Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server on Azure VM
In the Azure portal, the SQL virtual machines resource is an independent management service to manage SQL Server on Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) that have been registered with the SQL Server IaaS Agent extension. You can use the resource to view all of your SQL Server VMs simultaneously and modify settings dedicated to SQL Server:
The SQL virtual machines resource management point is different to the Virtual machine resource used to manage the underlying VM such as to start it, stop it, or restart it.
Prerequisites
The SQL virtual machines resource is only available to SQL Server VMs that have been registered with the SQL IaaS Agent extension.
Access the resource
To access the SQL virtual machines resource, follow these steps:
Open the Azure portal.
Select All Services.
Enter SQL virtual machines in the search box.
(Optional): Select the star next to SQL virtual machines to add this option to your Favorites menu.
Select SQL virtual machines.
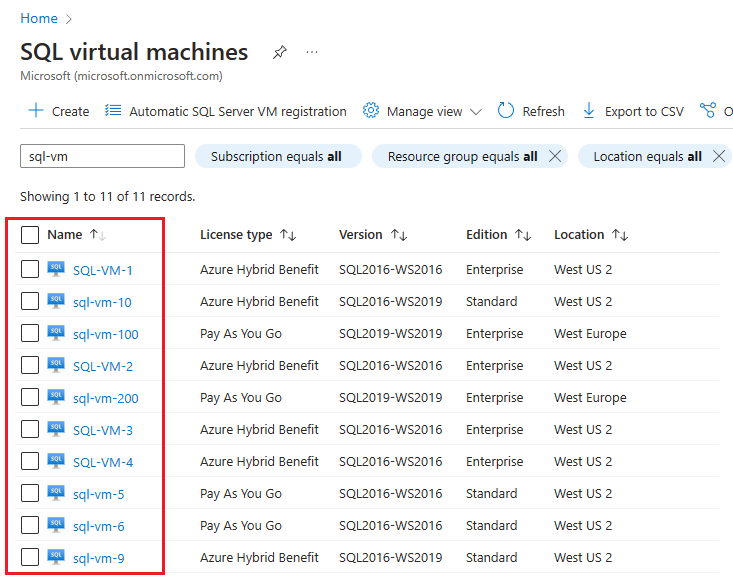
The portal lists all SQL Server VMs available within the selected subscription. Choose the one you want to manage to open the SQL virtual machines resource. Use the search box if your SQL Server VM isn't appearing, and make sure you've selected the correct subscription.
Selecting your SQL Server VM opens the SQL virtual machines resource.
Tip
The SQL virtual machines resource is to manage settings dedicated to the SQL Server instance. Select the name of the VM under Virtual machine on the Overview page to open settings that are specific to the underlying virtual machine.
Overview page
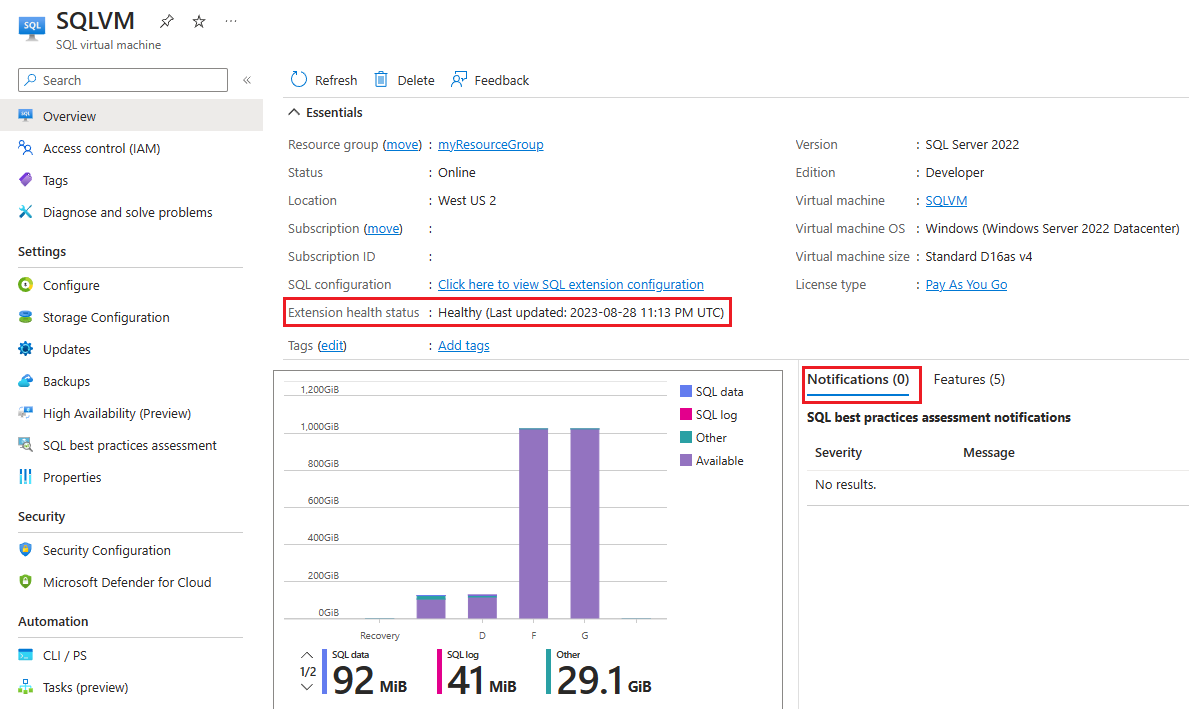
The Overview page of the SQL virtual machines resource provides basic information about the SQL Server VM, such as the resource group, location, license type, the name of the underlying Azure virtual machine, and storage utilization metrics.
You can also see the status of the SQL Iaas Agent extension under Extension health status. If your status is Unhealthy, or Failed, you can find out more information from the Notifications tab.
The Notifications tab displays information from SQL best practices assessments and extension health while the Features tab shows which recommended features are and aren't configured:
License and edition
Use the Configure page of the SQL virtual machines resource to change your SQL Server licensing metadata to Pay as you go, Azure Hybrid Benefit, or HA/DR for your free Azure replica for disaster recovery.
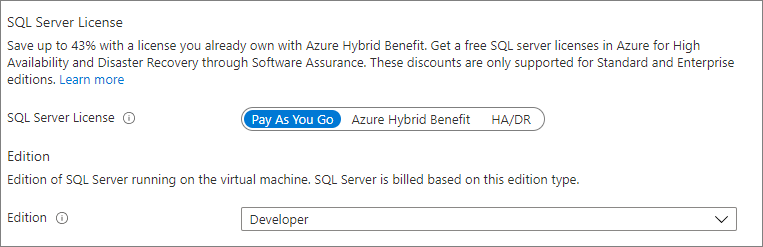
You can modify the edition of SQL Server from the Configure page as well, such as Enterprise, Standard, or Developer.
Changing the license and edition metadata in the Azure portal is only supported once the version and edition of SQL Server has been modified internally to the VM. To learn more see, change the version and edition of SQL Server on Azure VMs.
Storage
The Storage page of the SQL virtual machines resource allows you to analyze the I/O performance of your SQL Server workloads, identify missing best practices, and configure the storage settings for your SQL Server VM:

The Storage page has the following tabs:
- The I/O Analysis tab provides insights into the I/O performance of your SQL Server workloads. Use this tab to identify VM level or disk level I/O throttling, as well as suggestions for remediation.
- Run I/O related best practices assessments from the I/O Related Best Practices tab to identify missing storage best practices configurations for your SQL Server VM.
- Use the Storage Configuration tab to configure your data, log, and
tempdbdrives, such as to extend them. For guidance, review storage configuration and Storage: Performance best practices for SQL Server on Azure VMs.
Note
- Storage is only extendable for SQL Server VMs that were deployed from a SQL Server image in Azure Marketplace, and not currently supported for Premium SSD v2 disks.
- Making changes to Premium SSD v2 for SQL Server VMs in the Azure portal is not currently supported so the Storage Configuration page of the SQL virtual machines resource shows Not extendable for Premium SSD v2 disks. Review Adjust performance to manage your Premium SSD v2 disks.
Updates
You have two different options when automatically patching your SQL Server on Azure VMs - the new integrated Azure Update Manager experience, and the existing Automated Patching feature (which is scheduled to retire on September 17, 2027).
Update Manager allows you to choose which updates and patches to apply to multiple SQL Server VMs at scale, including Cumulative Updates. Automated Patching lets you manage patches for a single VM and only applies updates that are marked as Critical or Important (which doesn't include Cumulative Updates for SQL Server).
Choose the experience that best suits your business needs as enabling both can lead to unexpected behaviors, scheduling conflicts, and unintentionally applying patches outside of maintenance windows.
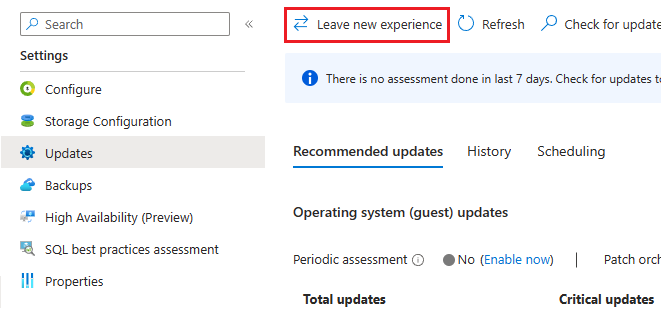
To use the Update Manager, select Updates under settings in the resource menu, make sure automated patching is disabled and then select Try Azure Update Manager in the navigation bar to integrate Update Manager into your Updates page. Once you enable this for any VM, all your other SQL Server VMs will also integrate the new experience unless you've already enabled Automated Patching for any specific VM. If you see Leave new experience instead of Try Azure Update Manager then you're already using the integrated Azure Update Manager experience.
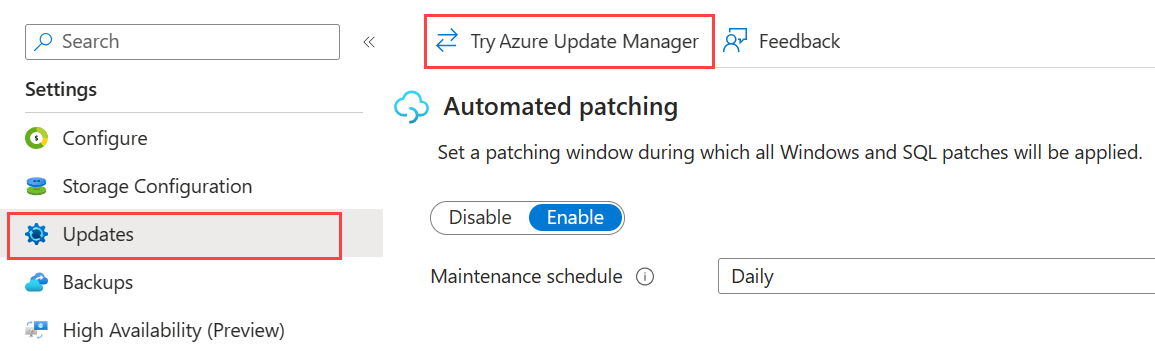
If you've never enabled Update Manager before, then to enable Automated Patching, select Enable on the Updates page. Otherwise, to go back to the Automated Patching page, choose Leave new experience:
Backups
Use the Backups page of the SQL virtual machines resource to choose between Azure Backup and Automated Backup.
Regardless of which backup solution you choose, you can use the Backups page to configure your backup settings, such as the retention period, backup storage location, encryption, whether or not to back up system databases, and a backup schedule.
Modernization Advisor (preview)
The Modernization Advisor (Preview) assesses your SQL Server workload to identify cost-saving or performance optimizations you may gain by migrating to Azure SQL Managed Instance. This feature is currently in preview.
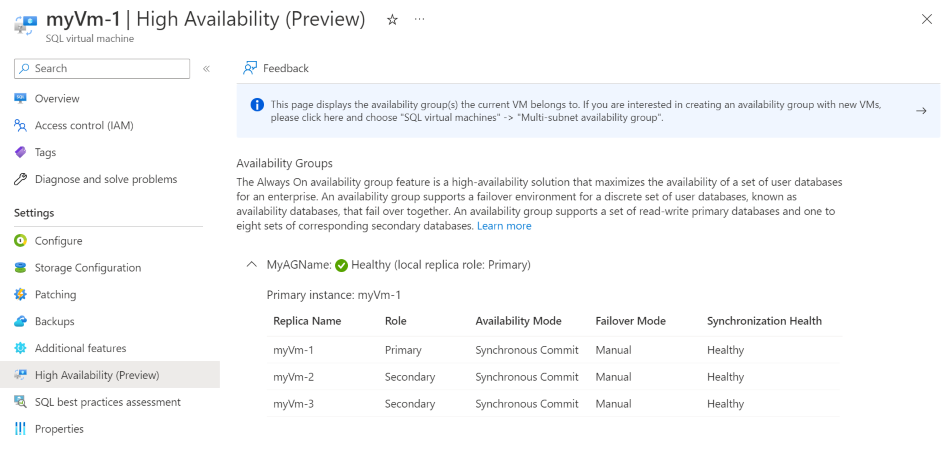
High availability (preview)
Once you've configured your availability group by using the Azure portal, use the High Availability page of the SQL virtual machines resource to monitor the health of your existing Always On availability group.
SQL best practices assessment
Use the SQL best practices assessment page of the SQL virtual machines resource to assess the health of your SQL Server VM. Once the feature is enabled, your SQL Server instances and databases are scanned and recommendations are surfaced to improve performance (indexes, statistics, trace flags, and so on) and identify missing best practices configurations.
To learn more, see SQL best practices assessment for SQL Server on Azure VMs.
Security Configuration
Use the Security Configuration page of the SQL virtual machines resource to configure SQL Server security settings such as Azure Key Vault integration, and if you're on SQL Server 2022, authentication with Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory).
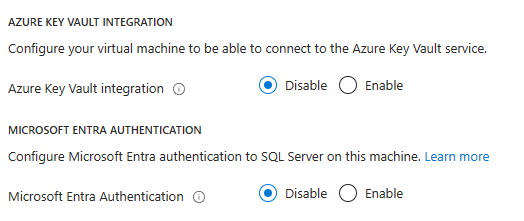
To learn more, see the Security best practices.
Note
The ability to change the connectivity and SQL Server authentication settings after the SQL Server VM is deployed was removed from the Azure portal in April 2023. You can still specify these settings during SQL Server VM deployment, or use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) to update these settings manually from within the SQL Server VM after deployment.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud
Use the Microsoft Defender for Cloud page of the SQL virtual machine's resource to view Microsoft Defender for SQL server on machines recommendations directly in the SQL virtual machine page. Enable Microsoft Defender for SQL to use this feature.
SQL IaaS Agent Extension Settings
From the SQL IaaS Agent Extension Settings page, you can repair the extension and enable auto upgrade to ensure you're automatically receiving updates for the extension each month.