Events
31 Mar, 23 - 2 Apr, 23
The ultimate Microsoft Fabric, Power BI, SQL, and AI community-led event. March 31 to April 2, 2025.
Register todayThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article describes what datasets are, how they’re defined in JSON format, and how they’re used in Azure Data Factory and Synapse pipelines.
If you’re new to Data Factory, see Introduction to Azure Data Factory for an overview. For more information about Azure Synapse, see What is Azure Synapse
An Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace can have one or more pipelines. A pipeline is a logical grouping of activities that together perform a task. The activities in a pipeline define actions to perform on your data. Now, a dataset is a named view of data that simply points or references the data you want to use in your activities as inputs and outputs. Datasets identify data within different data stores, such as tables, files, folders, and documents. For example, an Azure Blob dataset specifies the blob container and folder in Blob Storage from which the activity should read the data.
Before you create a dataset, you must create a linked service to link your data store to the service. Linked services are much like connection strings, which define the connection information needed for the service to connect to external resources. Think of it this way; the dataset represents the structure of the data within the linked data stores, and the linked service defines the connection to the data source. For example, an Azure Storage linked service links a storage account. An Azure Blob dataset represents the blob container and the folder within that Azure Storage account that contains the input blobs to be processed.
Here’s a sample scenario. To copy data from Blob storage to a SQL Database, you create two linked services: Azure Blob Storage and Azure SQL Database. Then, create two datasets: Delimited Text dataset (which refers to the Azure Blob Storage linked service, assuming you have text files as source) and Azure SQL Table dataset (which refers to the Azure SQL Database linked service). The Azure Blob Storage and Azure SQL Database linked services contain connection strings that the service uses at runtime to connect to your Azure Storage and Azure SQL Database, respectively. The Delimited Text dataset specifies the blob container and blob folder that contains the input blobs in your Blob Storage, along with format-related settings. The Azure SQL Table dataset specifies the SQL table in your SQL Database to which the data is to be copied.
The following diagram shows the relationships among pipeline, activity, dataset, and linked services:
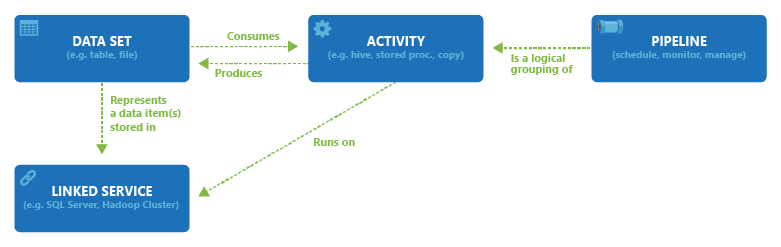
To create a dataset with the Azure Data Factory Studio, select the Author tab (with the pencil icon), and then the plus sign icon, to choose Dataset.
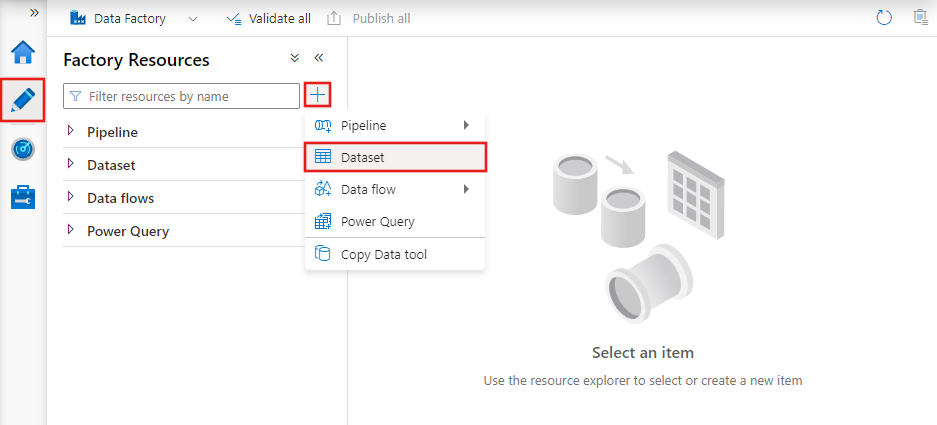
You’ll see the new dataset window to choose any of the connectors available in Azure Data Factory, to set up an existing or new linked service.
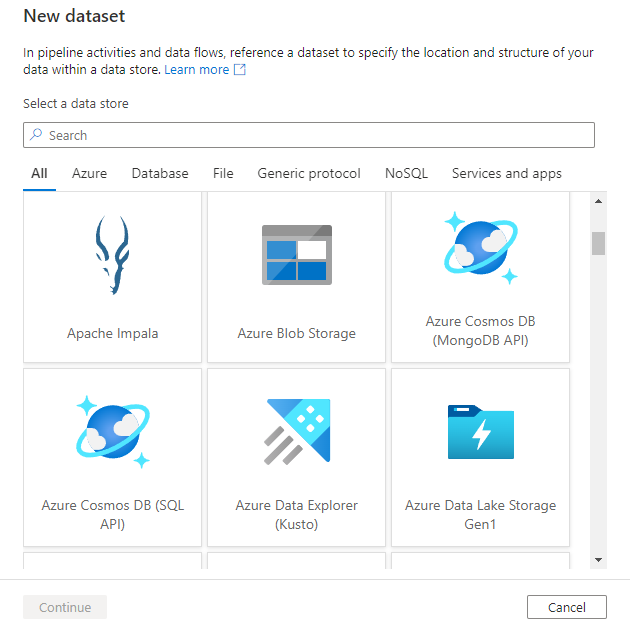
Next you’ll be prompted to choose the dataset format.

Finally, you can choose an existing linked service of the type you selected for the dataset, or create a new one if one isn’t already defined.
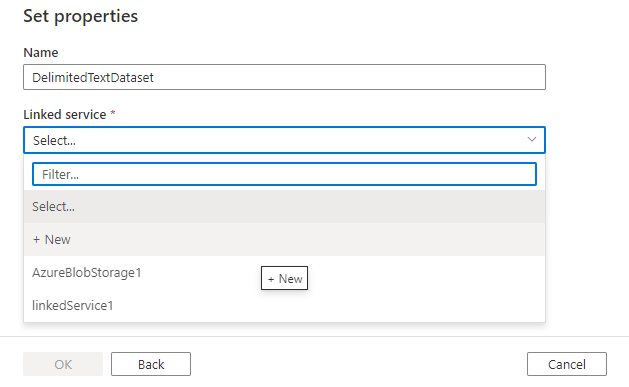
Once you create the dataset, you can use it within any pipelines in the Azure Data Factory.
A dataset is defined in the following JSON format:
{
"name": "<name of dataset>",
"properties": {
"type": "<type of dataset: DelimitedText, AzureSqlTable etc...>",
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<name of linked service>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference",
},
"schema":[
],
"typeProperties": {
"<type specific property>": "<value>",
"<type specific property 2>": "<value 2>",
}
}
}
The following table describes properties in the above JSON:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| name | Name of the dataset. See Naming rules. | Yes |
| type | Type of the dataset. Specify one of the types supported by Data Factory (for example: DelimitedText, AzureSqlTable). For details, see Dataset types. |
Yes |
| schema | Schema of the dataset, represents the physical data type and shape. | No |
| typeProperties | The type properties are different for each type. For details on the supported types and their properties, see Dataset type. | Yes |
When you import the schema of dataset, select the Import Schema button and choose to import from the source or from a local file. In most cases, you'll import the schema directly from the source. But if you already have a local schema file (a Parquet file or CSV with headers), you can direct the service to base the schema on that file.
In copy activity, datasets are used in source and sink. Schema defined in dataset is optional as reference. If you want to apply column/field mapping between source and sink, refer to Schema and type mapping.
In Data Flow, datasets are used in source and sink transformations. The datasets define the basic data schemas. If your data has no schema, you can use schema drift for your source and sink. Metadata from the datasets appears in your source transformation as the source projection. The projection in the source transformation represents the Data Flow data with defined names and types.
The service supports many different types of datasets, depending on the data stores you use. You can find the list of supported data stores from Connector overview article. Select a data store to learn how to create a linked service and a dataset for it.
For example, for a Delimited Text dataset, the dataset type is set to DelimitedText as shown in the following JSON sample:
{
"name": "DelimitedTextInput",
"properties": {
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "AzureBlobStorage",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"annotations": [],
"type": "DelimitedText",
"typeProperties": {
"location": {
"type": "AzureBlobStorageLocation",
"fileName": "input.log",
"folderPath": "inputdata",
"container": "adfgetstarted"
},
"columnDelimiter": ",",
"escapeChar": "\\",
"quoteChar": "\""
},
"schema": []
}
}
Note
The schema value is defined using JSON syntax. For more detailed information on schema mapping and data type mapping, refer to the Azure Data Factory Copy Activity Schema and Type Mapping documentation.
You can create datasets by using one of these tools or SDKs: .NET API, PowerShell, REST API, Azure Resource Manager Template, and Azure portal
Here are some differences between datasets in Data Factory current version (and Azure Synapse), and the legacy Data Factory version 1:
See the following tutorial for step-by-step instructions for creating pipelines and datasets by using one of these tools or SDKs.
Events
31 Mar, 23 - 2 Apr, 23
The ultimate Microsoft Fabric, Power BI, SQL, and AI community-led event. March 31 to April 2, 2025.
Register todayTraining
Module
Data integration with Azure Data Factory - Training
Integrate data with Azure Data Factory or Azure Synapse Pipeline
Certification
Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Engineer Associate - Certifications
Demonstrate understanding of common data engineering tasks to implement and manage data engineering workloads on Microsoft Azure, using a number of Azure services.