Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The invoice processing prebuilt AI model extracts key invoice data to help automate the processing of invoices. The invoice processing model is optimized to recognize common invoice elements like invoice ID, invoice date, amount due, and more.
The Invoices model allows you to augment the default behavior by building a custom Invoices model.
Use in Power Apps
Learn how to use the invoice processing prebuilt model in Power Apps in Use the invoice processing prebuilt model in Power Apps.
Use in Power Automate
Learn how to use the invoice processing prebuilt model in Power Automate in Use the invoice processing prebuilt model in Power Automate.
Supported languages and files
The following languages are supported: Albanian (Albania), Czech (Czech Republic), Chinese (simplified) China, Chinese (traditional) Hong Kong SAR, Chinese (traditional) Taiwan, Danish (Denmark), Croatian (Bosnia and Herzegovina), Croatian (Croatia), Croatian (Serbia), Dutch (Netherlands), English (Australia), English (Canada), English (India), English (United Kingdom), English (United States), Estonian (Estonia), Finnish (Finland), French (France), German (Germany), Hungarian (Hungary), Icelandic (Iceland), Italian (Italy), Japanese (Japan), Korean (Korea), Lithuanian (Lithuania), Latvian (Latvia), Malay (Malaysia), Norwegian (Norway), Polish (Poland), Portuguese (Portugal), Romanian (Romania), Slovak (Slovakia), Slovenian (Slovenia), Serbian (Serbia), Spanish (Spain), Swedish (Sweden).
To get the best results, provide one clear photo or scan per invoice.
- The image format must be JPEG, PNG, or PDF.
- The file size must not exceed 20 MB.
- The image dimensions must be between 50 x 50 pixels and 10,000 x 10,000 pixels.
- PDF dimensions must be at most 17 x 17 inches, which is the equivalent of the Legal or A3 paper sizes or smaller.
- For PDF documents, only the first 2,000 pages are processed.
Model output
If an invoice is detected, the invoice processing model outputs the following information:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
CustomerName |
Customer being invoiced |
CustomerId |
Reference ID for the customer |
PurchaseOrder |
A purchase order reference number |
InvoiceId |
ID for this specific invoice (often 'Invoice Number') |
InvoiceDate |
Date the invoice was issued |
DueDate |
Date payment for this invoice is due |
VendorName |
Vendor who created this invoice |
VendorAddress |
Mailing address for the Vendor |
VendorAddressRecipient |
Name associated with the VendorAddress |
CustomerAddress |
Mailing address for the Customer |
CustomerAddressRecipient |
Name associated with the CustomerAddress |
BillingAddress |
Explicit billing address for the customer |
BillingAddressRecipient |
Name associated with the BillingAddress |
ShippingAddress |
Explicit shipping address for the customer |
ShippingAddressRecipient |
Name associated with the ShippingAddress |
SubTotal |
Subtotal field identified on this invoice |
TotalDiscount |
Total discount field identified on this invoice |
TotalTax |
Total tax field identified on this invoice |
InvoiceTotal |
Total new charges associated with this invoice |
AmountDue |
Total Amount Due to the vendor |
PreviousUnpaidBalance |
Explicit previously unpaid balance |
RemittanceAddress |
Explicit remittance or payment address for the customer |
RemittanceAddressRecipient |
Name associated with the RemittanceAddress |
ServiceAddress |
Explicit service address or property address for the customer |
ServiceAddressRecipient |
Name associated with the ServiceAddress |
ServiceStartDate |
First date for the service period (for example, a utility bill service period) |
ServiceEndDate |
End date for the service period (for example, a utility bill service period) |
VendorTaxId |
The government ID number associated with the vendor |
CustomerTaxId |
The government ID number associated with the customer |
PaymentTerm |
The terms under which the payment is meant to be paid |
KVKNumber |
A unique identifier for businesses registered in the Netherlands |
PaymentDetails |
List of payment details
|
TaxDetails |
List of tax details
|
PaidInFourInstallements |
List of tax details
|
Items |
List of tax details
|
Confidence score
| Field | Confidence score |
|---|---|
CustomerName |
✔️ |
CustomerId |
✔️ |
PurchaseOrder |
✔️ |
InvoiceId |
✔️ |
InvoiceDate |
✔️ |
DueDate |
✔️ |
VendorName |
✔️ |
VendorAddress |
✔️ |
VendorAddressRecipient |
✔️ |
CustomerAddress |
✔️ |
CustomerAddressRecipient |
✔️ |
BillingAddress |
✔️ |
BillingAddressRecipient |
✔️ |
ShippingAddress |
✔️ |
ShippingAddressRecipient |
✔️ |
SubTotal |
✔️ |
TotalDiscount |
✔️ |
TotalTax |
✔️ |
InvoiceTotal |
✔️ |
AmountDue |
✔️ |
PreviousUnpaidBalance |
✔️ |
RemittanceAddress |
✔️ |
RemittanceAddressRecipient |
✔️ |
ServiceAddress |
✔️ |
ServiceAddressRecipient |
✔️ |
ServiceStartDate |
✔️ |
ServiceEndDate |
✔️ |
VendorTaxId |
✔️ |
CustomerTaxId |
✔️ |
PaymentTerm |
✔️ |
KVKNumber |
✔️ |
PaymentDetails.*.IBAN |
✔️ |
PaymentDetails.*.SWIFT |
✔️ |
PaymentDetails.*.BankAccountNumber |
✔️ |
PaymentDetails.*.BPayBillerCode |
✔️ |
PaymentDetails.*.BPayReference |
✔️ |
TaxDetails.*.Amount |
✔️ |
TaxDetails.*.Rate |
✔️ |
PaidInFourInstallements.*.Amount |
✔️ |
PaidInFourInstallements.*.DueDate |
✔️ |
Items.*.Amount |
✔️ |
Items.*.Date |
✔️ |
Items.*.Description |
✔️ |
Items.*.Quantity |
✔️ |
Items.*.ProductCode |
✔️ |
Items.*.Tax |
✔️ |
Items.*.TaxRate |
✔️ |
Items.*.Unit |
✔️ |
Items.*.UnitPrice |
✔️ |
Key-value pairs
Key-value pairs are all the identified labels or keys and their associated responses or values. You can use these to extract additional values that aren't part of the predefined list of fields.
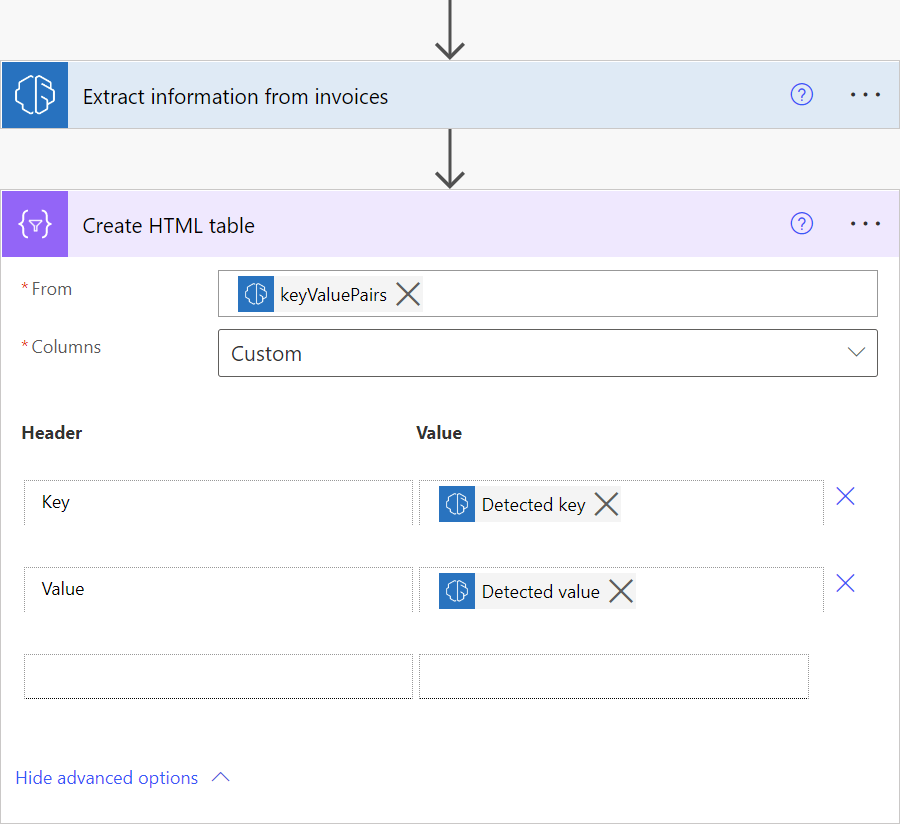
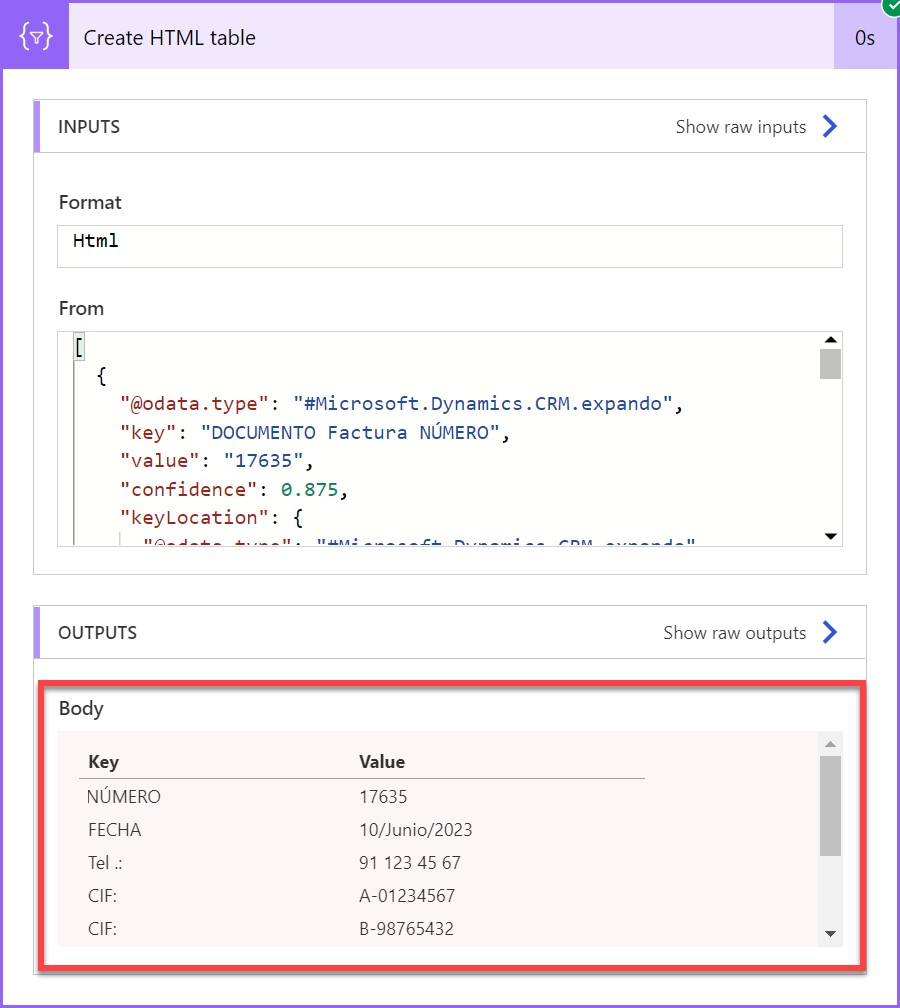
To visualize all key-value pairs detected by the invoice processing model, you can add a Create HTML table action in your cloud flow as shown in the screenshot and run the cloud flow.
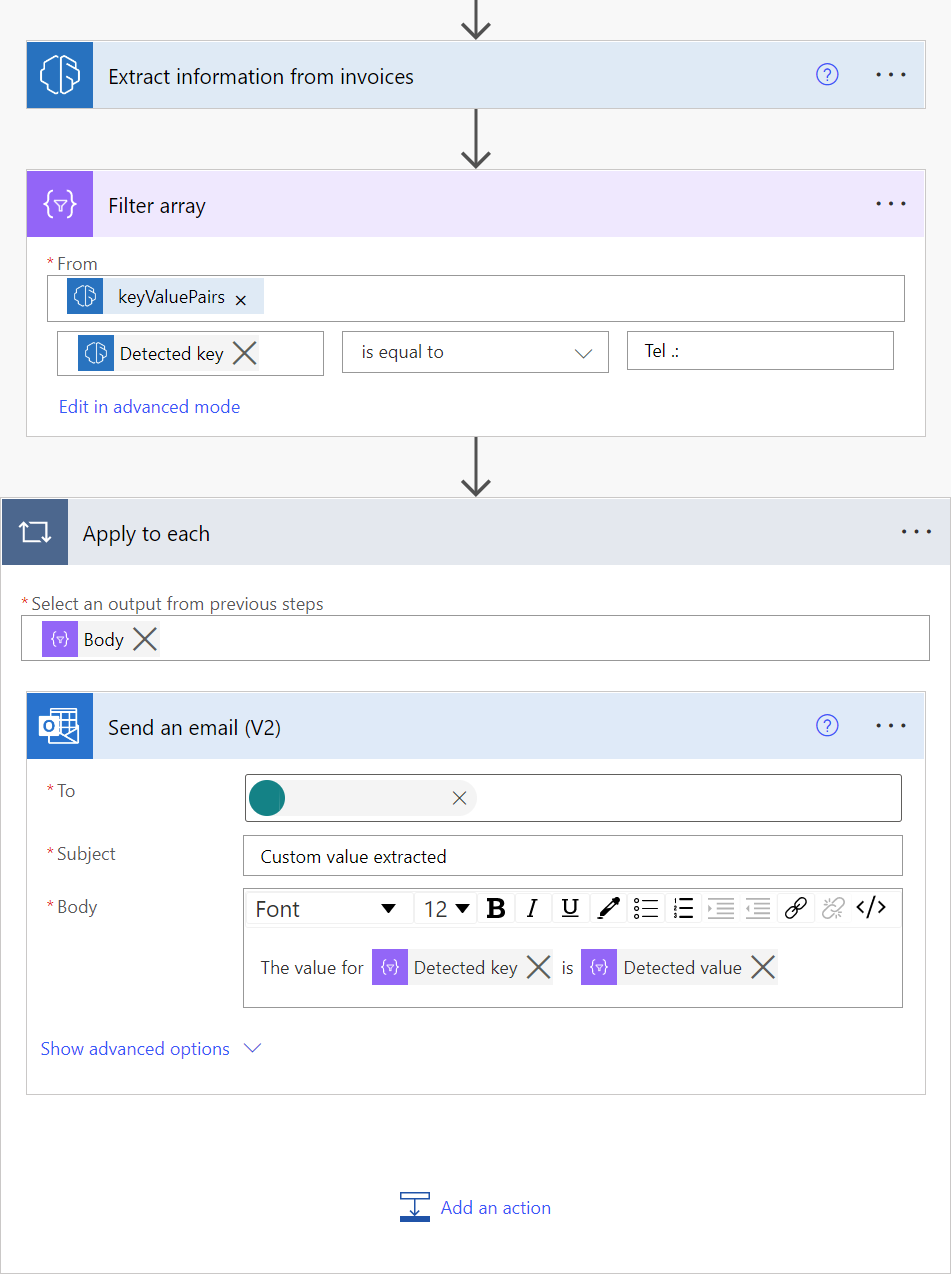
To extract a specific key for which you know its value, you can use the Filter array action as shown on the following screenshot. In the example of the screenshot, we want to extract the value for the key Tel .:
Limits
The following limit applies to calls made per environment across document processing models including prebuilt models: receipt processing and invoice processing.
| Action | Limit | Renewal period |
|---|---|---|
| Calls (per environment) | 360 | 60 seconds |
Create a custom invoice processing solution
The invoice processing prebuilt AI model is designed to extract common fields found in invoices. Because every business is unique, you might want to extract fields other than those included in this prebuilt model. It can also be the case that some standard fields aren't well extracted for a particular type of invoice you work with. To address this, there are two options:
Use the custom Invoices processing model: Augment the behaviors of the prebuilt invoice processing model by adding new fields to be extracted in addition to the ones by default, or samples of documents not properly extracted. To learn how to augment the prebuilt invoice processing model, go to Select the type of document.
View raw OCR results: Every time the invoice processing prebuilt AI model processes a file you provide, it also does an OCR operation to extract every word written on the file. You can access the raw OCR results on the detected text output provided by the model. A simple search on the content returned by detected text might be enough to get the data you need.
Use document processing: With AI Builder, you can also build your own custom AI model to extract specific fields and tables you need for the documents you work with. Just create a document processing model and train it to extract all the information from an invoice that doesn’t work well with the invoice extraction model.
Once you train your custom document processing model, you can combine it with the invoice processing prebuilt model in a Power Automate cloud flow.
Here are some examples:
Use a custom document processing model to extract additional fields that aren't returned by the invoice processing prebuilt model
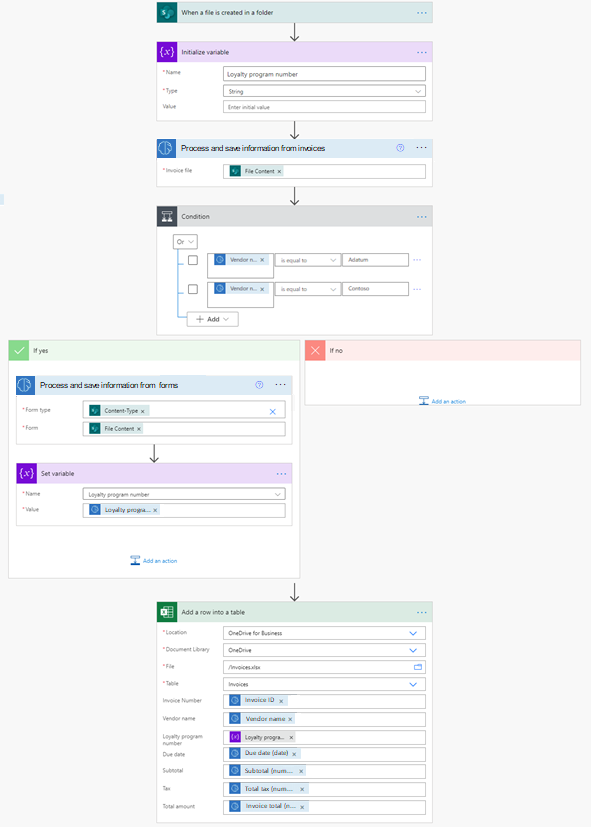
In this example, we trained a custom document processing model to extract a loyalty program number, only present in invoices from providers Adatum and Contoso.
The cloud flow is triggered when a new invoice is added to a SharePoint folder. It then calls the invoice processing prebuilt AI model to extract its data. Next, we check if the vendor for the invoice that was processed is either from Adatum or Contoso. If it's the case, we then call a custom document processing model that we trained to get that loyalty number. Finally, we save the extracted data from the invoice in an Excel file.
Use a custom document processing model if the confidence score for a field returned by the invoice processing prebuilt model is low
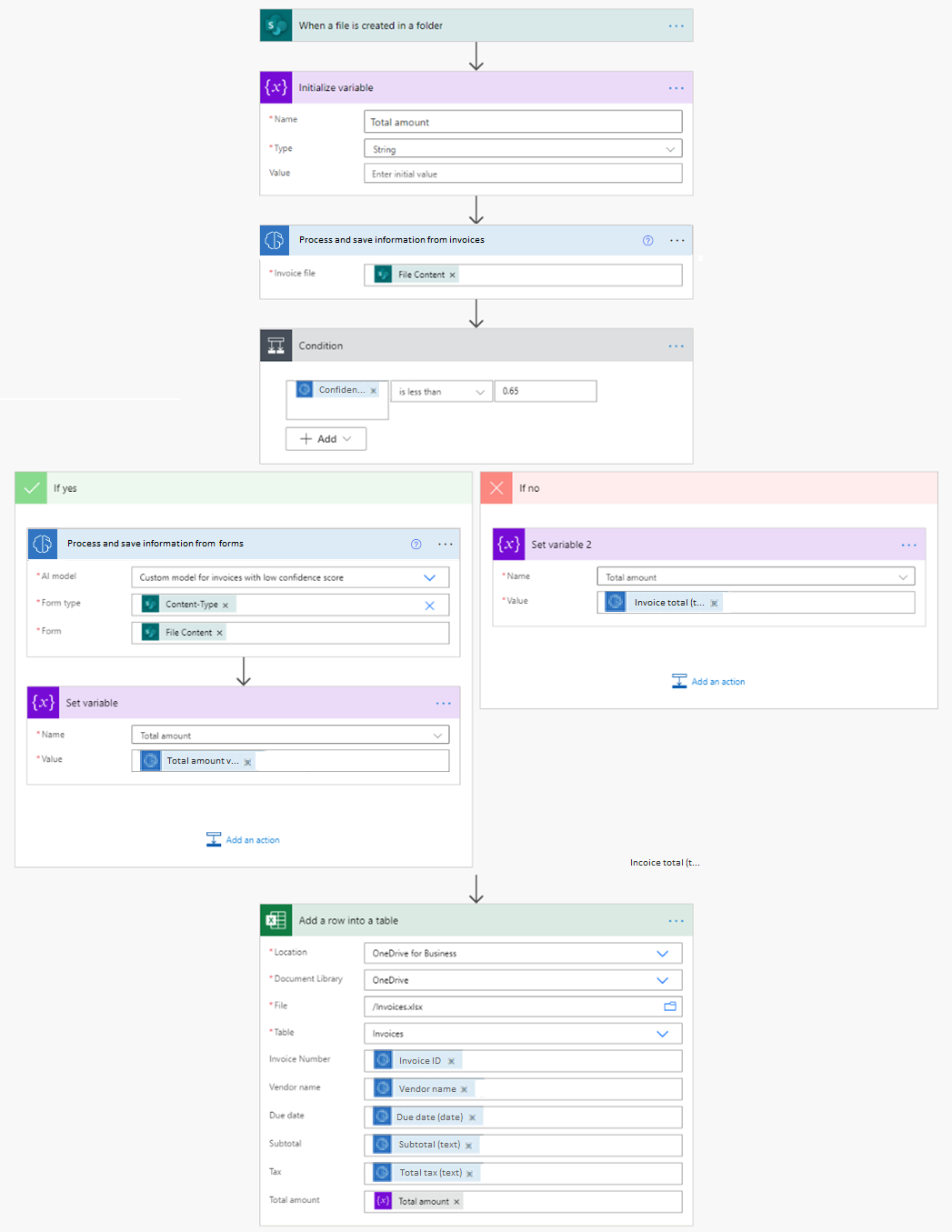
In this example, we trained a custom document processing model to extract the total amount from invoices where we usually get a low confidence score when using the invoice processing prebuilt model.
The cloud flow is triggered when a new invoice is added to a SharePoint folder. It then calls the invoice processing prebuilt AI model to extract its data. Next, we check if the confidence score for the Invoice total value property is less than 0.65. If it’s the case, we then call a custom document processing model that we trained with invoices where we usually get a low confidence score for the total field. Finally, we save the extracted data from the invoice into an Excel file.
Use the invoice processing prebuilt model to handle invoices that a custom document processing model isn't trained to handle
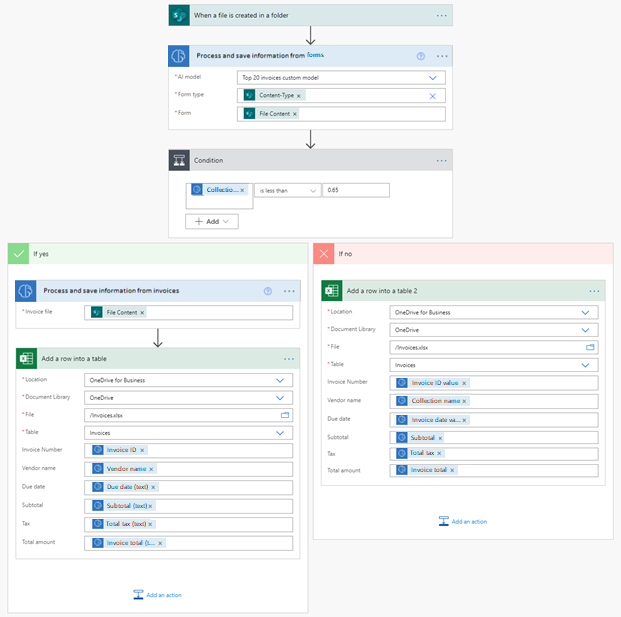
One way to use the invoice processing prebuilt model is to use it as a fallback model to handle invoices that you didn't train in your custom document processing model. For example, let's say you built a document processing model, and trained it to extract data from your top 20 invoice providers. You could then use the invoice processing prebuilt model to process all new invoices or lower volume invoices. Here’s an example of how you could do it:
This cloud flow is triggered when a new invoice is added to a SharePoint folder. It then calls a custom document processing model to extract its data. Next, we check if the confidence score for the detected collection is less than 0.65. If it’s the case, it probably means the provided invoice isn't a good match for the custom model. We then call the prebuilt invoice processing model. Finally, we save the extracted data from the invoice in an Excel file.