Get started with communication compliance
Important
Microsoft Purview Communication Compliance provides the tools to help organizations detect regulatory compliance (for example, SEC or FINRA) and business conduct violations such as sensitive or confidential information, harassing or threatening language, and sharing of adult content. Communication Compliance is built with privacy by design. Usernames are pseudonymized by default, role-based access controls are built in, investigators are opted in by an admin, and audit logs are in place to help ensure user-level privacy.
Use communication compliance policies to identify user communications for analysis by internal or external reviewers. For more information about how communication compliance policies can help you detect communications in your organization, see communication compliance policies. If you'd like to review how Contoso quickly configured a communication compliance policy to detect potentially inappropriate content in Microsoft Teams, Exchange Online, and Viva Engage communications, check out this case study.
Tip
If you're not an E5 customer, use the 90-day Microsoft Purview solutions trial to explore how additional Purview capabilities can help your organization manage data security and compliance needs. Start now at the Microsoft Purview trials hub. Learn details about signing up and trial terms.
Subscriptions and licensing
Before getting started with communication compliance, you should confirm your Microsoft 365 subscription and any add-ons. To access and use communication compliance, administrators need to verify that their organization has a supported subscription and the appropriate licenses are assigned to users. For more information about subscriptions and licensing, see the subscription requirements for communication compliance.
Important
Communication compliance is currently available for tenants hosted in geographical regions and countries supported by Azure service dependencies. To verify that communication compliance is supported for your organization, see Azure dependency availability by country/region.
If you don't have an existing Office 365 Enterprise E5 plan and want to try communication compliance, you can add Microsoft 365 to your existing subscription or sign up for a trial of Office 365 Enterprise E5.
Note
Office 365 Advanced Compliance is no longer sold as a standalone subscription. When current subscriptions expire, customers should transition to one of these subscriptions, which contain the same or additional compliance features.
Recommended actions
Recommended actions can help your organization quickly get started with communication compliance. Included on the Overview page, recommended actions help guide you through the steps to configure and deploy policies.
The following recommendations are available to help you get started and maximize your communication compliance configuration:
- Get to know communication compliance: Before completing set up, review our official documentation to learn about, plan for, and deploy communication compliance in your organization.
- Assign permissions to ensure your team can get their jobs done: Ensure that only the appropriate stakeholders can access the solution by assigning team members responsible for managing communication compliance features and investigating and reviewing alerts.
- Create distribution groups for users' whose communications you want to detect: Create distribution groups containing users who are included in communication compliance policies.
- Create your first policy to start detecting communications: Detect and investigate potential regulatory compliance violations by first setting up a policy that identifies potential violations across your organization's internal and/or external communications.
- Review alerts to investigate detected messages and take action: Identify and analyze messages that match a policy's conditions to trigger alerts that provide context around a policy violation, so you can investigate and take action if needed.
- Review reports for quick insights into how policies are performing: Get quick insights into how your policies are performing, view detailed reports to drill down further, and export results for further analyses.
Each action in communication compliance has three attributes:
- Action: The name and description of the recommended action.
- Recommended, required, or optional: Whether the recommended action is highly recommended, required, or optional for communication compliance features to function as expected.
- Estimated time to complete: Estimated time to complete the recommended action in minutes.
Select recommendations from the list to get started with configuring communication compliance. Each recommended action guides you through the required activities for the recommendation, including any requirements, what to expect, and the impact of configuring the feature in your organization. Some recommended actions are automatically marked as complete when configured. If not, you need to manually select the action as complete when configured.
Also included on the Policies page, recommended actions insights help summarize current sensitive information types and potential regulatory compliance violations in communications in your organization. Insights are supported by data classification and the application of sensitivity labels, retention labels, and sensitive information type classification. These insights are aggregated and don't include any personal data for users in your organization.
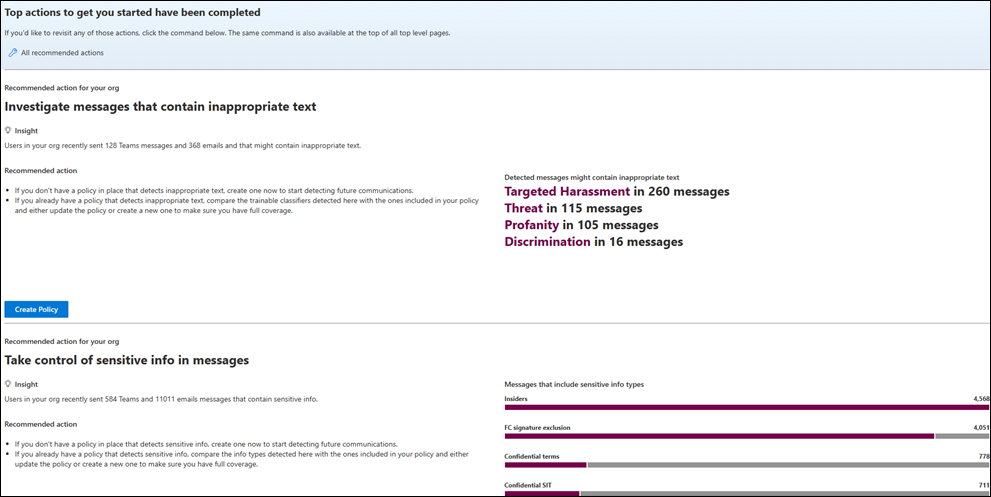
Activity in messages is aggregated by trainable classifier type from existing policies that use the Detect inappropriate text policy template or custom policies that use classifiers. Investigate alerts for these messages on the Alert dashboard for your policies.
Activity involving sensitive information types is detected in messages covered in existing policies and for messages that aren't covered by existing policies. Insight messages that aren't covered by existing policies can't be investigated and remediated, a new policy must be created to detect and remediate similar activity in future messages. Insights are aggregated for all sensitive information types, including ones that your organization hasn't previously defined in an existing communication compliance policy. Use these insights to create a new communication compliance policy or to update existing policies. After creating a new policy, messages alerts for this policy might or might not match an equal number of messages identified in a similar insight. Your policy might have different conditions, a different number of in-scope users, and only detects message activity that occurs after the policy is active.
Tip
Don't want to see the recommended action insights? Open a request with Microsoft Support to disable the display of these insight widgets for your organization.
Step 1 (required): Enable permissions for communication compliance
Important
After configuring your role groups, it may take up to 30 minutes for the role group permissions to apply to assigned users across your organization.
There are six role groups used to configure initial permissions to manage communication compliance features. To make Communication compliance available as a menu option in Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Purview compliance portal and to continue with these configuration steps, you must be assigned to one of the following roles or role groups:
- Microsoft Entra ID Global Administrator role
- Microsoft Entra ID Compliance Administrator role
- Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Purview compliance portal Organization Management role group
- Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Purview compliance portal Compliance Administrator role group
- Communication Compliance role group
- Communication Compliance Admins role group
Important
Microsoft recommends that you use roles with the fewest permissions. Minimizing the number of users with the Global Administrator role helps improve security for your organization. Learn more about Microsoft Purview roles and permissions.
Members of the following roles have the same solution permissions included with the Communication Compliance Admins role group:
- Microsoft Entra ID Global Administrator
- Microsoft Entra ID Compliance Administrator
- Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Purview compliance portal Organization Management
- Microsoft Purview and Microsoft Purview compliance portal Compliance Administrator
Important
Make sure you always have at least one user in the Communication Compliance or Communication Compliance Admins role groups (depending on the option you choose) so that your communication compliance configuration doesn't get in to a 'zero administrator' scenario if specific users leave your organization.
Depending on how you want to manage communication compliance policies and alerts, you need to assign users to specific role groups to manage different sets of communication compliance features. You have the option of assigning users with different compliance responsibilities to specific role groups to manage different areas of communication compliance features. Or you may decide to assign all user accounts for designated administrators, analysts, investigators, and viewers to the Communication Compliance role group. Use a single role group or multiple role groups to best fit your compliance management requirements.
Choose from these solution role group options when configuring and managing communication compliance:
| Actions | Communication Compliance | Communication Compliance Admins | Communication Compliance Analysts | Communication Compliance Investigators | Communication Compliance Viewers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configure policies and settings | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| Access and investigate alerts | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| View Conversation and Translation tabs for a specific message | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Take advanced remediation actions: - Escalate for investigation - Remove message in Teams - Download items and reports - Run Power Automate flows |
Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Create message details report | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Access reports | Yes | No | No | No | Yes |
| Manage privacy settings and notice templates | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| View and export policy updates | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
Consider admin units if you want to scope user permissions to a region or department
You can use administrative units in communication compliance (preview) to scope user permissions to a particular geography or department. For example, a global company that has subsidiaries throughout the world might want to create an admin unit that provides a German scope for investigators so that they only see user activity for German users.
To use admin units in communication compliance, you must first create the admin units (if they haven't already been created), and then assign the admin units to members of role groups. After you assign admin units to members of role groups, those members become restricted administrators and have limited access to communication compliance settings, policies, and user data in the organization. Members who aren't assigned administrative units are unrestricted administrators and have access to all settings, policies, and user data.
Important
At this time, you can't use administrative units together with adaptive scopes in communication compliance. SharePoint sites and inactive mailboxes can only be segmented through adaptive scopes.
Effect of admin unit scoping on communication compliance roles
The following table shows how admin units, when enforced, affect each combination of communication compliance task/role.
Note
Scoped, in the following table, means that the admin actions for that role are limited by their assigned admin unit.
| Task | Scoped Communication Compliance | Scoped Communication Compliance Admins | Scoped Communication Compliance Analysts | Scoped Communication Compliance Investigators | Scoped Communication Compliance Viewers |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configure settings (including notice templates) | No | No | No | No | No |
| Configure policies | Scoped | Scoped | No | No | No |
| Access and investigate alerts | Scoped | No | Scoped | Scoped | No |
| Access reports | No | No | No | No | No |
| View and export audit logs | No | No | No | No | No |
Option 1: Assign all compliance users to the Communication Compliance role group
Select the appropriate tab for the portal you're using. Depending on your Microsoft 365 plan, the Microsoft Purview compliance portal is retired or will be retired soon.
To learn more about the Microsoft Purview portal, see Microsoft Purview portal. To learn more about the Compliance portal, see Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Purview portal using credentials for an admin account in your Microsoft 365 organization.
- Select Settings in the upper-right corner of the page, select Roles and groups, then select Role groups in the left navigation pane.
- Select the Communication Compliance role group, and then select Edit.
- Select Choose users, and then select the checkboxes for all the users you want to add to the role group.
- Choose Select, and then select Next.
- Select Save to add the users to the role group, and then select Done.
Option 2: Assign users to specific communication compliance role groups
Use this option to assign users to specific role groups to segment communication compliance access and responsibilities among different users in your organization.
Select the appropriate tab for the portal you're using. Depending on your Microsoft 365 plan, the Microsoft Purview compliance portal is retired or will be retired soon.
To learn more about the Microsoft Purview portal, see Microsoft Purview portal. To learn more about the Compliance portal, see Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Purview portal using credentials for an admin account in your Microsoft 365 organization.
- Select Settings in the upper-right corner of the page, then select Role groups in the left navigation pane.
- Select one of the communication compliance role groups, and then select Edit.
- Select Choose users, and then select the checkboxes for all the users you want to add to the role group.
- Choose Select, and then select Next.
- Select Save to add the users to the role group.
- Select the next communication compliance role group, and then repeat the previous steps for each required role group.
- Select Close when you're done.
For more information about role groups and permissions, see Permissions in the Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
Step 2 (required): Enable the audit log
Communication compliance requires audit logs to show alerts and log remediation actions taken by reviewers. The audit logs are a summary of all activities associated with a defined organizational policy or anytime a communication compliance policy changes.
Auditing is enabled for Microsoft 365 organizations by default. Some organizations may have disabled auditing for specific reasons. If auditing is disabled for your organization, it might be because another administrator has turned it off. We recommend confirming that it's OK to turn auditing back on when completing this step.
For step-by-step instructions to turn on auditing, see Turn audit log search on or off. After you turn on auditing, a message is displayed that says the audit log is being prepared and that you can run a search in a couple of hours after the preparation is complete. You only have to do this action once. For more information about using the audit log, see Search the audit log.
Step 3 (optional): Set up groups for communication compliance
When you create a communication compliance policy, you define who has their communications reviewed and who performs reviews. In the policy, you'll use email addresses to identify individuals or groups of people. To simplify your setup, you can create groups for people who have their communication reviewed and groups for people who review those communications. If you're using groups, you may need several. For example, if you want to detect communications between two distinct groups of people or if you want to specify a group that isn't going to be scoped.
Use the following chart to help you configure groups in your organization for communication compliance policies:
| Policy Member | Supported Groups | Unsupported Groups |
|---|---|---|
| Scoped users Excluded users |
Distribution groups Microsoft 365 Groups Mail-enabled security groups |
Dynamic distribution groups Shared mailbox Nested distribution groups Microsoft 365 Groups with dynamic membership |
| Reviewers | None | Distribution groups Dynamic distribution groups Nested distribution groups Mail-enabled security groups |
When you assign a distribution group in the policy, the policy detects all emails and Teams chats from each user in the distribution group. When you assign a Microsoft 365 group in the policy, the policy detects all emails and Teams chats sent to the Microsoft 365 group,* not the individual emails and chats received by each group member. Using distribution groups in communication compliance policies are recommended so that individual emails and Teams chats from each user are automatically detected.
Tip
For a more flexible configuration and to reduce administrative overhead, consider using an adaptive scope instead of a distribution group.
If you're an organization with an Exchange on-premises deployment or an external email provider and you want to detect Microsoft Teams chats for your users, you must create a distribution group for the users with on-premises or external mailboxes. Later in these steps, you assign this distribution group by using the Choose users and groups selection in the policy workflow. For more information about the requirements and limitations for enabling cloud-based storage and Teams support for on-premises users, see Search for and export Teams chat data for on-premises users.
To manage scoped users in large enterprise organizations, you may need to detect messages for all users across large groups. You can use PowerShell to configure a distribution group for a global communication compliance policy for the assigned group. This enables you to detect messages for thousands of users with a single policy and keep the communication compliance policy updated as new employees join your organization.
Create a dedicated distribution group for your global communication compliance policy with the following properties: Make sure that this distribution group isn't used for other purposes or other Office 365 services.
- MemberDepartRestriction = Closed. Ensures that users can't remove themselves from the distribution group.
- MemberJoinRestriction = Closed. Ensures that users can't add themselves to the distribution group.
- ModerationEnabled = True. Ensures that all messages sent to this group are subject to approval and that the group isn't being used to communicate outside of the communication compliance policy configuration.
New-DistributionGroup -Name <your group name> -Alias <your group alias> -MemberDepartRestriction 'Closed' -MemberJoinRestriction 'Closed' -ModerationEnabled $trueSelect an unused Exchange custom attribute to log users added to the communication compliance policy in your organization.
Run the following PowerShell script on a recurring schedule to add users to the communication compliance policy:
$Mbx = (Get-Mailbox -RecipientTypeDetails UserMailbox -ResultSize Unlimited -Filter {CustomAttribute9 -eq $Null}) $i = 0 ForEach ($M in $Mbx) { Write-Host "Adding" $M.DisplayName Add-DistributionGroupMember -Identity <your group name> -Member $M.DistinguishedName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue Set-Mailbox -Identity $M.Alias -<your custom attribute name> SRAdded $i++ } Write-Host $i "Mailboxes added to supervisory review distribution group."
For more information about setting up groups, see:
Step 4 (optional): Verify your Viva Engage tenant is in Native Mode
In Native Mode, all Viva Engage users are in Microsoft Entra ID, all groups are Office 365 Groups, and all files are stored in SharePoint Online. Your Viva Engage tenant must be in Native Mode for communication compliance policies to check and identify risky conversations in private messages and community conversations in Viva Engage.
For more information about configuring Viva Engage in Native Mode, see:
- Overview of Viva Engage Native Mode in Microsoft 365
- Configure your Viva Engage network for Native Mode for Microsoft 365
Step 5 (required): Create a communication compliance policy
You can quickly create a communication compliance policy by choosing from several policy templates, or you can create a custom policy.
Important
If your role is scoped by one or more admin units, you can't create a policy based on a template. You can create a custom policy, however.
When you create a policy from a template, many settings are automatically chosen for you based on the template you choose. As the final step, you can customize the policy if you want to change any of the settings.
When you create a custom policy, you select all of the settings yourself.
Create a policy from a template
Select the appropriate tab for the portal you're using. Depending on your Microsoft 365 plan, the Microsoft Purview compliance portal is retired or will be retired soon.
To learn more about the Microsoft Purview portal, see Microsoft Purview portal. To learn more about the Compliance portal, see Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
Sign in to the Microsoft Purview portal using credentials for an admin account in your Microsoft 365 organization.
Go to the Communication Compliance solution.
Select Policies in the left navigation.
Select Create policy, and then select one of the policy templates. For example, select Detect inappropriate text.
In the pane on the right side of the screen:
- In the Policy name field, confirm or update the policy name. Policy names can't be changed once the policy is created.
- In the Users or groups in scope field, choose the users or groups to apply the policy to. If you selected the Detect conflict of interest template, select two scoped groups or two scoped users to detect internal communications.
- In the Reviewers field, choose the reviewers for the policy. Reviewers that you add in this field are the reviewers that you can choose from when escalating an alert in the investigation and remediation workflow. When reviewers are added to a policy, they automatically receive an email message that notifies them of the assignment to the policy and links to information about the review process. Reviewers are individual users and all reviewers must have mailboxes hosted on Exchange Online.
- Review the list of settings that are automatically chosen based on the template you chose. To customize any settings, select Customize policy, and then make the changes you want. If everything looks OK, select Create policy.
Note
To enable optical character recognition (OCR) to identify embedded or attached images in messages for printed or handwritten text that match policy conditions, select Customize policy, and then on the Choose conditions and percentage page, select the Use OCR to extract text from images checkbox.
Create a custom policy
Select the appropriate tab for the portal you're using. Depending on your Microsoft 365 plan, the Microsoft Purview compliance portal is retired or will be retired soon.
To learn more about the Microsoft Purview portal, see Microsoft Purview portal. To learn more about the Compliance portal, see Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
Sign in to the Microsoft Purview portal using credentials for an admin account in your Microsoft 365 organization.
Go to the Communication Compliance solution.
Select Policies in the left navigation.
Select Create policy, and then select Custom policy.
On the Name and describe your policy page, give the policy a name (required) and description (optional). Policy names can't be changed once the policy is created. Select Next when you're done with this page.
If one or more admin units have been created for your organization, you'll see the Admin units (preview) page. Otherwise, you'll see the Choose users and reviewers page (next step) and a banner with a link to learn more about admin units.
If you want to scope the policy to one or more admin units, select Add admin units, select the admin unit(s) that you want to apply to the policy, and then select Save.
Note
You can only see the admin units that are scoped to your role. If you're an unrestricted administrator, you can see all admin units for the organization. To view a summary of the role groups and admin units that you're assigned to, select View my permissions.
Select Next when you're done with the Admin units (preview) page.
On the Choose users and reviewers page:
- In the Choose users and groups section, select one of the following options:
All users: This is the most inclusive option and is recommended for the broadest protection.
Note
If the policy is scoped by one or more admin units, if you select this option, all of the users in the admin units are selected.
Select users: If you select this option, you can start typing to find specific users or groups. The Show insights and recommendations for users who match this policy's conditions but weren't included in the policy checkbox also appears when you select this option. Leave this checkbox selected if you want to reduce blind spots by receiving recommendations when users outside of the selected users match the policy conditions. This setting isn't available if you choose the All users option or the Select adaptive scopes option.
Note
If the policy is scoped by one or more admin units, you can only select users that are part of those admin units.
Select adaptive scopes: An adaptive scope uses a query that you specify to define the membership of users or groups. If you decide to use an adaptive policy, create the adaptive scope before you create your policy, and then select the scope(s) when you choose this option. Site scopes aren't applicable to communication compliance so you won't see them when you add a scope. Learn more about the advantages of using an adaptive scope.
Note
If the policy is scoped by one or more admin units the Select adaptive scopes option doesn't appear. At this time, you can't use adaptive scopes together with admin units.
In the Excluded users and groups section, add any users or groups that you want to exclude from the policy.
Note
If the policy is scoped by one or more admin units, you can only exclude users and groups that are part of those admin units.
In the Reviewers section, choose the reviewers for the policy. Reviewers that you add in this section are the reviewers that you can choose from when escalating an alert in the investigation and remediation workflow. When reviewers are added to a policy, they automatically receive an email message that notifies them of the assignment to the policy and links to information about the review process. Reviewers are individual users and all reviewers must have mailboxes hosted on Exchange Online.
Select Next when you're done with this page.
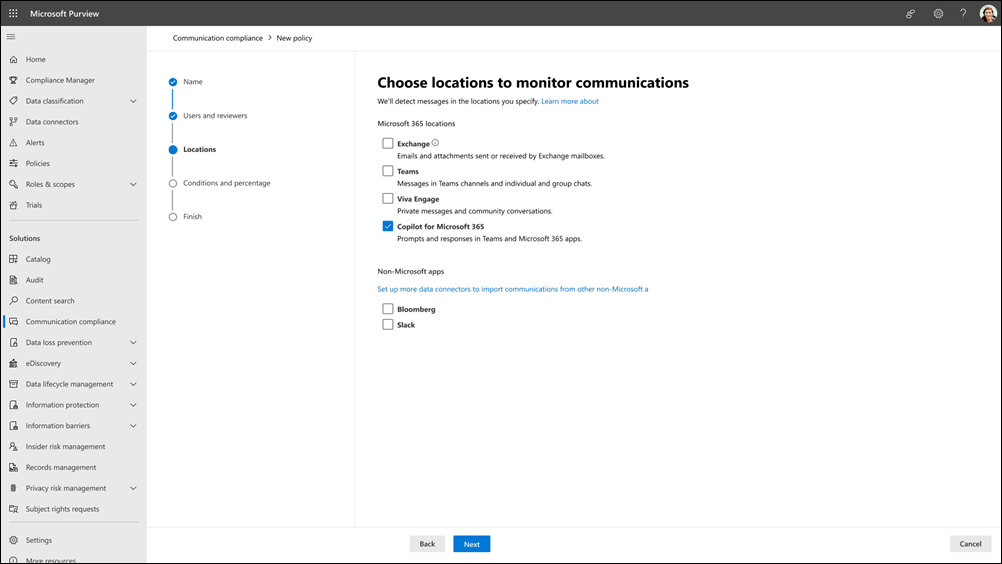
On the Choose locations to detect communications page, choose the communication channels to check, including Exchange, Teams, Viva Engage, or a specific generative AI channel. Supported generative AI channels include Microsoft Copilot experiences, Enterprise AI apps, and Other AI apps. You can also choose to check third-party sources if you've configured a connector in Microsoft 365. Select Next to move to the next page.
Note
Separate Teams, Copilot, and AI app locations are rolling out and may not yet be visible in your Purview tenant at this time.
On the Choose conditions and review percentage page:
- In the Communication direction section, choose the communication direction to detect, including inbound, outbound, or internal communications.
- In the Conditions section, add the conditions you want to detect. You can choose from many different conditions for messages and message attachments, including conditions that detect for:
- Default or custom sensitive information types. You can create sensitive info types before running the workflow or you can create them from the workflow.
- Default or custom keyword dictionaries.
- Trainable classifiers. Trainable classifiers can detect potentially inappropriate language and images sent or received in the body of email messages or other types of text. You can choose from the following built-in trainable classifiers: Targeted threat, Profanity, Targeted harassment, Adult images, Racy images, and Gory images. Communication compliance also includes content safety classifiers (preview) for Microsoft Teams that are based on large language models (LLMs). These classifiers include Hate, Sexual, Violence, and Self-harm. Learn more about content safety classifiers based on large language models.
- In the Optical character recognition (OCR) section, if you want to enable optical character recognition (OCR) to identify embedded or attached images in messages for printed or handwritten text that match policy conditions, select the Use OCR to extract text from images checkbox. One or more conditional settings associated with text, keywords, trainable classifiers, or sensitive info types must be configured in the policy to enable the selection of the checkbox.
- In the Review percentage section, move the slider if you want to change the amount of content to review.
- In the Filter email blasts section, the Filter out messages from email blasting services check box is selected by default. This setting causes messages sent from email blast services to be excluded. Messages that match specific conditions won't generate alerts. This includes bulk email (such as newsletters), spam, phishing, and malware. You can view a report containing the bulk email senders that are filtered out. The list of senders is filtered before the content is analyzed so there might be senders that don't match the content conditions (extra senders included in the report).
- Select Next to move to the next page.
On the Review and finish page, review your policy selections, and then select Create policy if everything looks OK.
Notes and tips on creating communication compliance policies
- After configuring a policy, learn about best practices for managing the volume of alerts.
- You can't use PowerShell to create and manage communication compliance policies. You must use the communication compliance solution.
- To see an in-depth walkthrough of setting up a new communication compliance policy and remediating an alert, check out this 15-minute video:
Test conditions (preview) when you create or edit a policy
If you create or edit a policy without testing conditions first, it might take a while before you can verify that the policy works as intended since you would typically need to create a pilot policy and test for several days before rolling the policy out to the wider organization. If you're a member of the Communication Compliance Admins role group or the Communication Compliance role group, you can save time by testing your conditions when you create or edit a policy, and fine-tune the conditions to make sure the policy works as intended before rolling it out to the wider organization.
Note
At this time, you can only test the following conditions:
- Content matches any of these classifiers
- Content contains any of these sensitive info types
Make sure you're a member of the Communication Compliance Admins role group or the Communication Compliance role group. You must be a member of one of these role groups to use this feature.
Create a policy or edit an existing policy.
On the Conditions and percentage page, after entering your conditions, select Test your conditions.

Tip
You can also access the Test your conditions command from the list of policies on the Policies page or in the policy details panel if you choose to edit the policy.
In the Test policy conditions pane that appears on the right side of the page, do one of the following actions:
- Select the Enter messages to test option, and then enter some messages that you expect would be detected by the policy. Separate messages with a comma.
- If you have a .txt file that includes a list of messages to detect, select Upload a file to test whether the trainable classifiers detects the matching elements you specified option, and then select Upload file to upload your text file.
Select Test to see a list of test results.
Tip
If you don't see the results you're looking for:
- Check the definition of the sensitive info type or the trainable classifier to make sure it's designed to detect the type of info you expect.
- Make sure that the message meets minimum word count requirements.
Step 6 (optional): Update compliance boundaries for communication compliance policies
Compliance boundaries create logical boundaries within an organization that control the user content locations (such as mailboxes, OneDrive accounts, and SharePoint sites) that eDiscovery managers can search.
If you've configured compliance boundaries in your organization, you must update the compliance boundaries to allow certain users access to mailboxes that support communication compliance policies. You need to allow access to communication compliance administrators and communication compliance reviewers for your policy management and investigation and remediation actions to work properly.
To allow access for communication compliance admins and reviewers, run the following PowerShell commands. You only need to run these commands once, even if you add new communication compliance policies in the future:
Import-Module ExchangeOnlineManagement
$UserCredential = Get-Credential
Connect-IPPSSession -Credential $UserCredential
New-ComplianceSecurityFilter -FilterName "CC_mailbox" -Users <list your communication compliance admins and reviewers user alias or email address> -Filters "Mailbox_Name -like 'SupervisoryReview{*'" -Action All
For more information about cmdlet syntax, see New-ComplianceSecurityFilter.
Step 7 (optional): Create notice templates and configure user anonymization
If you want to have the option of responding to a policy alert by sending a reminder notice to the associated user, you need to create at least one notice template in your organization. The notice template fields are editable before they're sent as part of the alert remediation process, and creating a customized notice template for each communication compliance policy is recommended.
You can also choose to enable anonymization for displayed usernames when investigating policy matches and taking action on messages.
Create templates and configure user anonymization
Select the appropriate tab for the portal you're using. Depending on your Microsoft 365 plan, the Microsoft Purview compliance portal is retired or will be retired soon.
To learn more about the Microsoft Purview portal, see Microsoft Purview portal. To learn more about the Compliance portal, see Microsoft Purview compliance portal.
Sign in to the Microsoft Purview portal using credentials for an admin account in your Microsoft 365 organization.
Go to the Communication Compliance solution.
Select Settings in the upper-right corner of the page, select Communication Compliance, select the Privacy tab, select Show anonymized versions of usernames, and then select Save.
Select the Notice templates tab, and then select Create notice template.
In the right pane that appears, complete the following fields:
- Template name (required)
- Send from (required)
- Cc and Bcc (optional)
- Subject (required)
- Message body (required)
Select Save to create and save the notice template.
Step 8 (optional): Test your communication compliance policy
After you create a communication compliance policy, it's a good idea to test it to make sure that the conditions you defined are being properly enforced by the policy. You may also want to test your Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies if your communication compliance policies include sensitive information types. Make sure you give your policies time to activate so that the communications you want to test are captured.
Tip
To save time, you can test the following conditions before creating your policy:
- Content matches any of these classifiers
- Content contains any of these sensitive information types
Learn more about testing conditions before creating a policy.
Follow these steps to test your communication compliance policy:
Open an email client, Microsoft Teams, or Viva Engage while signed in as a scoped user defined in the policy you want to test.
Send an email, Microsoft Teams chat, or Viva Engage message that meets the criteria you've defined in the communication compliance policy. This test can be a keyword, attachment size, domain, etc. Make sure you determine if your configured conditional settings in the policy are too restrictive or too lenient.
Note
Email messages can take approximately 24 hours to fully process in a policy. Communications in Microsoft Teams, Viva Engage, and third-party platforms can take approximately 48 hours to fully process in a policy.
Sign in to Microsoft 365 as a reviewer designated in the communication compliance policy. Navigate to Communication compliance > Alerts to view the alerts for your policies.
Remediate the alert using the remediation controls and verify that the alert is properly resolved.
Next steps
After you've completed these steps to create your first communication compliance policy, you'll start to receive alerts from activity indicators after 24-48 hours. Configure additional policies as needed using the guidance in Step 5 of this article.
To learn more about investigating communication compliance alerts, see Investigate and remediate communication compliance alerts.
To keep up with the latest communication compliance updates, select What's new in communication compliance for your organization.