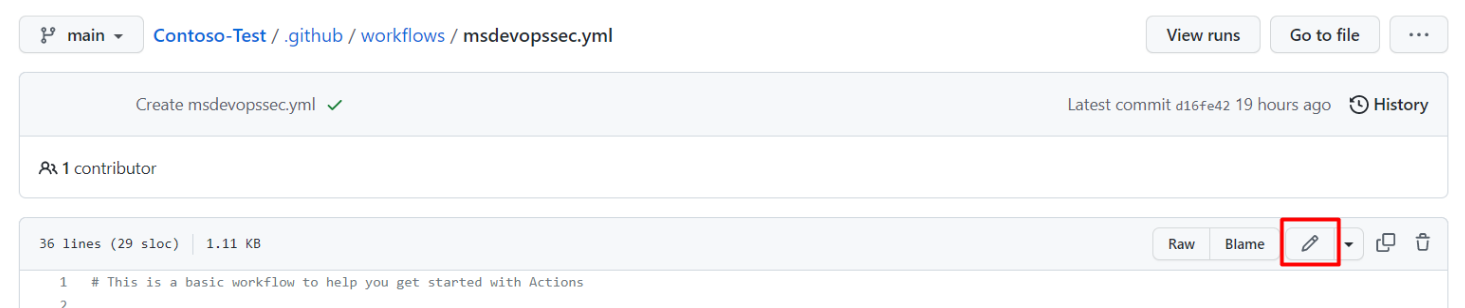Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
DevOps security exposes security findings as annotations in Pull Requests (PR). Security operators can enable PR annotations in Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Any exposed issues can be remedied by developers. This process can prevent and fix potential security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations before they enter the production stage. DevOps security annotates vulnerabilities within the differences introduced during the pull request rather than all the vulnerabilities detected across the entire file. Developers are able to see annotations in their source code management systems and Security operators can see any unresolved findings in Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
With Microsoft Defender for Cloud, you can configure PR annotations in Azure DevOps. You can get PR annotations in GitHub if you're a GitHub Advanced Security customer.
What are pull request annotations
Pull request annotations are comments that are added to a pull request in GitHub or Azure DevOps. These annotations provide feedback on the code changes made and identified security issues in the pull request and help reviewers understand the changes that are made.
Users with access to the repository can add annotations, to suggest changes, ask questions, or provide feedback on the code. Annotations can also be used to track issues and bugs that need to be fixed before the code is merged into the main branch. DevOps security in Defender for Cloud uses annotations to surface security findings.
Prerequisites
For GitHub:
- An Azure account. If you don't already have an Azure account, you can create your Azure free account today.
- Be a GitHub Advanced Security customer.
- Connect your GitHub repositories to Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
- Configure the Microsoft Security DevOps GitHub action.
For Azure DevOps:
- An Azure account. If you don't already have an Azure account, you can create your Azure free account today.
- Have write access (owner/contributor) to the Azure subscription.
- Connect your Azure DevOps repositories to Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
- Configure the Microsoft Security DevOps Azure DevOps extension.
Enable pull request annotations in GitHub
By enabling pull request annotations in GitHub, your developers gain the ability to see their security issues when they create a PR directly to the main branch.
To enable pull request annotations in GitHub:
Navigate to GitHub and sign in.
Select a repository that you've onboarded to Defender for Cloud.
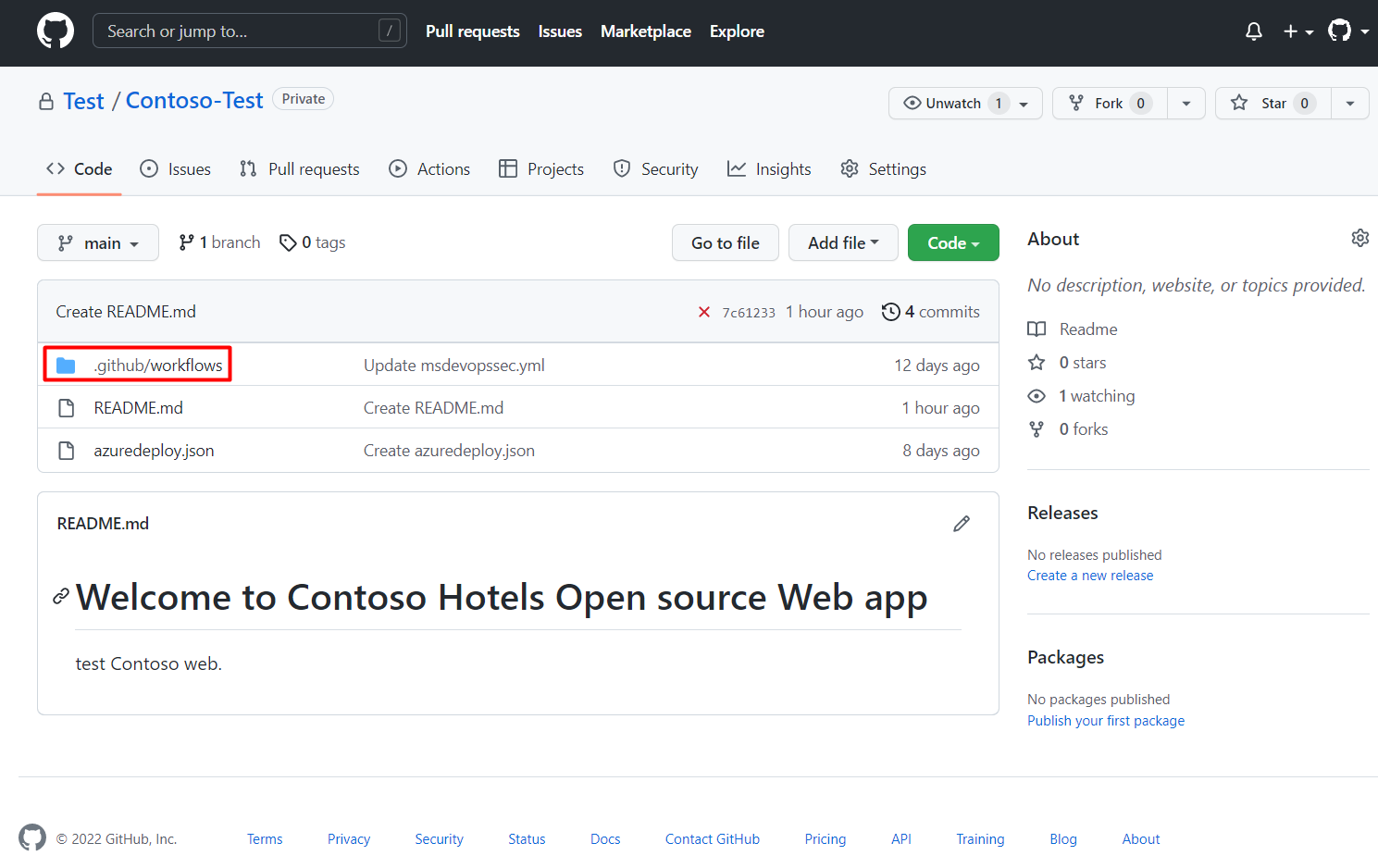
Navigate to
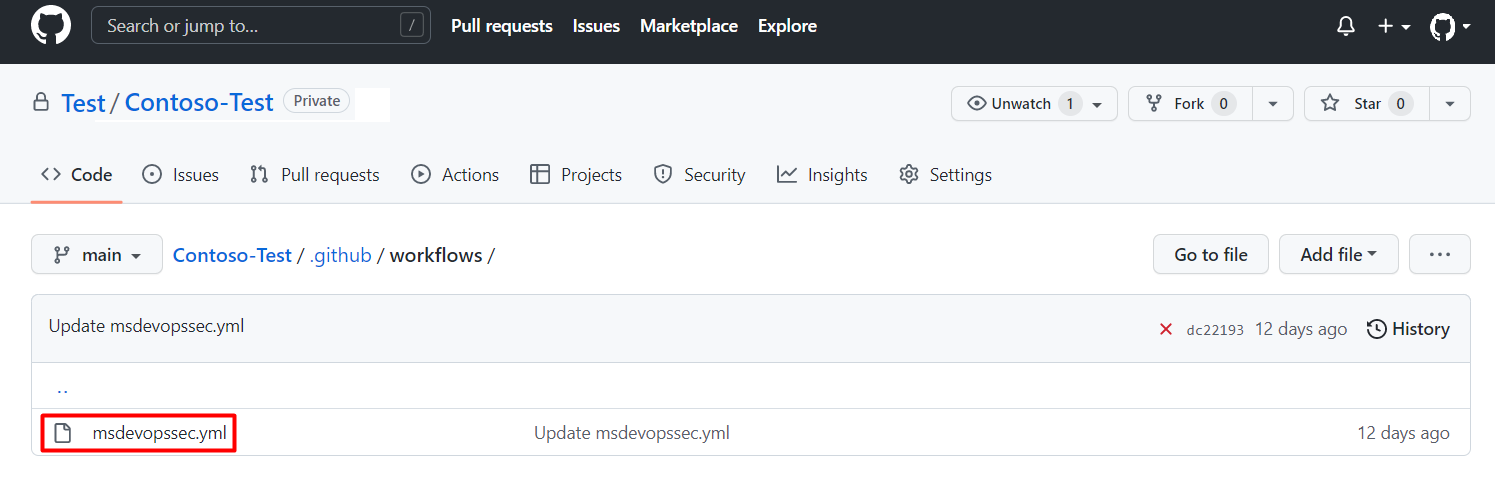
Your repository's home page> .github/workflows.Select msdevopssec.yml, which was created in the prerequisites.
Select edit.
Locate and update the trigger section to include:
# Triggers the workflow on push or pull request events but only for the main branch pull_request: branches: ["main"]You can also view a sample repository.
(Optional) You can select which branches you want to run it on by entering the branch(es) under the trigger section. If you want to include all branches remove the lines with the branch list.
Select Start commit.
Select Commit changes.
Any issues that are discovered by the scanner will be viewable in the Files changed section of your pull request.
- Used in tests - The alert isn't in the production code.
Enable pull request annotations in Azure DevOps
By enabling pull request annotations in Azure DevOps, your developers gain the ability to see their security issues when they create PRs directly to the main branch.
Enable Build Validation policy for the CI Build
Before you can enable pull request annotations, your main branch must have enabled Build Validation policy for the CI Build.
To enable Build Validation policy for the CI Build:
Sign in to your Azure DevOps project.
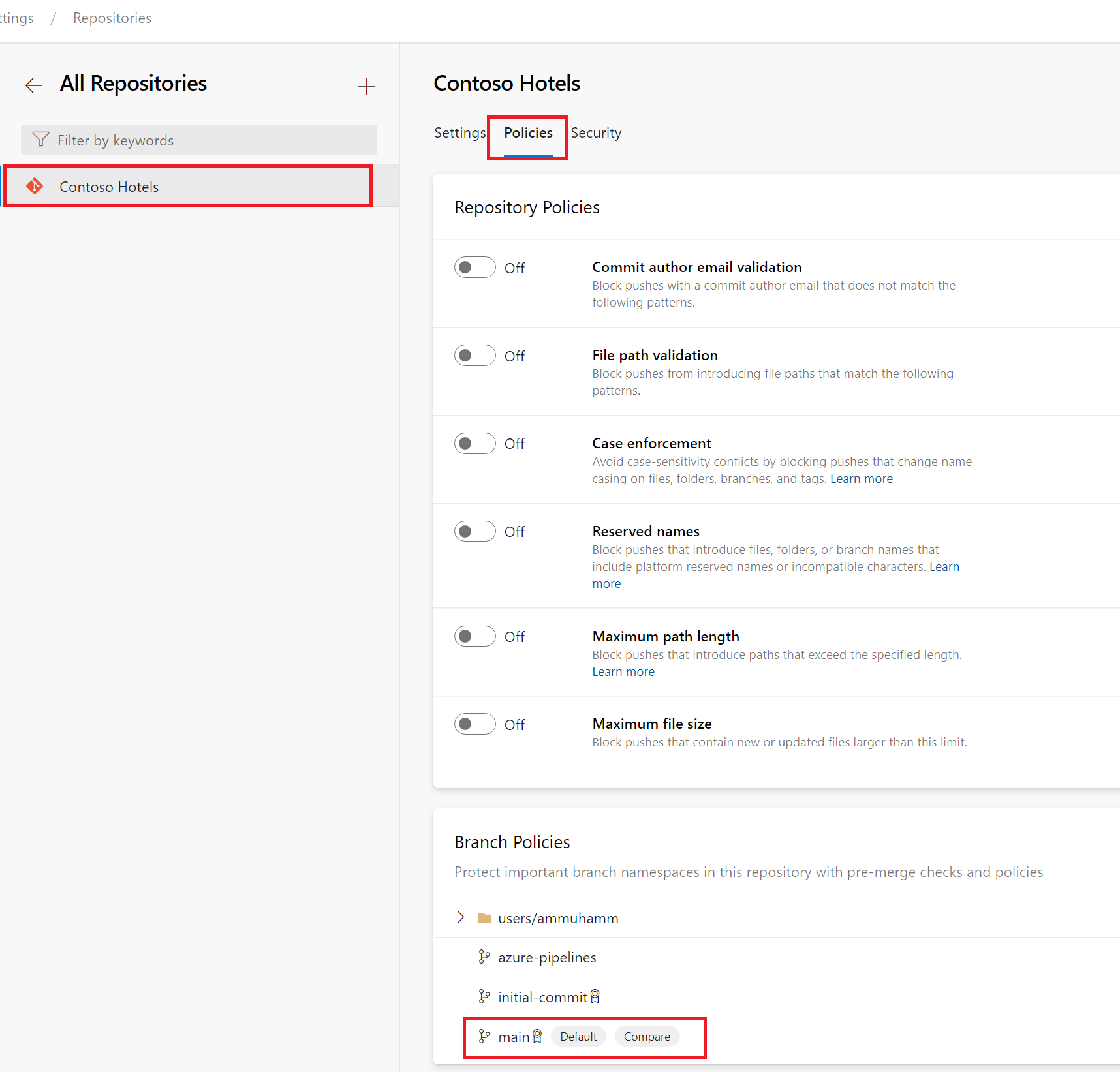
Navigate to Project settings > Repositories.
Select the repository to enable pull requests on.
Select Policies.
Navigate to Branch Policies > Main branch.
Locate the Build Validation section.
Ensure the build validation for your repository is toggled to On.
Select Save.
Once you've completed these steps, you can select the build pipeline you created previously and customize its settings to suit your needs.
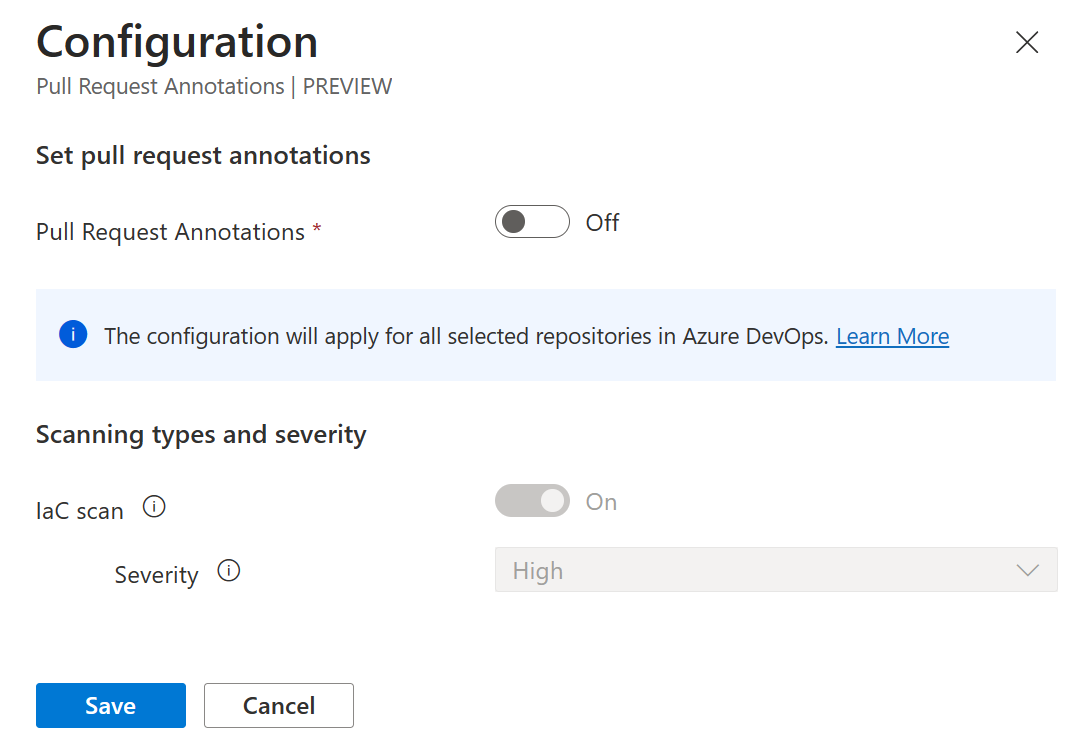
Enable pull request annotations
To enable pull request annotations in Azure DevOps:
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Navigate to Defender for Cloud > DevOps security.
Select all relevant repositories to enable the pull request annotations on.
Select Manage resources.
Toggle pull request annotations to On.
(Optional) Select a category from the drop-down menu.
Note
Only Infrastructure-as-Code misconfigurations (ARM, Bicep, Terraform, CloudFormation, Dockerfiles, Helm Charts, and more) results are currently supported.
(Optional) Select a severity level from the drop-down menu.
Select Save.
All annotations on your pull requests will be displayed from now on based on your configurations.
To enable pull request annotations for my Projects and Organizations in Azure DevOps:
You can do this programmatically by calling the Update Azure DevOps Resource API exposed the Microsoft. Security Resource Provider.
API Info:
Http Method: PATCH URLs:
- Azure DevOps Project Update:
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<subId>/resourcegroups/<resourceGroupName>/providers/Microsoft.Security/securityConnectors/<connectorName>/devops/default/azureDevOpsOrgs/<adoOrgName>/projects/<adoProjectName>?api-version=2023-09-01-preview - Azure DevOps Org Update]:
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<subId>/resourcegroups/<resourceGroupName>/providers/Microsoft.Security/securityConnectors/<connectorName>/devops/default/azureDevOpsOrgs/<adoOrgName>?api-version=2023-09-01-preview
Request Body:
{
"properties": {
"actionableRemediation": {
"state": <ActionableRemediationState>,
"categoryConfigurations":[
{"category": <Category>,"minimumSeverityLevel": <Severity>}
]
}
}
}
Parameters / Options Available
<ActionableRemediationState>
Description: State of the PR Annotation Configuration
Options: Enabled | Disabled
<Category>
Description: Category of Findings that are annotated on pull requests.
Options: IaC | Code | Artifacts | Dependencies | Containers
Note: Only IaC is supported currently
<Severity>
Description: The minimum severity of a finding that is considered when creating PR annotations.
Options: High | Medium | Low
Example of enabling an Azure DevOps Org's PR Annotations for the IaC category with a minimum severity of Medium using the az cli tool.
Update Org:
az --method patch --uri https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/4383331f-878a-426f-822d-530fb00e440e/resourcegroups/myrg/providers/Microsoft.Security/securityConnectors/myconnector/devops/default/azureDevOpsOrgs/testOrg?api-version=2023-09-01-preview --body "{'properties':{'actionableRemediation':{'state':'Enabled','categoryConfigurations':[{'category':'IaC','minimumSeverityLevel':'Medium'}]}}}
Example of enabling an Azure DevOps Project's PR Annotations for the IaC category with a minimum severity of High using the az cli tool.
Update Project:
az --method patch --uri https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/4383331f-878a-426f-822d-530fb00e440e/resourcegroups/myrg/providers/Microsoft.Security/securityConnectors/myconnector/devops/default/azureDevOpsOrgs/testOrg/projects/testProject?api-version=2023-09-01-preview --body "{'properties':{'actionableRemediation':{'state':'Enabled','categoryConfigurations':[{'category':'IaC','minimumSeverityLevel':'High'}]}}}"
Learn more
- Learn more about DevOps security.
- Learn more about DevOps security in Infrastructure as Code.
Next steps
Now learn more about DevOps security.