Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This tutorial presents an end-to-end example of a Synapse Data Science workflow, in Microsoft Fabric. The scenario builds a fraud detection model with machine learning algorithms trained on historical data. It then uses the model to detect future fraudulent transactions.
This tutorial covers these steps:
- Install custom libraries
- Load the data
- Understand and process the data through exploratory data analysis
- Use scikit-learn to train a machine learning model, and track experiments with the MLflow and Fabric Autologging features
- Save and register the machine learning model that has the highest performance
- Load the machine learning model for scoring and to make predictions
Prerequisites
Get a Microsoft Fabric subscription. Or, sign up for a free Microsoft Fabric trial.
Sign in to Microsoft Fabric.
Switch to Fabric by using the experience switcher on the lower-left side of your home page.

- If necessary, create a Microsoft Fabric lakehouse as described in Create a lakehouse in Microsoft Fabric.
Follow along in a notebook
You can choose one of these options to follow along in a notebook:
- Open and run the built-in notebook.
- Upload your notebook from GitHub.
Open the built-in notebook
The sample Fraud detection notebook accompanies this tutorial.
To open the sample notebook for this tutorial, follow the instructions in Prepare your system for data science tutorials.
Make sure to attach a lakehouse to the notebook before you start running code.
Import the notebook from GitHub
The AIsample - Fraud Detection.ipynb notebook accompanies this tutorial.
To open the accompanying notebook for this tutorial, follow the instructions in Prepare your system for data science tutorials to import the notebook to your workspace.
If you'd rather copy and paste the code from this page, you can create a new notebook.
Be sure to attach a lakehouse to the notebook before you start running code.
Step 1: Install custom libraries
For machine learning model development or ad-hoc data analysis, you might need to quickly install a custom library for your Apache Spark session. You have two options to install libraries.
- Use the inline installation capabilities (
%pipor%conda) of your notebook to install a library, in your current notebook only. - Alternatively, you can create a Fabric environment, install libraries from public sources or upload custom libraries to it, and then your workspace admin can attach the environment as the default for the workspace. All the libraries in the environment will then become available for use in any notebooks and Spark job definitions in the workspace. For more information on environments, see create, configure, and use an environment in Microsoft Fabric.
For this tutorial, use %pip install to install the imblearn library in your notebook.
Note
The PySpark kernel restarts after %pip install runs. Install the needed libraries before you run any other cells.
# Use pip to install imblearn
%pip install imblearn
Step 2: Load the data
The fraud detection dataset contains credit card transactions, from September 2013, that European cardholders made over the course of two days. The dataset contains only numerical features because of a Principal Component Analysis (PCA) transformation applied to the original features. PCA transformed all features except for Time and Amount. To protect confidentiality, we can't provide the original features or more background information about the dataset.
These details describe the dataset:
- The
V1,V2,V3, …,V28features are the principal components obtained with PCA - The
Timefeature contains the elapsed seconds between a transaction and the first transaction in the dataset - The
Amountfeature is the transaction amount. You can use this feature for example-dependent, cost-sensitive learning - The
Classcolumn is the response (target) variable. It has the value1for fraud, and0otherwise
Only 492 transactions, out of 284,807 transactions total, are fraudulent. The dataset is highly imbalanced, because the minority (fraudulent) class accounts for only about 0.172% of the data.
This table shows a preview of the creditcard.csv data:
| Time | V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | V9 | V10 | V11 | V12 | V13 | V14 | V15 | V16 | V17 | V18 | V19 | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | V25 | V26 | V27 | V28 | Amount | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.3598071336738 | -0.0727811733098497 | 2.53634673796914 | 1.37815522427443 | -0.338320769942518 | 0.462387777762292 | 0.239598554061257 | 0.0986979012610507 | 0.363786969611213 | 0.0907941719789316 | -0.551599533260813 | -0.617800855762348 | -0.991389847235408 | -0.311169353699879 | 1.46817697209427 | -0.470400525259478 | 0.207971241929242 | 0.0257905801985591 | 0.403992960255733 | 0.251412098239705 | -0.018306777944153 | 0.277837575558899 | -0.110473910188767 | 0.0669280749146731 | 0.128539358273528 | -0.189114843888824 | 0.133558376740387 | -0.0210530534538215 | 149.62 | "0" |
| 0 | 1.19185711131486 | 0.26615071205963 | 0.16648011335321 | 0.448154078460911 | 0.0600176492822243 | -0.0823608088155687 | -0.0788029833323113 | 0.0851016549148104 | -0.255425128109186 | -0.166974414004614 | 1.61272666105479 | 1.06523531137287 | 0.48909501589608 | -0.143772296441519 | 0.635558093258208 | 0.463917041022171 | -0.114804663102346 | -0.183361270123994 | -0.145783041325259 | -0.0690831352230203 | -0.225775248033138 | -0.638671952771851 | 0.101288021253234 | -0.339846475529127 | 0.167170404418143 | 0.125894532368176 | -0.00898309914322813 | 0.0147241691924927 | 2.69 | "0" |
Download the dataset and upload to the lakehouse
Define these parameters, so that you can use this notebook with different datasets:
IS_CUSTOM_DATA = False # If True, the dataset has to be uploaded manually
TARGET_COL = "Class" # Target column name
IS_SAMPLE = False # If True, use only <SAMPLE_ROWS> rows of data for training; otherwise, use all data
SAMPLE_ROWS = 5000 # If IS_SAMPLE is True, use only this number of rows for training
DATA_FOLDER = "Files/fraud-detection/" # Folder with data files
DATA_FILE = "creditcard.csv" # Data file name
EXPERIMENT_NAME = "aisample-fraud" # MLflow experiment name
This code downloads a publicly available version of the dataset, and then stores it in a Fabric lakehouse.
Important
Be sure to add a lakehouse to the notebook before you run it. Otherwise, you'll get an error.
if not IS_CUSTOM_DATA:
# Download data files into the lakehouse if they're not already there
import os, requests
remote_url = "https://synapseaisolutionsa.z13.web.core.windows.net/data/Credit_Card_Fraud_Detection"
fname = "creditcard.csv"
download_path = f"/lakehouse/default/{DATA_FOLDER}/raw"
if not os.path.exists("/lakehouse/default"):
raise FileNotFoundError("Default lakehouse not found, please add a lakehouse and restart the session.")
os.makedirs(download_path, exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(f"{download_path}/{fname}"):
r = requests.get(f"{remote_url}/{fname}", timeout=30)
with open(f"{download_path}/{fname}", "wb") as f:
f.write(r.content)
print("Downloaded demo data files into lakehouse.")
Set up MLflow experiment tracking
The experiment tracking process saves all relevant experiment-related information for every experiment that you run. Sometimes, you have no way to obtain better results when you run a specific experiment. In those cases, you should stop the experiment and try a new one.
The Synapse Data Science experience in Microsoft Fabric includes an autologging feature. This feature reduces the amount of code needed to automatically log the parameters, metrics, and items of a machine learning model during training. The feature extends the MLflow autologging capabilities. It has deep integration in the Data Science experience.
With autologging, you can easily track and compare the performance of different models and experiments, without the need for manual tracking. For more information, see Autologging in Microsoft Fabric.
To disable Microsoft Fabric autologging in a notebook session, call mlflow.autolog() and set disable=True:
# Set up MLflow for experiment tracking
import mlflow
mlflow.set_experiment(EXPERIMENT_NAME)
mlflow.autolog(disable=True) # Disable MLflow autologging
Read raw data from the lakehouse
This code reads raw data from the lakehouse:
df = (
spark.read.format("csv")
.option("header", "true")
.option("inferSchema", True)
.load(f"{DATA_FOLDER}/raw/{DATA_FILE}")
.cache()
)
Step 3: Perform exploratory data analysis
In this section, you first explore the raw data and high-level statistics. Then, to transform the data, cast the columns into the correct types, and convert them from the Spark DataFrame into a pandas DataFrame for easier visualization. Finally, you explore and visualize the class distributions in the data.
Display the raw data
Explore the raw data, and view high-level statistics, with the
displaycommand. For more information about data visualization, see Notebook visualization in Microsoft Fabric.display(df)Print some basic information about the dataset:
# Print dataset basic information print("records read: " + str(df.count())) print("Schema: ") df.printSchema()
Transform the data
Cast the dataset columns into the correct types:
import pyspark.sql.functions as F df_columns = df.columns df_columns.remove(TARGET_COL) # Ensure that TARGET_COL is the last column df = df.select(df_columns + [TARGET_COL]).withColumn(TARGET_COL, F.col(TARGET_COL).cast("int")) if IS_SAMPLE: df = df.limit(SAMPLE_ROWS)Convert the Spark DataFrame to a pandas DataFrame for easier visualization and processing:
df_pd = df.toPandas()
Explore the class distribution in the dataset
Display the class distribution in the dataset:
# The distribution of classes in the dataset print('No Frauds', round(df_pd['Class'].value_counts()[0]/len(df_pd) * 100,2), '% of the dataset') print('Frauds', round(df_pd['Class'].value_counts()[1]/len(df_pd) * 100,2), '% of the dataset')The code returns this dataset class distribution: 99.83%
No Fraudsand 0.17%Frauds. This class distribution shows that most of the transactions are nonfraudulent. Therefore, data preprocessing is required before model training, to avoid overfitting.Use a plot to show the class imbalance in the dataset, by viewing the distribution of fraudulent versus nonfraudulent transactions:
import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt colors = ["#0101DF", "#DF0101"] sns.countplot(x='Class', data=df_pd, palette=colors) plt.title('Class Distributions \n (0: No Fraud || 1: Fraud)', fontsize=10)Show the five-number summary (minimum score, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum score) for the transaction amount, with box plots:
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=(12,5)) s = sns.boxplot(ax = ax1, x="Class", y="Amount", hue="Class",data=df_pd, palette="PRGn", showfliers=True) # Remove outliers from the plot s = sns.boxplot(ax = ax2, x="Class", y="Amount", hue="Class",data=df_pd, palette="PRGn", showfliers=False) # Keep outliers from the plot plt.show()For highly imbalanced data, box plots might not show accurate insights. However, you can address the
Classimbalance problem first, and then create the same plots for more accurate insights.
Step 4: Train and evaluate the models
Here, you train a LightGBM model to classify the fraud transactions. You train a LightGBM model on both the imbalanced dataset and the balanced dataset. Then, you compare the performance of both models.
Prepare training and test datasets
Before training, split the data into the training and test datasets:
# Split the dataset into training and testing sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train, test = train_test_split(df_pd, test_size=0.15)
feature_cols = [c for c in df_pd.columns.tolist() if c not in [TARGET_COL]]
Apply SMOTE to the training dataset
The imblearn library uses the Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) approach to address the problem of imbalanced classification. Imbalanced classification happens when too few examples of the minority class are available, for a model to effectively learn the decision boundary. SMOTE is the most widely used approach to synthesize new samples for the minority class.
Apply SMOTE only to the training dataset, instead of the test dataset. When you score the model with the test data, you need an approximation of the model performance on unseen data in production. For a valid approximation, your test data relies on the original imbalanced distribution to represent production data as closely as possible.
# Apply SMOTE to the training data
import pandas as pd
from collections import Counter
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
X = train[feature_cols]
y = train[TARGET_COL]
print("Original dataset shape %s" % Counter(y))
sm = SMOTE(random_state=42)
X_res, y_res = sm.fit_resample(X, y)
print("Resampled dataset shape %s" % Counter(y_res))
new_train = pd.concat([X_res, y_res], axis=1)
For more information about SMOTE, see the scikit-learn reference page for the SMOTE method and the scikit-learn user guide on oversampling resources.
Train machine learning models and run experiments
Apache Spark, in Microsoft Fabric, enables machine learning with big data. With Apache Spark, you can get valuable insights from large amounts of structured, unstructured, and fast-moving data.
You have several available options to train machine learning models with Apache Spark in Microsoft Fabric: Apache Spark MLlib, SynapseML, and other open-source libraries. For more information, see Train machine learning models in Microsoft Fabric.
A machine learning experiment serves as the primary unit of organization and control for all related machine learning runs. A run corresponds to a single execution of model code. Machine learning experiment tracking involves the management of all the experiments and their components, such as parameters, metrics, models, and other artifacts.
For experiment tracking, you can organize all the required components of a specific machine learning experiment. Additionally, you can easily reproduce past results with saved experiments. For more information about machine learning experiments, see Machine learning experiments in Microsoft Fabric.
To track more metrics, parameters, and files, set
exclusive=Falseto update the MLflow autologging configuration:mlflow.autolog(exclusive=False)Train two models with LightGBM. One model handles the imbalanced dataset, and the other model handles the balanced dataset (via SMOTE). Then compare the performance of the two models.
import lightgbm as lgb model = lgb.LGBMClassifier(objective="binary") # Imbalanced dataset smote_model = lgb.LGBMClassifier(objective="binary") # Balanced dataset# Train LightGBM for both imbalanced and balanced datasets and define the evaluation metrics print("Start training with imbalanced data:\n") with mlflow.start_run(run_name="raw_data") as raw_run: model = model.fit( train[feature_cols], train[TARGET_COL], eval_set=[(test[feature_cols], test[TARGET_COL])], eval_metric="auc", callbacks=[ lgb.log_evaluation(10), ], ) print(f"\n\nStart training with balanced data:\n") with mlflow.start_run(run_name="smote_data") as smote_run: smote_model = smote_model.fit( new_train[feature_cols], new_train[TARGET_COL], eval_set=[(test[feature_cols], test[TARGET_COL])], eval_metric="auc", callbacks=[ lgb.log_evaluation(10), ], )
Determine feature importance for training
Determine feature importance for the model that you trained on the imbalanced dataset:
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=raw_run.info.run_id): importance = lgb.plot_importance( model, title="Feature importance for imbalanced data" ) importance.figure.savefig("feauture_importance.png") mlflow.log_figure(importance.figure, "feature_importance.png")Determine feature importance for the model that you trained on balanced data. SMOTE generated the balanced data:
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=smote_run.info.run_id): smote_importance = lgb.plot_importance( smote_model, title="Feature importance for balanced (via SMOTE) data" ) smote_importance.figure.savefig("feauture_importance_smote.png") mlflow.log_figure(smote_importance.figure, "feauture_importance_smote.png")
To train a model with the imbalanced dataset, the important features have significant differences when compared with a model trained with the balanced dataset.
Evaluate the models
Here, you evaluate the two trained models:
modeltrained on raw, imbalanced datasmote_modeltrained on balanced data
Compute model metrics
Define a
prediction_to_sparkfunction that performs predictions, and converts the prediction results into a Spark DataFrame. You can then compute model statistics on the prediction results with SynapseML.from pyspark.sql.functions import col from pyspark.sql.types import IntegerType, DoubleType def prediction_to_spark(model, test): predictions = model.predict(test[feature_cols], num_iteration=model.best_iteration_) predictions = tuple(zip(test[TARGET_COL].tolist(), predictions.tolist())) dataColumns = [TARGET_COL, "prediction"] predictions = ( spark.createDataFrame(data=predictions, schema=dataColumns) .withColumn(TARGET_COL, col(TARGET_COL).cast(IntegerType())) .withColumn("prediction", col("prediction").cast(DoubleType())) ) return predictionsUse the
prediction_to_sparkfunction to perform predictions with the two models,modelandsmote_model:predictions = prediction_to_spark(model, test) smote_predictions = prediction_to_spark(smote_model, test) predictions.limit(10).toPandas()Compute metrics for the two models:
from synapse.ml.train import ComputeModelStatistics metrics = ComputeModelStatistics( evaluationMetric="classification", labelCol=TARGET_COL, scoredLabelsCol="prediction" ).transform(predictions) smote_metrics = ComputeModelStatistics( evaluationMetric="classification", labelCol=TARGET_COL, scoredLabelsCol="prediction" ).transform(smote_predictions) display(metrics)
Evaluate model performance with a confusion matrix
A confusion matrix displays the number of
- true positives (TP)
- true negatives (TN)
- false positives (FP)
- false negatives (FN)
that a model produces when scored with test data. For binary classification, the model returns a 2x2 confusion matrix. For multiclass classification, the model returns an nxn confusion matrix, where n is the number of classes.
Use a confusion matrix to summarize the performances of the trained machine learning models on the test data:
# Collect confusion matrix values cm = metrics.select("confusion_matrix").collect()[0][0].toArray() smote_cm = smote_metrics.select("confusion_matrix").collect()[0][0].toArray() print(cm)Plot the confusion matrix for the predictions of
smote_model(trained on balanced data):# Plot the confusion matrix import seaborn as sns def plot(cm): """ Plot the confusion matrix. """ sns.set(rc={"figure.figsize": (5, 3.5)}) ax = sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt=".20g") ax.set_title("Confusion Matrix") ax.set_xlabel("Predicted label") ax.set_ylabel("True label") return ax with mlflow.start_run(run_id=smote_run.info.run_id): ax = plot(smote_cm) mlflow.log_figure(ax.figure, "ConfusionMatrix.png")Plot the confusion matrix for the predictions of
model(trained on raw, imbalanced data):with mlflow.start_run(run_id=raw_run.info.run_id): ax = plot(cm) mlflow.log_figure(ax.figure, "ConfusionMatrix.png")
Evaluate model performance with AUC-ROC and AUPRC measures
The Area Under the Curve Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUC-ROC) measure assesses the performance of binary classifiers. The AUC-ROC chart visualizes the trade-off between the true positive rate (TPR) and the false positive rate (FPR).
In some cases, it's more appropriate to evaluate your classifier based on the Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve (AUPRC) measure. The AUPRC curve combines these rates:
- The precision, or the positive predictive value (PPV)
- The recall, or TPR
To evaluate performance with the AUC-ROC and AUPRC measures:
Define a function that returns the AUC-ROC and AUPRC measures:
from pyspark.ml.evaluation import BinaryClassificationEvaluator def evaluate(predictions): """ Evaluate the model by computing AUROC and AUPRC with the predictions. """ # Initialize the binary evaluator evaluator = BinaryClassificationEvaluator(rawPredictionCol="prediction", labelCol=TARGET_COL) _evaluator = lambda metric: evaluator.setMetricName(metric).evaluate(predictions) # Calculate AUROC, baseline 0.5 auroc = _evaluator("areaUnderROC") print(f"The AUROC is: {auroc:.4f}") # Calculate AUPRC, baseline positive rate (0.172% in the data) auprc = _evaluator("areaUnderPR") print(f"The AUPRC is: {auprc:.4f}") return auroc, auprcLog the AUC-ROC and AUPRC metrics for the model that you trained on imbalanced data:
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=raw_run.info.run_id): auroc, auprc = evaluate(predictions) mlflow.log_metrics({"AUPRC": auprc, "AUROC": auroc}) mlflow.log_params({"Data_Enhancement": "None", "DATA_FILE": DATA_FILE})Log the AUC-ROC and AUPRC metrics for the model that you trained on balanced data:
with mlflow.start_run(run_id=smote_run.info.run_id): auroc, auprc = evaluate(smote_predictions) mlflow.log_metrics({"AUPRC": auprc, "AUROC": auroc}) mlflow.log_params({"Data_Enhancement": "SMOTE", "DATA_FILE": DATA_FILE})
The model trained on the balanced data returns higher AUC-ROC and AUPRC values compared to the model trained on the imbalanced data. Based on these measures, SMOTE seems like an effective technique to enhance model performance when working with highly imbalanced data.
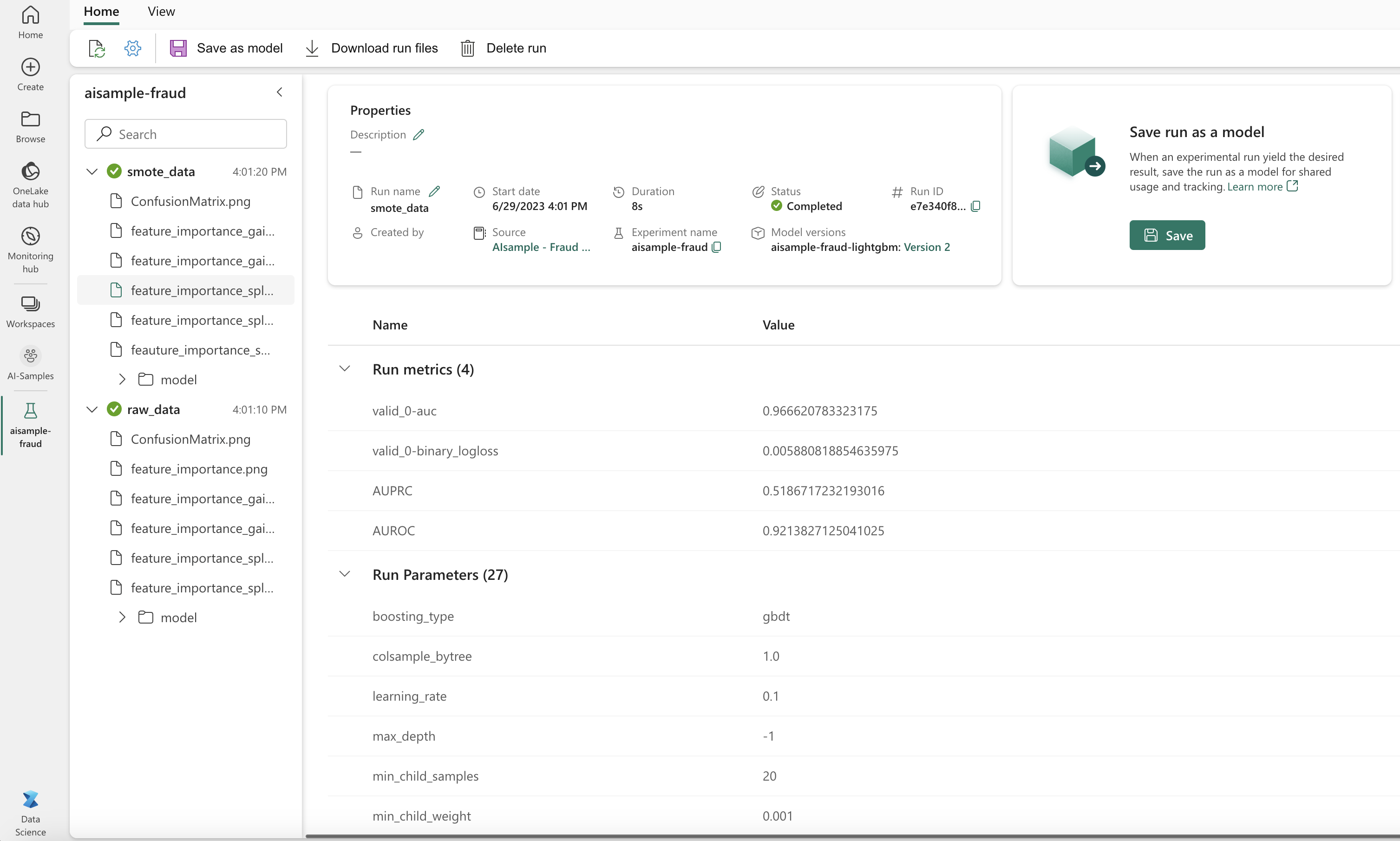
As the next image shows, any experiment is logged with its respective name. You can track the experiment parameters and performance metrics in your workspace.
This image shows the performance metrics for the model trained on the balanced dataset (in Version 2):
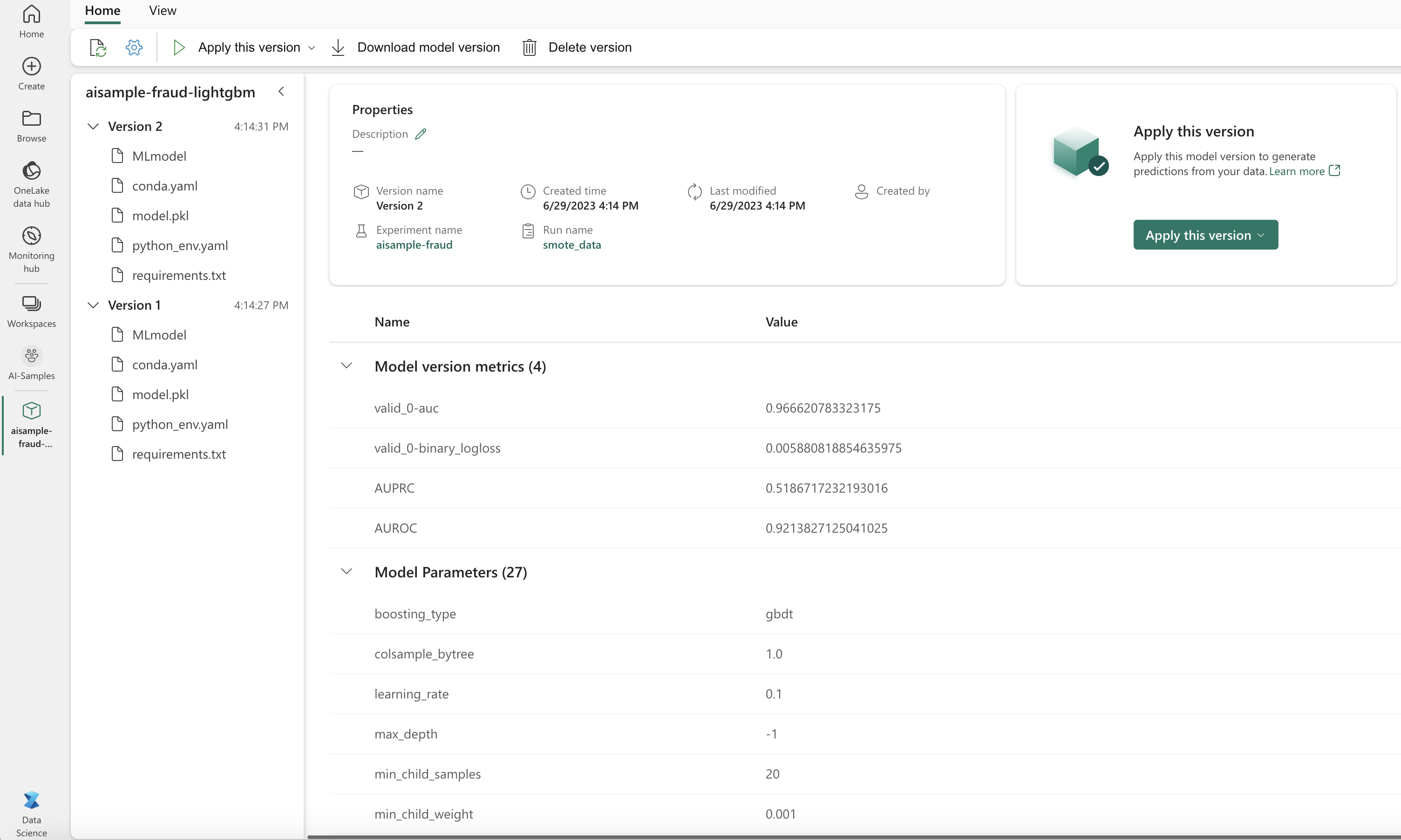
You can select Version 1 to see the metrics for the model trained on the imbalanced dataset. When you compare the metrics, the AUROC is higher for the model trained with the balanced dataset. These results indicate that this model is better at correctly predicting 0 classes as 0, and predicting 1 classes as 1.
Step 5: Register the models
Use MLflow to register the two models:
# Register the model
registered_model_name = f"{EXPERIMENT_NAME}-lightgbm"
raw_model_uri = "runs:/{}/model".format(raw_run.info.run_id)
mlflow.register_model(raw_model_uri, registered_model_name)
smote_model_uri = "runs:/{}/model".format(smote_run.info.run_id)
mlflow.register_model(smote_model_uri, registered_model_name)
Step 6: Save the prediction results
Microsoft Fabric allows users to operationalize machine learning models with the PREDICT scalable function. This function supports batch scoring (or batch inferencing) in any compute engine.
You can generate batch predictions directly from the Microsoft Fabric notebook or from a model's item page. For more information about PREDICT, see Model scoring with PREDICT in Microsoft Fabric.
Load the better-performing model (Version 2) for batch scoring, and generate the prediction results:
from synapse.ml.predict import MLFlowTransformer spark.conf.set("spark.synapse.ml.predict.enabled", "true") model = MLFlowTransformer( inputCols=feature_cols, outputCol="prediction", modelName=f"{EXPERIMENT_NAME}-lightgbm", modelVersion=2, ) test_spark = spark.createDataFrame(data=test, schema=test.columns.to_list()) batch_predictions = model.transform(test_spark)Save predictions to the lakehouse:
# Save the predictions to the lakehouse batch_predictions.write.format("delta").mode("overwrite").save(f"{DATA_FOLDER}/predictions/batch_predictions")