Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes the strategy to deploy the SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence (SAP BOBI) platform on Azure for Windows. In this example, two virtual machines (VMs) with Azure Premium SSD managed disks as their installation directory are configured. Azure SQL Database, a platform as a service (PaaS) offering, is used for the central management server (CMS) and audit databases. Azure Premium Files, an SMB protocol, is used as a file store that's shared across both VMs. The default Tomcat Java web application and business intelligence (BI) platform application are installed together on both VMs. To load balance the user requests, Azure Application Gateway is used, which has native TLS/SSL offloading capabilities.
This type of architecture is effective for small deployment or nonproduction environments. For production or large-scale deployment, you should separate hosts for web applications, and you can have multiple SAP BOBI application hosts, which allows the server to process more information.

In this example, the following product versions and file system layout are used:
- SAP BusinessObjects platform 4.3 SP01 Patch 1
- Windows Server 2019
- SQL Database (Version: 12.0.2000.8)
- Microsoft ODBC driver - msodbcsql.msi (Version: 13.1)
| File system | Description | Size (GB) | Required access | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F: | The file system for installation of an SAP BOBI instance, default Tomcat web application, and database drivers (if necessary). | SAP sizing guidelines | Local administrative privileges | Azure Premium SSD managed disks |
| \\azusbobi.file.core.windows.net\frsinput | The mount directory is for the shared files across all SAP BOBI hosts that will be used as the Input Filestore directory. | Business need | Local administrative privileges | Azure NetApp Files |
| \\azusbobi.file.core.windows.net\frsoutput | The mount directory is for the shared files across all SAP BOBI hosts that will be used as the Output Filestore directory. | Business need | Local administrative privileges | Azure NetApp Files |
Deploy a Windows virtual machine via the Azure portal
In this section, we'll create two VMs with a Windows operating system (OS) image for the SAP BOBI platform. The high-level steps to create VMs are as follows:
Create a resource group.
Create a virtual network:
- Don't use a single subnet for all Azure services in an SAP BI platform deployment. Based on SAP BI platform architecture, you might need to create multiple subnets. In this deployment, we'll create two subnets: a BI application subnet and an Application Gateway subnet.
- Follow SAP Note 2276646 to identify ports for SAP BOBI platform communication across different components.
- SQL Database communicates over port 1433. Outbound traffic over port 1433 should be allowed from your SAP BOBI application servers.
- In Azure, Application Gateway must be on a separate subnet. For more information, see Application Gateway configuration overview.
- If you're using Azure NetApp Files for a file store instead of Azure Files, create a separate subnet for Azure NetApp Files. For more information, see Guidelines for Azure NetApp Files network planning.
Select the suitable availability options depending on your preferred system configuration within an Azure region, whether it involves spanning across zones, residing within a single zone, or operating in a zone-less region.
Create virtual machine 1 (azuswinboap1):
- You can either use a custom image or choose an image from Azure Marketplace. Based on your need, see Deploy a VM from Azure Marketplace for SAP or Deploy a VM with a custom image for SAP.
Create virtual machine 2 (azuswinboap2).
Add one Premium SSD disk. It will be used as an SAP BOBI installation directory.
Provision Azure Premium Files
Before you continue with the setup for Azure Files, familiarize yourself with the Azure Files documentation.
Azure Files offers standard file shares hosted on HDD-based hardware and premium file shares hosted on SSD-based hardware. For an SAP BusinessObjects file store, use Azure Premium Files.
Azure premium file shares are available with local and zone redundancy in a subset of regions. To find out if premium file shares are currently available in your region, see Products available by region. For information about regions that support zone-redundant storage (ZRS), see Azure Storage redundancy.
Deploy an Azure files storage account and NFS shares
Azure file shares are deployed into storage accounts, which are top-level objects that represent a shared pool of storage. This pool of storage can be used to deploy multiple file shares. Azure supports multiple types of storage accounts for different storage scenarios customers might have. For SAP BusinessObjects file storage, you need to create a FileStorage account. You use it to deploy Azure file shares on Premium SSD-based hardware.
Note
FileStorage accounts can only be used to store Azure file shares. No other storage resources, such as blobs, containers, queues, or tables, can be deployed in a FileStorage account.
The storage account will be accessed via private endpoint and deployed in the same virtual network of an SAP BOBI platform. With this setup, the traffic from your SAP system never leaves the virtual network security boundaries. SAP systems often contain sensitive and business-critical data, so staying within the boundaries of the virtual network is an important security consideration for many customers.
If you need to access the storage account from a different virtual network, you can use Azure Virtual Network peering.
Azure files storage account
To create a storage account via the Azure portal, select Create a resource > Storage > Storage account.
On the Basics tab, complete all required fields to create a storage account:
Select Subscription > Resource group > Region.
Enter the Storage account name. For example, enter azusbobi. This name must be globally unique, but otherwise you can provide any name you want.
Select Premium as the performance tier, and select FileStorage as the account kind.
For Replication label, choose a redundancy level. Select Locally redundant storage (LRS).
For Premium FileStorage, ZRS and LRS are the only options available. Based on your VM deployment strategy (flexible scale set, availability zone or availability set), choose the appropriate redundancy level. For more information, see Azure Storage redundancy.
Select Next.
On the Networking tab, select private endpoint as the connectivity method. For more information, see Azure Files networking considerations.
Select Add in the private endpoint section.
Select Subscription > Resource group > Location.
Enter the Name of the private endpoint. For example, enter azusbobi-pe.
Select file in storage sub-resource.
In the Networking section, select the Virtual network and Subnet on which the SAP BusinessObjects BI application is deployed.
Accept the default (yes) for Integrate with private DNS zone.
Select your private DNS zone from the dropdown list.
Select OK to go back to the Networking tab in Create storage account.
On the Data protection tab, configure the soft-delete policy for Azure file shares in your storage account. By default, soft-delete functionality is turned off. To learn more about soft delete, see Prevent accidental deletion of Azure file shares.
On the Advanced tab, select different security options.
The Secure transfer required field indicates whether the storage account requires encryption in transit for communication to the storage account. If you require SMB 2.1 support, you must disable this field. For the SAP BOBI platform, keep it default (enabled).
Continue and create the storage account.
For details on how to create a storage account, see Create a FileStorage storage account.
Create Azure file shares
The next step is to create Azure files in the storage account. Azure files use a provisioned model for premium file shares. In a provisioned business model, you proactively specify to Azure files what your storage requirements are, rather than being billed based on what you use. To understand more about this model, see Provisioned model. In this example, we create two Azure files: frsinput (256 GB) and frsoutput (256 GB) for the SAP BOBI file store.
- Go to the storage account azusbobi > File shares.
- Select New file share.
- Enter the Name of the file share. For example, enter frsinput or frsoutput.
- Insert the required file share size in Provisioned capacity. For example, enter 256 GB.
- Choose SMB as Protocol.
- Select Create.
Configure a data disk on a Windows virtual machine
The steps in this section use the following prefix:
[A]: The step applies to all hosts.
Initialize a new data disk
The SAP BusinessObjects BI application requires a partition on which its binaries can be installed. You can install an SAP BOBI application on the OS partition (C:), but you must make sure to have enough space for the deployment and the OS. We recommend that you have at least 2 GB available for temporary files and web applications. Also, it's advisable to separate SAP BOBI installation binaries in separate partitions.
In this example, an SAP BOBI application is installed on a separate partition (F:). Initialize the Premium SSD disk that you attached during the VM provisioning:
- [A] If no data disk is attached to the VM (azuswinboap1 and azuswinboap2), follow the steps in Add a data disk to attach a new managed data disk.
- [A] After the managed disk is attached to the VM, initialize the disk by following the steps in Initialize a new data disk.
Mount Azure Premium Files
To use Azure Files as a file store, you must mount it, which means you assign it a drive letter or mount point path.
[A] To mount the Azure file share, follow the steps in Mount the Azure file share.
To mount an Azure file share on a Windows server, the SMB protocol requires TCP port 445 to be open. Connections will fail if port 445 is blocked. You can check if your firewall or ISP is blocking port 445 by using the Test-NetConnection cmdlet. See Port 445 is blocked.
Configure a CMS database: Azure SQL
This section provides details on how to provision Azure SQL by using the Azure portal. It also provides instructions on how to create the CMS and the audit database for an SAP BOBI platform and a user account to access the databases.
The guidelines are applicable only if you're using SQL Database. For other databases, see SAP or database-specific documentation for instructions.
Create a SQL Database server
SQL Database offers different deployment options: single database, elastic pool, and database server. For an SAP BOBI platform, we need two databases, CMS and audit. Instead of creating two single databases, you can create a SQL Database server that can manage the group of single databases and elastic pools. Follow these steps to create a SQL Database server:
Browse to the Select SQL deployment option page.
Under SQL databases, change Resource type to Database server. Select Create.
On the Basics tab, fill in all the required fields to Create SQL Database Server:
Under Project details, select the Subscription and Resource group.
Enter a Server name. For example, enter azussqlbodb. The server name must be globally unique, but otherwise, you can provide any name you want.
Select the Location.
Enter the Server admin login. For example, enter boadmin. Then enter a Password.
On the Networking tab, change Allow Azure services and resources to access this server to No under Firewall rules.
On Additional settings, keep the default settings.
Continue and create SQL Database Server.
In the next step, create the CMS and the audit databases in the SQL Database server (azussqlbodb.database.windows.net).
Create the CMS and the audit database
After you provision the SQL Database server, browse to the resource azussqlbodb. Then follow these steps to create CMS and audit databases.
On the azussqlbodb overview page, select Create database.
On the Basics tab, fill in all the required fields:
Enter the Database name. For example, enter bocms or boaudit.
On the Compute + storage option, select Configure database. Choose the appropriate model based on your sizing result. For insight on the options, see Sizing models for Azure SQL Database.
On the Networking tab, select private endpoint for the connectivity method. The private endpoint will be used to access SQL Database within the configured virtual network.
Select Add private endpoint.
Select Subscription > Resource group > Location.
Enter the Name of the private endpoint. For example, enter azusbodb-pe.
In Target sub-resource, select SqlServer.
In the Networking section, select the Virtual network and Subnet on which the SAP BusinessObjects BI application is deployed.
Accept default (yes) for Integrate with private DNS zone.
Select your private DNS zone from the dropdown list.
Select OK to go back to the Networking tab in Create SQL database.
On the Additional settings tab, change the Collation setting to SQL_Latin1_General_CP850_BIN2.
Continue and create the CMS database.
Similarly, you can create the audit database. For example, enter boaudit.
Download and install an ODBC driver
SAP BOBI application servers require database client/drivers to access the CMS or audit database. A Microsoft ODBC driver is used to access CMS and audit databases running on SQL Database. This section provides instructions on how to download and set up an ODBC driver on Windows.
- See the CMS + Audit repository support by OS section in the Product Availability Matrix (PAM) for SAP BusinessObjects BI platform to find out the database connectors that are compatible with SQL Database.
- Download the ODBC driver version from the link. In this example, we're downloading ODBC driver 13.1.
- Install the ODBC driver on all BI servers (azuswinboap1 and azuswinboap2).
- After you install the driver in azuswinboap1, go to Start > Windows Administrative Tools > ODBC Data Sources (64-bit).
- Go to the System DSN tab.
- Select Add to create a connection to the CMS database.
- Select ODBC Driver 13 for SQL Server, and select Finish.
- Enter the information of your CMS database like the following, and select Next:
- Name: The name of the database created in the section "Create the CMS and the audit database." For example, enter bocms or boaudit.
- Description: A description that describes the data source. For example, enter CMS database or Audit database.
- Server: The name of the server created in the section "Create a SQL Database server." For example, enter azussqlbodb.database.windows.net.
- Select With SQL Server authentication using a login ID and password entered by user to verify authenticity to Azure SQL Server. Enter the user credential that was created at the time of the SQL Database server creation. For example, enter boadmin. Select Next.
- Change the default database to bocms, and keep everything else as default. Select Next.
- Select the Use strong encryption for data checkbox, and keep everything else as default. Select Finish.
- The data source to the CMS database has been created. Now you can select Test Data Source to validate the connection to the CMS database from the BI application. It should complete successfully. If it fails, troubleshoot the connectivity issue.
Note
SQL Database communicates over port 1433. Outbound traffic over port 1433 should be allowed from your SAP BOBI application servers.
Repeat the preceding steps to create a connection for the audit database on the server azuswinboap1. Similarly, install and configure both ODBC data sources (bocms and boaudit) on all BI application servers (azuswinboap2).
Server preparation
Follow the latest guide by SAP to prepare servers for the installation of the BI platform. For the most up-to-date information, see the "Preparation" section in the SAP Business Intelligence Platform Installation Guide for Windows.
Installation
To install the BI platform on a Windows host, sign in with a user that has local administrative privileges.
Go to the media of the SAP BusinessObjects BI platform, and run setup.exe.
Follow the instructions in the SAP Business Intelligence Platform Installation Guide for Windows that are specific to your version. Here are a few points to note while you install the SAP BOBI platform on Windows:
On the Configure Destination Folder screen, provide the destination folder where you want to install the BI platform. For example, enter F:\SAP BusinessObjects*.
On the Configure Product Registration screen, you can either use a temporary license key for SAP BusinessObjects Solutions from SAP Note 1288121 or generate a license key in SAP Service Marketplace.
On the Select Install Type screen, select Full installation on the first server (azuswinboap1). For the other server (azuswinboap2), select Custom / Expand, which expands the existing SAP BOBI setup.
On the Select Default or Existing Database screen, select configure an existing database, which prompts you to select the CMS and the audit database. Select Microsoft SQL Server using ODBC for the CMS Database type and the Audit Database type.
You can also select No auditing database if you don't want to configure auditing during installation.
Select the appropriate options on the Select Java Web Application Server screen based on your SAP BOBI architecture. In this example, we've selected option 1, which installs a Tomcat server on the same SAP BOBI platform.
Enter CMS database information in Configure CMS Repository Database - SQL Server (ODBC). The following image shows example input for CMS database information for a Windows installation.
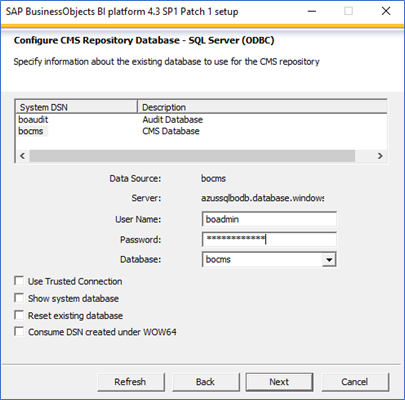
(Optional) Enter audit database information in Configure Auditing Database - SQL Server (ODBC). The following image shows example input for audit database information for a Windows installation.

Follow the instructions, and enter the required inputs to finish the installation.
For a multi-instance deployment, run the installation setup on the second host (azuswinboap2). In the Select Install Type screen, select Custom / Expand, which expands the existing SAP BOBI setup. For more information, see the SAP blog SAP BusinessObjects Business Intelligence platform setup with Azure SQL Database.
Important
The database engine version numbers for SQL Server and SQL Database aren't comparable with each other. They're internal build numbers for these separate products. The database engine for SQL Database is based on the same code base as the SQL Server database engine. Most importantly, the database engine in SQL Database always has the newest SQL Database engine bits. Version 12 of SQL Database is newer than version 15 of SQL Server.
To find out the current SQL Database version, you can either check in the settings of the Central Management Console (CMC) or run the following query by using sqlcmd or SQL Server Management Studio. The alignment of SQL versions to default compatibility can be found in the database compatibility level article.

1> select @@version as version;
2> go
version
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Microsoft SQL Azure (RTM) - 12.0.2000.8
Feb 20 2021 17:51:58
Copyright (C) 2019 Microsoft Corporation
(1 rows affected)
1> select name, compatibility_level from sys.databases;
2> go
name compatibility_level
--------------------------------------------------------------------- -------------------
master 150
bocms 150
boaudit 150
(3 rows affected)
Post installation
After a multi-instance installation of the SAP BOBI platform, more post-configuration steps need to be performed to support application high availability.
Configure a cluster name
In a multi-instance deployment of the SAP BOBI platform, you want to run several CMS servers together in a cluster. A cluster consists of two or more CMS servers working together against a common CMS system database. If a node that's running on CMS fails, a node with another CMS will continue to service BI platform requests. By default in an SAP BOBI platform, a cluster name reflects the hostname of the first CMS that you install.
To configure the cluster name on Windows, follow the instructions in the SAP Business Intelligence Platform Administrator Guide. After you configure the cluster name, follow SAP Note 1660440 to set the default system entry on the CMC or BI Launchpad sign-in page.
Configure the input and output filestore location to Azure Premium Files
Filestore refers to the disk directories where the actual SAP BusinessObjects BI files are located. The default location of the file repository server for the SAP BOBI platform is located in the local installation directory. In a multi-instance deployment, it's important to set up a filestore on shared storage like Azure Premium Files or Azure NetApp Files so that it can be accessed from all storage tier servers.
If not created, follow the instructions provided in the preceding section, "Provision Azure Premium Files," to create and mount Azure Premium Files.
Tip
Based on whether the virtual machine is deployed in a zonal or regional manner, the selection of storage redundancy for Azure Premium Files (ZRS or LRS) should be determined.
Follow SAP Note 2512660 to change the path of the file repository (Input and Output).
Tomcat clustering: Session replication
Tomcat supports clustering of two or more application servers for session replication and failover. If SAP BOBI platform sessions are serialized, a user session can fail over seamlessly to another instance of Tomcat, even when an application server fails. For example, a user might be connected to a web server that fails while the user is navigating a folder hierarchy in an SAP BI application. On a correctly configured cluster, the user can continue navigating the folder hierarchy without being redirected to a sign-in page.
In SAP Note 2808640, steps to configure Tomcat clustering are provided by using multicast. But multicast isn't supported in Azure. To make a Tomcat cluster work in Azure, you must use StaticMembershipInterceptor (SAP Note 2764907). To set up a Tomcat cluster in Azure, see Tomcat clustering using static membership for the SAP BusinessObjects BI platform on the SAP blog.
Load balance a web tier of an SAP BI platform
In an SAP BOBI multi-instance deployment, Java web application servers (web tier) are running on two or more hosts. To distribute the user load evenly across web servers, you can use a load balancer between end users and web servers. You can use Azure Load Balancer or Application Gateway to manage traffic to your web application servers. The offerings are explained in the following sections:
Load Balancer is a high-performance, low-latency, layer 4 (TCP, UDP) load balancer that distributes traffic among healthy VMs. A load balancer health probe monitors a given port on each VM and only distributes traffic to operational VMs. You can choose either a public load balancer or an internal load balancer depending on whether you want the SAP BI platform accessible from the internet or not. It's zone redundant, which ensures high availability across availability zones.
In the following figure, see the "Internal Load Balancer" section where the web application server runs on port 8080 (default Tomcat HTTP port), which will be monitored by a health probe. Any incoming request that comes from users will get redirected to the web application servers (azuswinboap1 or azuswinboap2) in the back-end pool. Load Balancer doesn't support TLS/SSL termination, which is also known as TLS/SSL offloading. If you're using Load Balancer to distribute traffic across web servers, we recommend using Standard Load Balancer.
Note
When VMs without public IP addresses are placed in the back-end pool of internal (no public IP address) Standard Load Balancer, there will be no outbound internet connectivity, unless additional configuration is performed to allow routing to public endpoints. For information on how to achieve outbound connectivity, see Public endpoint connectivity for virtual machines using Azure Standard Load Balancer in SAP high-availability scenarios.
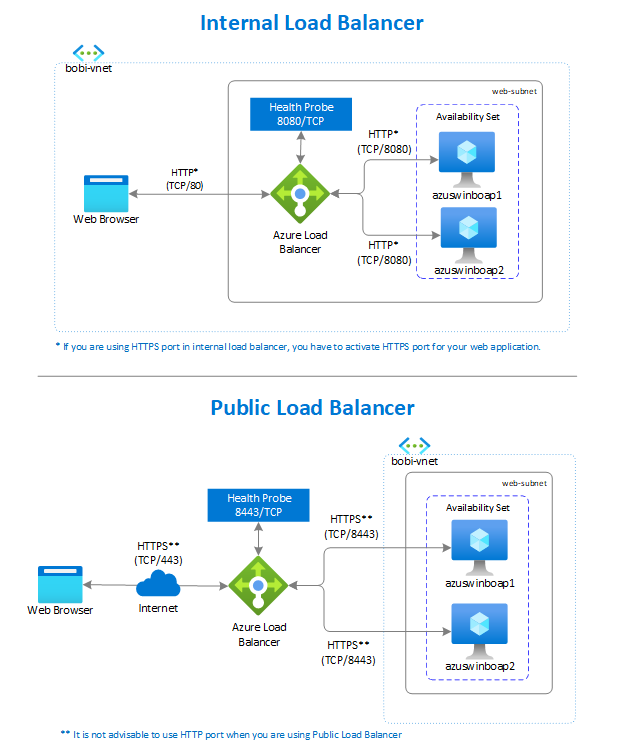
Application Gateway provides an application delivery controller as a service, which is used to help applications direct user traffic to one or more web application servers. It offers various layer 7 load-balancing capabilities like TLS/SSL offloading, Web Application Firewall, and cookie-based session affinity for your applications.
In an SAP BI platform, Application Gateway directs application web traffic to the specified resources in a back-end pool. In this case, it's either azuswinboap1 or azuswinboap2. You assign a listener to the port, create rules, and add resources to a back-end pool. In the following figure, Application Gateway with a private front-end IP address (10.31.3.25) acts as an entry point for users, handles incoming TLS/SSL (HTTPS - TCP/443) connections, decrypts the TLS/SSL, and passes the request (HTTP - TCP/8080) to the servers in the back-end pool. With the built-in TLS/SSL termination feature, you need to maintain only one TLS/SSL certificate on the application gateway, which simplifies operations.

To configure Application Gateway for an SAP BOBI web server, see Load balancing SAP BOBI web servers by using Application Gateway on the SAP blog.
Note
Use Application Gateway to load balance the traffic to the web server because it provides features like SSL offloading, centralized SSL management to reduce encryption and decryption overhead on the server, round-robin algorithms to distribute traffic, Web Application Firewall capabilities, and high availability.
SAP BusinessObjects BI platform reliability on Azure
The SAP BusinessObjects BI platform includes different tiers, which are optimized for specific tasks and operations. When a component from any one tier becomes unavailable, the SAP BOBI application will either become inaccessible or certain functionality of the application won't work. You need to make sure that each tier is designed to be reliable to keep the application operational without any business disruption.
This guide explores how features native to Azure in combination with an SAP BOBI platform configuration improve the availability of an SAP deployment. This section focuses on the following options for SAP BOBI platform reliability on Azure:
- Backup and restore: This process creates periodic copies of data and applications to separate locations. If the original data or applications are lost or damaged, the copies can be used to restore or recover to the previous state.
- High availability: A high-availability platform has at least two of everything within an Azure region to keep the application operational if one of the servers becomes unavailable.
- Disaster recovery (DR): This process restores your application functionality if there are any catastrophic losses. For example, an entire Azure region might become unavailable because of a natural disaster.
Implementation of this solution varies based on the nature of the system set up in Azure. You need to tailor your backup and restore, high-availability, and DR solutions based on your business requirements.
Backup and restore
Backup and restore is a process of creating periodic copies of data and applications to a separate location so that they can be restored or recovered to a previous state if the original data or applications are lost or damaged. It's also an essential component of any business DR strategy. These backups enable application and database restore to a point in time within the configured retention period.
To develop a comprehensive backup and restore strategy for an SAP BOBI platform, identify the components that lead to system downtime or disruption in the application. In an SAP BOBI platform, backup of the following components is vital to protect the application:
- SAP BOBI installation directory (Managed Premium Disks)
- Filestore (Azure Premium Files or Azure NetApp Files for distributed installation)
- CMS and audit database (SQL Database, Azure Database for MySQL, or a database on Azure Virtual Machines)
The following section describes how to implement a backup and restore strategy for each component on an SAP BOBI platform.
Backup and restore for an SAP BOBI installation directory
In Azure, the simplest way to back up VMs and all the attached disks is by using Azure Backup. It provides an independent and isolated backup to guard against unintended destruction of the data on your VMs. Backups are stored in a Recovery Services vault with built-in management of recovery points. Configuration and scaling are simple. Backups are optimized and can be restored easily when needed.
As part of the backup process, a snapshot is taken. The data is transferred to the Recovery Services vault with no effect on production workloads. The snapshot provides a different level of consistency as described in Snapshot consistency. Backup also offers side-by-side support for backup of managed disks by using Azure disk backup in addition to an Azure VM backup solution. It's useful when you need consistent backups of VMs once a day and more frequent backups of OS disks, or a specific data disk, that are crash consistent. For more information, see About Azure VM backup, Azure disk backup, and FAQs: Back up Azure VMs.
Backup and restore for filestore
Based on your deployment, filestore of an SAP BOBI platform can be on Azure NetApp Files or Azure Files. Choose from the following options for backup and restore based on the storage you use for filestore:
- Azure NetApp Files: For Azure NetApp Files, you can create on-demand snapshots and schedule an automatic snapshot by using snapshot policies. Snapshot copies provide a point-in-time copy of your Azure NetApp Files volume. For more information, see Manage snapshots by using Azure NetApp Files.
- Azure Files: Azure Files backup is integrated with a native instance of Backup, which centralizes the backup and restore function along with VM backup and simplifies operation work. For more information, see Azure file share backup and FAQs: Back up Azure Files.
If you've created a separate NFS server, make sure you implement the backup and restore strategy for the same.
Backup and restore for the CMS and audit database
For an SAP BOBI platform running on Windows VMs, the CMS and audit database can run on any of the supported databases as described in the support matrix of the SAP BOBI platform planning and implementation guide on Azure. So it's important that you adopt the backup and restore strategy based on the database you used for CMS and audit data storage.
SQL Database uses SQL Server technology to create full backups every week, differential backups every 12 to 24 hours, and transaction log backups every 5 to 10 minutes. The frequency of transaction log backups is based on the compute size and the amount of database activity.
Users can choose an option to configure backup storage redundancy between LRS, ZRS, or GRS blobs. Storage redundancy mechanisms store multiple copies of your data to protect it from planned and unplanned events, which includes transient hardware failure, network or power outages, or massive natural disasters. By default, SQL Database stores backup in GRS blobs that are replicated to a paired region. It can be changed based on the business requirement to either LRS or ZRS blobs. For more up-to-date information on SQL Database backup scheduling, retention, and storage consumption, see Automated backups: Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance.
Azure Database for MySQL automatically creates server backups and stores in user-configured LRS or GRS. Azure Database for MySQL takes backups of the data files and the transaction log. Depending on the supported maximum storage size, it either takes full and differential backups (4-TB max storage servers) or snapshot backups (up to 16-TB max storage servers). These backups allow you to restore a server at any point in time within your configured backup retention period. The default backup retention period is 7 days, which you can optionally configure up to 35 days. All backups are encrypted by using AES 256-bit encryption. These backup files aren't user exposed and can't be exported. These backups can only be used for restore operations in Azure Database for MySQL. You can use mysqldump to copy a database. For more information, see Backup and restore in Azure Database for MySQL.
For a database installed on an Azure VM, you can use standard backup tools or Backup for supported databases. Also, if the Azure services and tools don't meet your requirements, you can use supported third-party backup tools that provide an agent for backup and recovery of all SAP BOBI platform components.
High availability
High availability refers to a set of technologies that can minimize IT disruptions by providing business continuity of applications or services through redundant, fault-tolerant, or failover-protected components inside the same datacenter. In our case, the datacenters are within one Azure region. The article High-availability architecture and scenarios for SAP provides insight on different high-availability techniques and recommendations offered on Azure for SAP applications, which complement the instructions in this section.
Based on the sizing result of the SAP BOBI platform, you need to design the landscape and determine the distribution of BI components across Azure VMs and subnets. The level of redundancy in the distributed architecture depends on the business-required recovery time objective (RTO) and recovery point objective (RPO). The SAP BOBI platform includes different tiers, and components on each tier should be designed to achieve redundancy. Then if one component fails, there's little to no disruption to your SAP BOBI application. For example:
- Redundant application servers like BI application servers and web servers
- Unique components like CMS database, filestore, and load balancer
The following section describes how to achieve high availability on each component of an SAP BOBI platform.
High availability for application servers
BI and web application servers don't need a specific high-availability solution, no matter whether they're installed separately or together. You can achieve high availability by redundancy, that is, by configuring multiple instances of BI and web servers in various Azure VMs. You can deploy the VMs in either flexible scale set, availability sets or availability zones based on business-required RTO. For deployment across availability zones, make sure all other components in the SAP BOBI platform are designed to be zone redundant too.
Currently, not all Azure regions offer availability zones, so you need to adopt the deployment strategy based on your region. The Azure regions that offer zones are listed in Azure availability zones.
Important
- The concepts of Azure availability zones and Azure availability sets are mutually exclusive. You can deploy a pair or multiple VMs into either a specific availability zone or an availability set, but you can't do both.
- If you planning to deploy across availability zones, it is advised to use flexible scale set with FD=1 over standard availability zone deployment.
High availability for the CMS database
If you're using an Azure database as a solution for your CMS and audit database, a locally redundant high-availability framework is provided by default. Select the region and service inherent high-availability, redundancy, and resiliency capabilities without requiring you to configure any more components. If the deployment strategy for an SAP BOBI platform is across an availability zone, make sure you achieve zone redundancy for your CMS and audit database. For more information on high availability for supported database offerings in Azure, see High availability for Azure SQL Database and High availability in Azure Database for MySQL.
For other database management system (DBMS) deployment for a CMS database, see DBMS deployment guides for SAP workload for insight on a different DBMS deployment and its approach to achieving high availability.
High availability for filestore
Filestore refers to the disk directories where contents like reports, universes, and connections are stored. It's being shared across all application servers of that system. So, you must make sure that it's highly available, alongside other SAP BOBI platform components.
For an SAP BOBI platform running on Windows, you can either choose Azure Premium Files or Azure NetApp Files for filestore, which is designed to be highly available and highly durable in nature. Azure Premium Files support ZRS, which can be useful for cross-zone deployment of an SAP BOBI platform. For more information, see the Redundancy section for Azure Files.
Because the file share service isn't available in all regions, make sure you see the list of products available by region to find up-to-date information. If the service isn't available in your region, you can create an NFS server from which you can share the file system to an SAP BOBI application. But you'll also need to consider its high availability.
High availability for the load balancer
To distribute traffic across a web server, you can use Load Balancer or Application Gateway. The redundancy for either of the load balancers can be achieved based on the SKU you choose for deployment:
- Load Balancer: Redundancy can be achieved by configuring the Standard Load Balancer front end as zone redundant. For more information, see Standard Load Balancer and availability zones.
- Application Gateway: High availability can be achieved based on the type of tier selected during deployment:
- The v1 SKU supports high-availability scenarios when you've deployed two or more instances. Azure distributes these instances across update and fault domains to ensure that instances don't all fail at the same time. With this SKU, redundancy can be achieved within the zone.
- The v2 SKU automatically ensures that new instances are spread across fault domains and update domains. If you choose zone redundancy, the newest instances are also spread across availability zones to offer zonal failure resiliency. For more information, see Autoscaling and zone-redundant Application Gateway v2.
Reference high-availability architecture for the SAP BusinessObjects BI platform
The following reference architecture describes the setup of an SAP BOBI platform across availability zones running on a Windows server. The architecture showcases the use of different Azure services like Application Gateway, Azure Premium Files (filestore), and SQL Database (CMS and audit database). The SAP BOBI platform offers built-in zone redundancy, which reduces the complexity of managing different high-availability solutions.
In the following figure, the incoming traffic (HTTPS - TCP/443) is load balanced by using Application Gateway v2 SKU, which spans multiple availability zones. The application gateway distributes the user request across web servers, which are distributed across availability zones. The web server forwards the request to management and processing server instances that are deployed in separate VMs across availability zones. Azure premium files with ZRS are attached via private link to management and storage tier VMs to access the contents like reports, universe, and connections. The application accesses the CMS and audit database running on a zone-redundant instance of SQL Database, which replicates databases across multiple physical locations within an Azure region.

The preceding architecture provides insight on how an SAP BOBI deployment on Azure can be done. But it doesn't cover all possible configuration options for an SAP BOBI platform on Azure. You can tailor your deployment based on your business requirements by choosing different products or services for components like Load Balancer, File Repository Server, and DBMS.
If availability zones aren't available in your selected region, you can deploy Azure VMs in availability sets. Azure makes sure the VMs you place within an availability set run across multiple physical servers, compute racks, storage units, and network switches. If hardware or software failure occurs, only a subset of your VMs is affected and the overall solution stays operational.
Disaster recovery
This section explains the strategy to provide DR protection for an SAP BOBI platform. It complements the Disaster recovery for SAP document, which represents the primary resources for an overall SAP DR approach. For the SAP BOBI platform, see SAP Note 2056228, which describes the following methods to implement a DR environment safely:
- Fully or selectively use Lifecycle Management or federation to promote or distribute the content from the primary system.
- Periodically copy over the CMS and FRS contents.
In this guide, we'll talk about the second option to implement a DR environment. We won't cover an exhaustive list of all possible configuration options for DR. We'll cover a solution that features native Azure services in combination with SAP BOBI platform configuration.
Important
- Availability of each component in the SAP BOBI platform should be factored in to the secondary region. The entire DR strategy must be thoroughly tested.
- In case where your SAP BI platform is configured with flexible scale set with FD=1, then you need to use PowerShell to set up Azure Site Recovery for disaster recovery. Currently, it's the only method available to configure disaster recovery for VMs deployed in scale set.
Reference DR architecture for an SAP BusinessObjects BI platform
This reference architecture is running a multi-instance deployment of the SAP BOBI platform with redundant application servers. For DR, you should fail over all the components of the SAP BOBI platform to a secondary region. In the following figure, Azure Premium Files is used as the filestore, SQL Database is used as the CMS and audit repository, and Application Gateway is used to load balance traffic. The strategy to achieve DR protection for each component is different, which is described in the following section.

Load Balancer
Load Balancer is used to distribute traffic across web application servers of an SAP BOBI platform. On Azure, you can use Load Balancer or Application Gateway to load balance the traffic across web servers. To achieve DR for the load balancer services, you need to implement another load balancer or application gateway on a secondary region. To keep the same URL after DR failover, change the entry in DNS and point to the load-balancing service that runs on the secondary region.
Virtual machines that run web and BI application servers
Azure Site Recovery can be used to replicate VMs running web and BI application servers on the secondary region. It replicates the servers and all the attached managed disks to the secondary region so that when disasters and outages occur, you can easily fail over to your replicated environment and continue working. To start replicating all the SAP application VMs to the Azure DR datacenter, follow the guidance in Replicate a virtual machine to Azure.
Filestore
Filestore is a disk directory where the actual files like reports and BI documents are stored. It's important that all the files in the filestore are in sync to the DR region. Based on the type of file share service you use for the SAP BOBI platform running on Windows, the necessary DR strategy needs to be adopted to sync the content. For example:
Azure Premium Files only supports LRS and ZRS. For Azure Premium Files DR strategy, you can use AzCopy or Azure PowerShell to copy your files to another storage account in a different region. For more information, see Disaster recovery and storage account failover.
Azure NetApp Files provides NFS and SMB volumes, so any file-based copy tool can be used to replicate data between Azure regions. For more information on how to copy Azure NetApp Files volume in another region, see FAQs about Azure NetApp Files.
You can use Azure NetApp Files Cross-Region Replication, currently in preview, which uses NetApp SnapMirror technology. With this technology, only changed blocks are sent over the network in a compressed, efficient format. This proprietary technology minimizes the amount of data required to replicate across the regions, which saves data transfer costs. It also shortens the replication time so that you can achieve a smaller RPO. For more information, see Requirements and considerations for using cross-region replication.
CMS database
The CMS and audit database in the DR region must be a copy of the databases running in the primary region. Based on the database type, it's important to copy the database to a DR region based on business-required RTO and RPO. This section describes different options available for each database solution in Azure that's supported for an SAP BOBI application running on Windows.
Azure SQL Database
For a SQL Database DR strategy, two options are available to copy the database to the secondary region. Both recovery options offer different levels of RTO and RPO. For more information on the RTO and RPO for each recovery option, see Recover a database to an existing server.
Option 1: Geo-redundant database backup restore
By default, SQL Database stores data in GRS blobs that are replicated to a paired region. For a SQL database, the backup storage redundancy can be configured at the time of CMS and audit database creation, or it can be updated for an existing database. The changes made to an existing database apply to future backups only. You can restore a database on any SQL database in any Azure region from the most recent geo-replicated backups. Geo-restore uses a geo-replicated backup as its source. There's a delay between when a backup is taken and when it's geo-replicated to an Azure blob in a different region. As a result, the restored database can be up to one hour behind the original database.
Important
Geo-restore is available for SQL databases configured with geo-redundant backup storage.
Option 2: Geo-replication or an auto-failover group
Geo-replication is a SQL Database feature that allows you to create readable secondary databases of individual databases on a server in the same or different region. If geo-replication is enabled for the CMS and audit database, the application can initiate failover to a secondary database in a different Azure region. Geo-replication is enabled for individual databases, but to enable transparent and coordinated failover of multiple databases (CMS and audit) for an SAP BOBI application, it's advisable to use an auto-failover group. It provides the group semantics on top of active geo-replication, which means the entire SQL server (all databases) is replicated to another region instead of individual databases. Check the capabilities table that compares geo-replication with failover groups.
Auto-failover groups provide read/write and read-only listener endpoints that remain unchanged during failover. The read/write endpoint can be maintained as a listener in the ODBC connection entry for the CMS and audit database. So whether you use manual or automatic failover activation, failover switches all secondary databases in the group to primary. After the database failover is completed, the DNS record is automatically updated to redirect the endpoints to the new region. The application is automatically connected to the CMS database as the read/write endpoint is maintained as a listener in the ODBC connection.
In the following image, an auto-failover group for the SQL server (azussqlbodb) running on the East US 2 region is replicated to the East US secondary region (DR site). The read/write listener endpoint is maintained as a listener in an ODBC connection for the BI application server running on Windows. After failover, the endpoint will remain the same. No manual intervention is required to connect the BI application to the SQL database on the secondary region.

This option provides a lower RTO and RPO than option 1. For more information about this option, see Use auto-failover groups to enable transparent and coordinated failover of multiple databases.
Azure Database for MySQL
Azure Database for MySQL provides options to recover a database if there's a disaster. Choose the appropriate option that works for your business:
Enable cross-region read replicas to enhance your business continuity and DR planning. You can replicate from a source server up to five replicas. Read replicas are updated asynchronously by using the Azure Database for MySQL binary log replication technology. Replicas are new servers that you manage similar to regular Azure Database for MySQL servers. To learn more about read replicas, available regions, restrictions, and how to fail over, see Read replicas in Azure Database for MySQL.
Use the Azure Database for MySQL geo-restore feature that restores the server by using geo-redundant backups. These backups are accessible even when the region on which your server is hosted is offline. You can restore from these backups to any other region and bring your server back online.
Important
Geo-restore is only possible if you provisioned the server with geo-redundant backup storage. Changing the backup redundancy options after server creation isn't supported. For more information, see Backup redundancy.
The following table lists the recommendations for DR for each tier used in this example.
| SAP BOBI platform tiers | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Azure Application Gateway or Azure Load Balancer | Parallel setup of Application Gateway on a secondary region |
| Web application servers | Replicate by using Azure Site Recovery |
| BI application servers | Replicate by using Site Recovery |
| Azure Premium Files | AzCopy or Azure PowerShell |
| Azure NetApp Files | File-based copy tool to replicate data to a secondary region or Azure NetApp Files Cross-Region Replication Preview |
| Azure SQL Database | Geo-replication/auto-failover groups or geo-restore |
| Azure Database for MySQL | Cross-region read replicas or restore backup from geo-redundant backups |