Create users
You use the Microsoft 365 admin center to create user accounts for every user who needs access to apps, flows, or chatbots. The user account registers the user with Microsoft Online Services environment.
Create a user account
When you create a user account in the Microsoft 365 admin center, the system generates a user ID and temporary password for the user. You can let the service send an email message to the user as clear text. Although the password is temporary, you might consider copying the information to send to the user through a more secure channel, such as from an email service that can digitally encrypt the contents.
For step-by-step instructions for creating a Microsoft Online Services user account, see Add users individually or in bulk.
Note
When you create a user and assign a license in the Microsoft 365 admin center, the user is also created in customer engagement apps. It can take a few minutes to complete the synchronization process between the Microsoft 365 admin center and customer engagement apps.
By entering a user ID and password, a user can access the Microsoft 365 admin center to view information about the service. However, the user won't have access to customer engagement apps until the user has a security role assigned either directly or indirectly as a member of a group team.
Tip
To force an immediate synchronization between the Microsoft 365 admin center and customer engagement apps, do the following:
- Sign out of the customer engagement app and the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Close all open browsers used for the customer engagement app and the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Sign back in to the customer engagement app and the Microsoft 365 admin center.
User types
Regular users
These users are the regular synchronized users from Microsoft Entra ID.
Application users
Identified by the presence of ApplicationId attribute in the system user record. To check the Microsoft Entra application ID, see View or edit the details of an application user.
Non-interactive users
- License-specific provisioning business rules don't apply to these users after they're marked as non-interactive. Note: security group specific rules still apply.
- Can't access Microsoft Dataverse web interface or admin portals.
- Can only access Dataverse via SDK/API calls.
- There's a maximum limit of seven non-interactive users per instance.
Support user
See System and application users.
- Not synchronized with Microsoft Entra ID, and created by Dataverse out of the box.
- Placeholder user record for all of the internal Microsoft support users.
- Key identifiers:
- UPN (User Principal Name) value is crmoln@microsoft.com.
- Access mode value is 3.
- All Microsoft support users are mapped to this well-known record at runtime.
Delegated administrator
See the following articles:
For partners: the Delegated Administrator
System and application users
- Not synchronized with Microsoft Entra ID, and created by Dataverse out of the box.
- Placeholder user record for all of customer’s delegated admin partner users to access Dataverse as delegated administrators.
- Key identifiers:
- UPN value is crmoln2@microsoft.com.
- Access mode value is 5.
- All the delegated admin partner users are mapped to this well-known record at runtime.
User profile information
Some user profile information is maintained and managed in the Microsoft 365 admin center. After you create or update a user, these user profile fields are automatically updated and synchronized in your Microsoft Power Platform environments.
The following table shows the fields that are managed in the Users section of the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Customer engagement apps user form | Dataverse SystemUser object | Microsoft 365/Microsoft Entra user |
|---|---|---|
| User Name | DomainName | Username |
| Full Name* | Full Name | Full Name |
| Title | JobTitle | Job title |
| First Name | FirstName | First Name |
| Last Name | LastName | Last Name |
| Primary Email** | InternalEmailAddress*** | |
| Main Phone | Address1_Telephone1 | Office phone |
| Mobile Phone | MobilePhone | Mobile phone |
| Street | Address1_Line1 | Street address |
| City | Address1_City | City |
| State/Province | Address1_StateOrProvince | State or province |
| Postal Code | Address1_PostalCode | Postal Code |
| Country | Address1_Country | Country or region |
| AzureActiveDirectoryObjectId**** | AzureActiveDirectoryObjectId | ObjectId |
| * Full Name isn't automatically updated and synchronized with customer engagement apps. ** To prevent data loss, the PrimaryEmail field isn't automatically updated and synchronized with customer engagement apps. ***InternalEmailAddress can be updated by customers; after which, sync will no longer update this field. **** ObjectID of a user or a service principal in Microsoft Entra ID. | ||
Note
Custom fields are never synchronized between Microsoft 365, Microsoft Entra, and Power Platform.
All the fields are always synchronized, except fields explicitly mentioned as not automatically updated (custom fields, Full Name, Primary Email, and Internal Email Address after a customer update).
The system adds a "#" as the First Name if the First Name was originally blank.
The following image shows Microsoft 365 user contact fields.
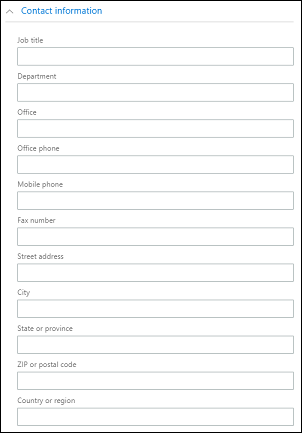
View and edit a user profile
To view and edit a user's profile in the Power Platform admin center:
- Select an environment and go to Settings > Users + permissions > Users.
- Select a user in the list.
On the user profile page you can view and make changes to important user profile information such as security roles, team membership, business unit, manager, position, and more. You can also Run diagnostics to troubleshoot access issues or Refresh User to resync from Microsoft Entra ID.
Add a license to a user account
You can license the user when you create the user account, or you can license the user later. You must assign a license to every user account that you want to access the online service. See Assign licenses.
Assign a security role
Security roles control a user's access to data through a set of access levels and permissions. The combination of access levels and permissions that are included in a specific security role sets limits on the user's view of data and on the user's interactions with that data. See Assign a security role to a user.
Enable or disable user accounts
User enablement and disablement only apply to environments that have a Dataverse database. To enable a user in an environment that has a Dataverse database, ensure that they're allowed to sign in, assign a license to the user, and then add the user to the security group that's associated with the environment. These are the same criteria used to add users to an environment.
To enable a user, assign a license to the user and add the user to the security group that's associated with an environment. If you enable a user account that was disabled, you must send a new invitation for the user to access the system.
To disable a user account, remove a license from the user or remove the user from the security group that's associated with an environment. Removing a user from the security group doesn't remove the user's license. If you want to make the license available to another user, you have to remove the license from the user account that was disabled.
Note
You can also remove all security roles from a user to prevent the user from signing in to and accessing customer engagement apps. However, this doesn't remove the license from the user, and the user will remain in the list of enabled users. We don't recommend using this method to remove access from a user.
When you use a security group to manage enabling or disabling users or provisioning access to an org, nested security groups within the selected security group aren't supported and are ignored.
You can assign records to a disabled user account and also share reports and accounts with them. This can be useful when migrating on-premises versions to online. If you need to assign a security role to users who have a Disabled status, you can do so by enabling the allowRoleAssignmentOnDisabledUsers in OrgDBOrgSettings.
A Global admin, Power Platform admin, or a Dynamics 365 admin doesn't need a license to be enabled in an environment. Learn more in Global admins and Power Platform admins can administer without a license. But since they're unlicensed, they're set in the Administrative access mode.
You must be a member of an appropriate administrator role to do these tasks. More information: Assign admin roles
Enable a user account in an environment
To enable a user in an environment that has a Dataverse database, you enable sign-in for the user, assign a license to the user, and then add the user to a security group.
To enable sign-in
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Select Users > Active users, and then select the user.
- Ensure that under the user's display name, you see Sign in allowed. If you don't, select Block this user, and then unblock sign in.
To assign a license
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Select Users > Active users, and then select the user.
- Select the Licenses and Apps tab, and then select the licenses you want to assign.
- Select Save changes.
To add a user to a security group
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Select Teams & groups > Active teams & groups.
- Select the security group that's associated with your environment.
- Select the Members tab.
- Under Members, select View all and manage members >Add members.
- Choose users from the list or search for users, and then select Save.
Disable a user account in an environment
To disable a user account in an environment that has a Dataverse database, you can either remove the user from the security group or remove the license from the user.
To remove a user from a security group
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Select Teams & groups > Active teams & groups.
- Select the security group that's associated with your environment.
- Select the Members tab.
- Under Members, select View all and manage members.
- Select the users in the list to remove them, and then select Save.
To remove a license from a user
- Sign in to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Select Users > Active users, and then select the user.
- Select the Licenses and Apps tab, and then select the licenses you want to remove.
- Select Save changes.
Removing a license from a user might not always result in disabling the user account, though the license is freed up for assigning to another user. The recommended approach to disabling a user account in an environment is to remove them from the security group that's associated with the environment.
Note
You can also delete users in the Microsoft 365 admin center. When you remove a user from your subscription, the license assigned to that user automatically becomes available to be assigned to a different user. If you want the user to still have access to other applications you manage through Microsoft 365—for example, Microsoft Exchange Online or SharePoint—don't delete them as a user. Instead, simply remove the license you've assigned to them.
When you sign out of the Microsoft 365 admin center, you aren't signing out of customer engagement apps. You have to do that separately.
Tip
To force an immediate synchronization between the Microsoft 365 admin center and customer engagement apps, do the following:
- Sign out of the customer engagement app and the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Close all open browsers used for the customer engagement app and the Microsoft 365 admin center.
- Sign back in to the customer engagement app and the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Add users to Dataverse
For users to have access to applications and data in an environment, at a minimum the SystemUser table in Dataverse must have a record corresponding to the respective user identity. There are different mechanisms to add users in Dataverse, either automatic or on demand:
Tip
Check out the following video: Adding users to Dataverse.
A system background process runs periodically to synchronize changes from Microsoft Entra and updates the SystemUser records in Dataverse based on predetermined set of requirements. The time taken to synchronize all changes into Dataverse is dependent on total number of users must be added or updated. For large organizations with thousands of users in Microsoft Entra ID, we recommend creating security groups associated with each environment, so only the required subset of users is added into Dataverse.
Note
Not all users added in Microsoft Entra ID are picked up by the automatic synchronization process. This section details the eligibility criteria the system background process applies to add a user from Microsoft Entra ID into Dataverse.
If users already exist in Microsoft Entra ID, they're automatically added to SystemUsers table at first attempt to access the environment. If a user already exists in Dataverse, but in a disabled state, attempting to access the environment will result in the user’s state to be updated to “enabled”, assuming they're entitled at the time of access.
Users that have the necessary permissions, can use the API to add or update users in Dataverse on demand.
Administrators can use the Power Platform admin center user management experience to add users in Dataverse on demand.
Categories of users not added automatically in Dataverse
In certain conditions, the above-mentioned system background process isn't adding users automatically into Dataverse. In these cases, users are added on demand either when they first attempt to access the environment or by an administrator using the API or the Power Platform admin center. These conditions are:
- Users are part of a Dataverse for Teams environment type.
- Users are part of an environment with a Dataverse database and have a free Dataverse service plan from Microsoft 365 licenses.
- Users are part of an environment with a Dataverse database and environment level app-pass license type.
Note
Users can't be added to SystemUser table either automatically or on demand in case of environments without Dataverse database.
Requirements for successfully adding users in Dataverse
Below criteria must be met for successfully adding the user in the Dataverse table:
User must be enabled and not deleted or soft-deleted in Microsoft Entra ID. User must be enabled in Microsoft Entra to be enabled in a Dataverse database. If user is added to Dataverse and then deleted in Microsoft Entra ID, the state in the Dataverse table is updated to “disabled”.
User must have a valid license with these exceptions:
- Admin users don't require a license. Unlicensed Microsoft Entra admins are enabled in the systems as “Setup user” and have administrative only access mode.
- Individual users don't need to have a license when the environment has app pass capacity. This only applies to adding users on demand (either at first attempt to access the environment or through API/Power Platform admin center).
- Individual users don't need to have a license when the tenant they're part of has a tenant level Marketing license. This only applies to adding users on demand (either at first attempt to access the environment or through API/Power Platform admin center).
- Non-interactive users don't need a license.
- Free Dataverse plans from Microsoft 365 license are honored when users added on-demand (either at first attempt to access the environment or through API/Power Platform admin center).
Note
Guest users should also have a license from the environment’s tenant. License from Guest user's tenant isn't considered as valid license.
- If the environment has a security group defined, user must be part of the respective security group, unless the user is a Tenant or Power Platform Administrator. Nonadmin users or Dynamics 365 service admin must be in the security group to access the system. When the owner of the security group is added to Dataverse through an on-demand action, the user is considered a valid member of the security group and is added to Dataverse successfully.
Adding users to Dataverse has different implications depending on the environment type:
If users are part of a trial environment, then they won't need email approval for being added to Dataverse. Users will only be added to Dataverse on demand. The background sync process will still run to keep the users in the environment up-to-date, but won't add users automatically.
Only the initial user that created the developer environment type is added to Dataverse.
Users that are part of a Dataverse for Teams environment will only be added to Dataverse’s SystemUser table as a result of the user’s first attempt to access the environment.
Create a Read-Write user account
By default, all licensed users are created with an access mode of Read-Write. This access mode provides full access rights to the user based on the security privileges that are assigned.
To update the access mode of a user
- In the Power Platform admin center, select an environment, and go to Settings > Users + permissions > Users.
- Select Enabled Users, and then open a user from the list.
- On the user pane command bar, select ... > Manage user in Dynamics 365.
- In the user form, scroll down under Administration to the Client Access License (CAL) Information section. In the Access Mode list, select Read-Write.
- Select the Save icon.
Create an administrative user account
An administrative user is a user who has access to the settings and administration features, but has no access to any of the functionalities. Use this account to assign administrative users to perform day-to-day maintenance functions such as creating user accounts, managing security roles, and so on. Because an administrative user doesn't have access to customer data, apps, or any functionality, the user doesn't require a license after setup.
You need to have the System Administrator security role or equivalent permissions to create an administrative user. First, you create a user account in Microsoft 365, and then in to the customer engagement app, select the Administrative access mode for the account.
Note
Any admin user with the Global admin, Power Platform admin, or Dynamics 365 Service admin role will receive the Administrative access mode as long as there are no user licenses assigned. This is true regardless of enabling app-passes or pay-as-you-go use at the tenant level.
See Create an administrative user and prevent elevation of security role privilege for an example of how an Administrative user account can be used.
Create a user account in the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Be sure to assign a license to the account. You'll remove the license in a later step after you've assigned the Administrative access mode.
In the Optional settings form, expand Roles.
Scroll down the form, and then select Show all by category.
Select the Power Platform Administrator or Dynamics 365 Administrator checkbox.
Wait for the user to sync to the environments.
In the Power Platform admin center, select an environment, and go to Settings > Users + permissions > Users.
Select a user from the list.
On the user pane command bar, select ... > Manage user in Dynamics 365.
In the user form, scroll down under Administration to the Client Access License (CAL) Information section. In the Access Mode list, select Administrative.
Now you need to remove the license from the account.
Go to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Select Users > Active Users.
Select the Administrative user account, and then select the Licenses and apps tab.
Clear the license boxes, and then select Save changes.
Create a non-interactive user account
The non-interactive user isn't a "user" in the typical sense—it doesn't represent a person, it's an access mode that's created with a user account. It's used for programmatic access to and from customer engagement apps between applications. A non-interactive user account lets these applications or tools—such as a connector from customer engagement apps to ERP—authenticate and access customer engagement apps without requiring a license. For each environment, you can create up to seven non-interactive user accounts.
You need to have the System Administrator security role or equivalent permissions to create a non-interactive user. First, you create a user account in Microsoft 365. Then, in customer engagement apps, select the non-interactive access mode for the account.
Create a user account in the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Be sure to assign a license to the account.
In the Power Platform admin center, select an environment, and go to Settings > Users + permissions > Users.
Select Enabled Users, and then open a user from the list.
On the user pane command bar, select ... > Manage user in Dynamics 365.
In the user form, scroll down under Administration to the Client Access License (CAL) Information section. In the Access Mode list, select Non-interactive.
You then need to remove the license from the account.
Go to the Microsoft 365 admin center.
Select Users > Active Users.
On the Licenses and Apps tab, select the non-interactive user account.
Clear the license boxes, and then select Save changes.
Go back to the customer engagement app and confirm that the non-interactive user account Access Mode is still set for Non-interactive.
Create an application user
You can use server-to-server (S2S) authentication to securely and seamlessly communicate between Dataverse and your web applications and services. S2S authentication is the common way that apps registered on Microsoft AppSource use to access the Dataverse data of their subscribers. All operations performed by your application or service by using S2S are performed as the application user you provide, rather than the user who's accessing your application.
All application users are created with a non-interactive user account, however they aren't counted toward the limit of seven non-interactive user accounts. In addition, there's no limit on how many application users you can create in an environment.
Caution
The system adds a "#" as the First Name for the Application User you create. This is by design.
For step-by-step information about creating an application user, see Create an application user.
Enable or disable application users
When application users are created, they're automatically enabled. The default Application User form shows the status in the form footer; the Status field can't be updated.
You can customize the default Application User form to allow updates to the Status field so that you can enable or disable application users, if necessary. For step-by-step information about customizing the default Application User form, see Enable or disable application users.
Caution
Disabling an application user will break all the integration scenarios that use the application user.
Manage application users in the Power Platform admin center
We are in the process of moving application user management from the legacy web client as documented in Enable or disable application users. See the following topic for managing application users from the Power Platform admin center: Manage application users in the Power Platform admin center.
How stub users are created
A stub user is a user record that has been created as a placeholder. For example, records have been imported that refer to this user but the user doesn't exist in customer engagement apps. This user can't sign in, can't be enabled, and can't be synchronized to Microsoft 365. This type of user can only be created through data import.
Caution
To prevent creating duplicate user records with the same UPN or throw errors during data import workflows, ensure that users exist in Entra ID and are sufficiently licensed for pre-provisioning. Office licenses aren't supported for pre-provisioning, but any Power Apps Premium or Dynamics 365 licenses are supported for pre-provisioning. Once users meet these requirements, they're synchronized with Dataverse environments.
If you must reassign records from a stub user to another user, use the Add-BulkRecordsToUsers.
A default security role is automatically assigned to these imported users. The Salesperson security role is assigned in a Dynamics 365 Sales environment and the Basic User security role is assigned in other environments.
Note
By default, a security role can only be assigned to users with an Enabled status. If you need to assign a security role to users who have a Disabled status, you can do so by enabling the allowRoleAssignmentOnDisabledUsers OrgDBOrgSettings.
View stub users
To view a stub user's profile in the Power Platform admin center, complete the following steps.
Select an environment and go to Settings > Users + permissions > Users.
From the Search bar, search for stub users.
Select a stub user to view user details.
Note
Refresh user and user diagnostics options are not available for a stub user.
Update a user record to reflect changes in Microsoft Entra ID
When you create a new user or update an existing user in Dynamics 365 Customer Engagement (on-premises), some fields in the user records, such as name and phone number, are populated with the information obtained from Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS). After the user record is created, no further synchronization occurs between Microsoft Entra user accounts and customer engagement apps user records. If you make changes to the Microsoft Entra user account, you must manually edit the user record to reflect the changes.
In the Power Platform admin center, select an environment, and go to Settings > Users + permissions > Users.
In the list, select the user record you want to update, and then select Edit.
The following table shows the fields that are populated on the user form (user record) from the Microsoft Entra user account.
User form |
Active Directory user |
Active Directory object tab |
|---|---|---|
User name |
User logon name |
Account |
First name |
First name |
General |
Last name |
Last name |
General |
Main Phone |
Telephone number |
General |
Primary Email |
General |
|
Address* |
City |
Address |
Address* |
State/province |
Address |
Home phone |
Home |
Telephones |
| * The Address field comprises the values from the City and State/province fields in Microsoft Entra ID. | ||
FAQ
If a user that is added to Dataverse SystemUser table becomes disabled or unlicensed in Microsoft Entra ID, how is that reflected in Dataverse?
User record isn't deleted, but its state in Dataverse is updated to “disabled”.
Are all users in Microsoft Entra being added to Dataverse?
Users from Microsoft Entra are added to Dataverse only if they meet the criteria. If already existing users don't meet the criteria, their state is updated to “disabled”.
How can the admin increase the performance of adding users in Dataverse?
Assigning a Microsoft Entra security group to the environment is a best practice in general. It can also result in a performance increase when adding users that are part of the security group to Dataverse.
See also
User settings
Get started with security roles in Dataverse
Assign a security role to a user
Opt-out of automatic license-based user roles management