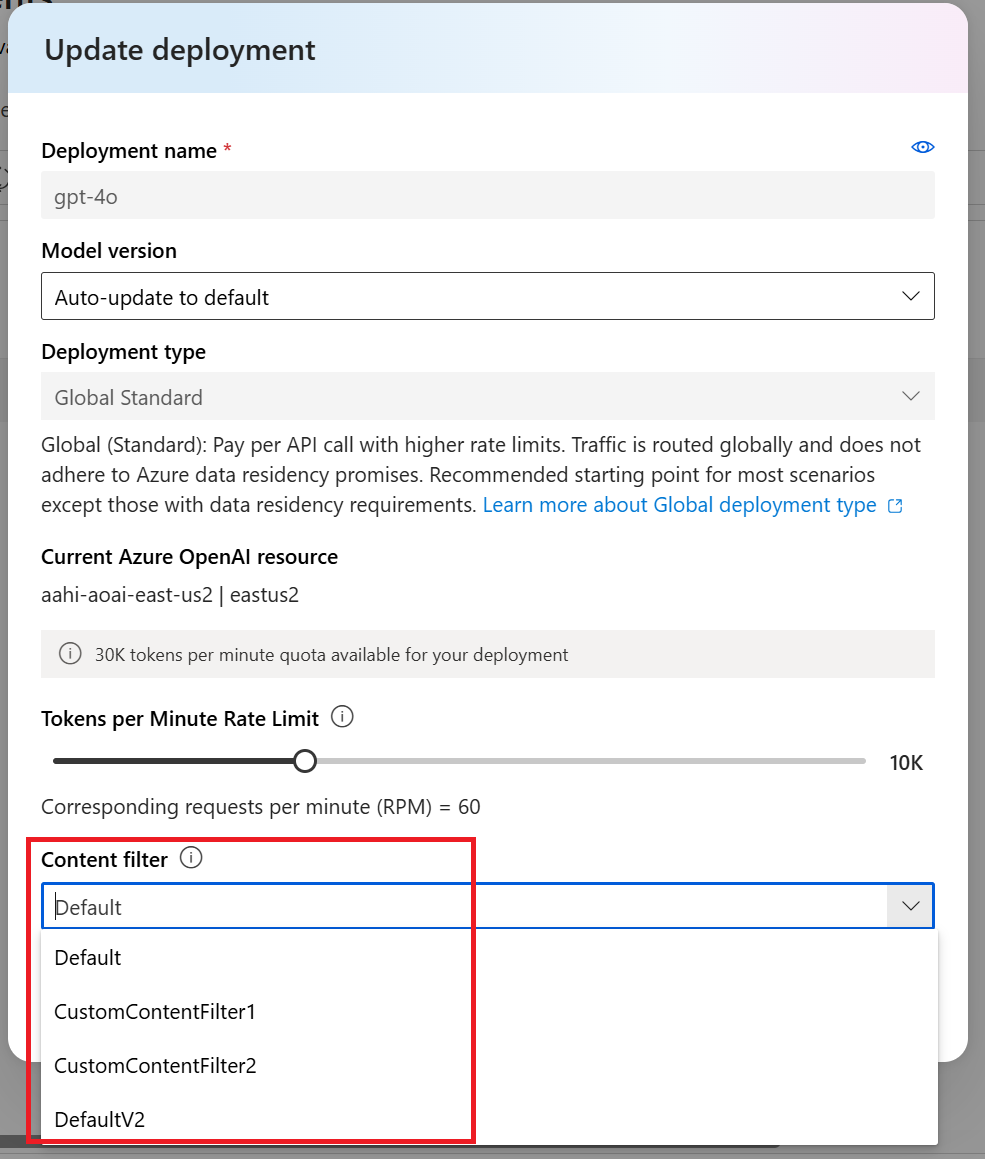
In the Update deployment window that appears, select your custom filter from the Content filter dropdown menu. Then select Save and close to apply the selected configuration to the deployment.
You can also edit and delete a content filter configuration if required. To do this, navigate to the content filters tab and select a configuration. Then select the desired action. You can only edit one filtering configuration at a time.
Note
Before deleting a content filtering configuration, you will need to unassign it from any deployment in the Deployments tab.
Follow best practices
We recommend informing your content filtering configuration decisions through an iterative identification (for example, red team testing, stress-testing, and analysis) and measurement process to address the potential harms that are relevant for a specific model, application, and deployment scenario. After you implement mitigations such as content filtering, repeat measurement to test effectiveness. Recommendations and best practices for Responsible AI for Azure OpenAI, grounded in the Microsoft Responsible AI Standard can be found in the Responsible AI Overview for Azure OpenAI.
Related content
- Learn more about Responsible AI practices for Azure OpenAI: Overview of Responsible AI practices for Azure OpenAI models.
- Read more about content filtering categories and severity levels with Azure OpenAI Service.
- Learn more about red teaming from our: Introduction to red teaming large language models (LLMs) article.