Key concepts for Azure Lab Services
Important
Azure Lab Services will be retired on June 28, 2027. For more information, see the retirement guide.
This article describes key Azure Lab Services concepts and definitions.
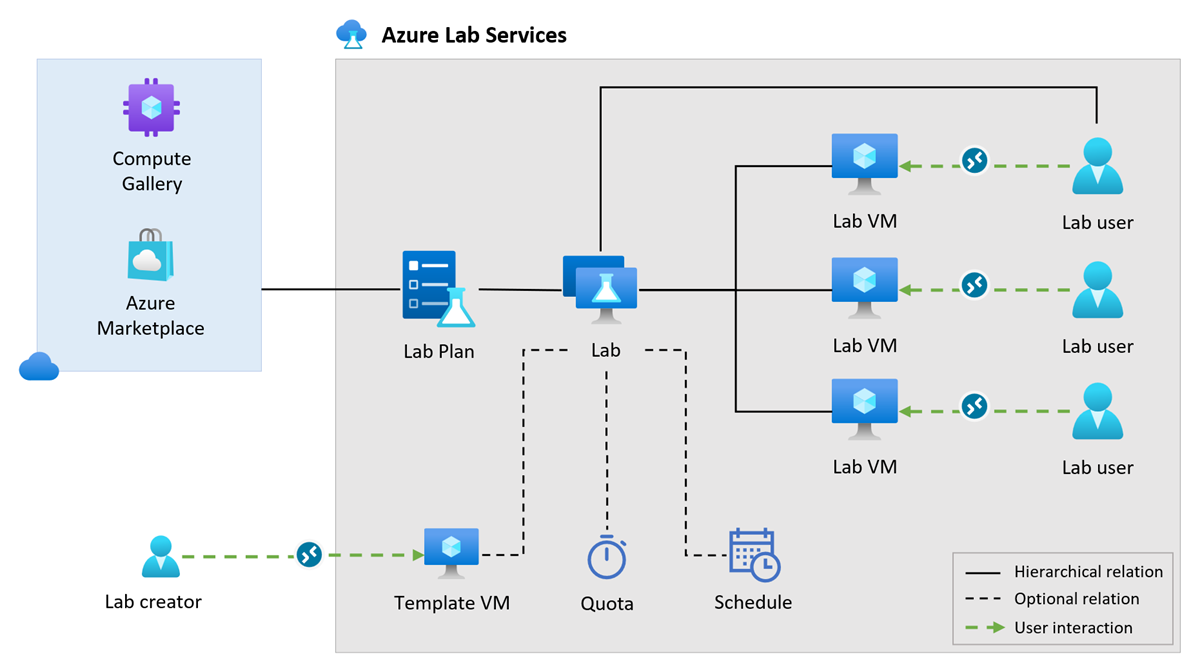
The following conceptual diagram shows how the different Azure Lab Services components are related.
Lab plan
In Azure Lab Services, a lab plan is an Azure resource and serves as a collection of configurations and settings that apply to all the labs created from it. For example, lab plans specify the networking setup, the list of available VM images and VM sizes, and if Canvas integration can be used for a lab. Learn more about planning your lab plan settings.
You can associate a lab plan with zero or more labs. Each lab uses the configuration settings from the lab plan. Azure Lab Services uses Azure RBAC roles to grant permissions for creating labs. Learn more about Azure Lab Services built-in roles.
Lab
A lab contains the configuration and settings for creating and running lab virtual machines. For example, you specify the base VM image for the lab VMs by selecting an image from the Azure Marketplace or an Azure compute gallery. Optionally, you can customize this VM image by using a template VM.
You can further configure the lab behavior by creating lab schedules or configuring automatic shutdown settings to optimize cost.
When you publish a lab, Azure Lab Services provisions the lab VMs. All lab VMs for a lab share the same configuration and are identical.
To create labs in Azure Lab Services, your Azure account needs to have the Lab Creator Azure RBAC role, or you need to be the owner of the corresponding lab plan. Learn more about Azure Lab Services built-in roles.
You use the Azure Lab Services website (https://labs.azure.com) to create labs for a lab plan. Alternately, you can also configure Microsoft Teams integration or Canvas integration with Azure Lab Services to create labs directly in Microsoft Teams or Canvas.
By default, access to lab virtual machines is restricted. For a lab, you can configure the list of lab users that have access to the lab.
Get started by creating a lab using the Azure portal.
Azure Compute Gallery
When you create a lab, you select the base VM image for the lab VMs. You can use an Azure compute gallery to store and share custom VM images. By using a compute gallery, you avoid having to repeatedly apply the same customizations when you create a new lab. If you've customized a lab with a template VM, you can export the template VM to your compute gallery.
To use VM images from a compute gallery, you attach the Azure compute gallery to your lab plan. You can attach zero or more Azure compute galleries to a lab plan. After attaching a compute gallery, you can further enable or disable specific images.
Learn how to attach or detach an Azure compute gallery.
Template virtual machine
You can choose to create a customizable lab, which enables you to modify the base image for the lab virtual machines. In this case, Azure Lab Services creates a lab template VM, which you can connect to and customize. For example, you might install extra software components, such as Visual Studio, or configure the operating system to disable the web server process.
When you publish the lab, Azure Lab Services creates the lab VMs, based on the template VM image. If you modify the template VM at a later stage, when you republish the template VM, all lab VMs are updated to match the new template. When you republish a template VM, Azure Lab Services reimages the lab VMs and removes all changes and data on the VM.
With the introduction of lab plans, you can also create a templateless lab. In a templateless lab, you select the base image for the lab VMs from the Azure Marketplace or an Azure compute gallery, and you can't further customize the image of a templateless lab. You might use templateless labs because you manage your golden VM images in an Azure compute gallery. The advantage of templateless labs is that all labs use your golden images without changes. Another benefit is that lab creation is faster because there's no need to create a template VM.
Learn how to create and manage a template in Azure Lab Services.
Lab virtual machine
In Azure Lab Services, lab VMs are managed virtual machines that get their configuration from the lab. All VMs for a lab are identical. Azure Lab Services provisions the lab VMs when you publish the lab.
After you publish the lab VMs, lab users can connect to their VM through remote desktop (RDP) or secure shell (SSH). Before they can connect to the lab VM, lab users have to first register for the lab by using a registration link. Azure Lab Services then assigns the user to a specific lab VM.
In the lab settings, you can optionally configure one or more schedules and assign user quota.
Schedule
Schedules are the time slots that define when the lab VMs are available for class time. With schedules, you can avoid that lab users need to wait for their VM to start up. Schedules can be one-time or recurring. The lab creator can define schedules for a lab.
The use of schedules for a lab is optional and you might specify user quota instead, or use a combination of both. User quota is the time that lab users can run their lab VM outside of scheduled time. For example, to complete assignments or homework. Any scheduled time doesn't count against extra time that lab users have. A lab can use quota time, scheduled time, or a combination of both.
Example scenarios for using schedules are:
- A class happens at regular intervals or at a predefined time. You assign one or multiple schedules that match the class time slots, and that enables the students to follow the educator's directions during class hours.
- A class happens at regular intervals, and students need to complete assignments after class hours. You assign a schedule that matches the class time slots, and you assign user quota for students to complete after-hours assignments.
There are two types of schedules.
- Standard. This schedule starts all lab VMs, except VMs that aren't assigned yet, at the specified start time and shuts down all lab VMs at the specified stop time.
- Stop only. This schedule stops all lab VMs at the specified time, even if the lab creator or lab user started the VM manually.
Azure Lab Services starts a lab VM, regardless if the user signs into the VM or not. To help reduce the cost of running VMs that are unused, see how you can configure automatic shutdown of lab VMs.
For more information about schedules, see Create and manage schedules for labs in Azure Lab Services.
Quota
A quota is the limit of time a lab user can use their VM outside of scheduled lab events. The use of quota is optional, and you can use lab schedules instead, or use a combination of both. If no quota is assigned, lab users can only use their VM during scheduled time, or if the lab creator manually starts a lab VM for them.
Example scenarios for using quotas are:
- Students need to use their lab VMs outside of class time to complete their homework. You can assign a schedule for the class time, and additionally assign quota hours for homework.
- There are no regular class times, for example with students in different geographical areas. The lab has no scheduled events, and you only specify quota hours for lab users.
When a lab user starts their lab VM, quota hours for the lab start counting. If a lab creator manually starts the lab VM for a user, quota hours aren't used for that student.
The quota applies to a lab for each lab user individually, for the entire duration of the lab.
A lab can use either quota time, scheduled time, or a combination of both.
Advanced networking
With lab plans, you have more control over the virtual network for labs by using advanced networking. With advanced networking, you can connect to a virtual network.
Use advanced networking to connect to on premise resources such as licensing servers and use user defined routes (UDRs). Some organizations also have advanced network requirements and configurations that they want to apply to labs. For example, network requirements can include a network traffic control, ports management, access to resources in an internal network, and more.
Azure Lab Services advanced networking uses virtual network (VNET) injection to connect a lab plan to your virtual network. VNET injection replaces the Azure Lab Services virtual network peering that was used with lab accounts.
Learn more about how to connect a lab plan to a virtual network.