The TDSP is an agile and iterative data science methodology that you can use to deliver predictive analytics solutions and AI applications efficiently. The TDSP enhances team collaboration and learning by recommending optimal ways for team roles to work together. The TDSP incorporates best practices and frameworks from Microsoft and other industry leaders to help your team effectively implement data science initiatives. The TDSP enables you to fully realize the benefits of your analytics program.
This article provides an overview of the TDSP and its main components. It presents guidance about how to implement the TDSP by using Microsoft tools and infrastructure. You can find more detailed resources throughout the article.
Key components of the TDSP
The TDSP has the following key components:
- Data science lifecycle definition
- Standardized project structure
- Infrastructure and resources that are ideal for data science projects
- Responsible AI: and a commitment to the advancement of AI, driven by ethical principles
Data science lifecycle
The TDSP provides a lifecycle that you can use to structure the development of your data science projects. The lifecycle outlines the full steps that successful projects follow.
You can combine the task-based TDSP with other data science lifecycles, such as cross-industry standard process for data mining (CRISP-DM), the knowledge discovery in databases (KDD) process, or another custom process. At a high level, these different methodologies have much in common.
Use this lifecycle if you have a data science project that's part of an intelligent application. Intelligent applications deploy machine learning or AI models for predictive analytics. You can also use this process for exploratory data science projects and improvised analytics projects.
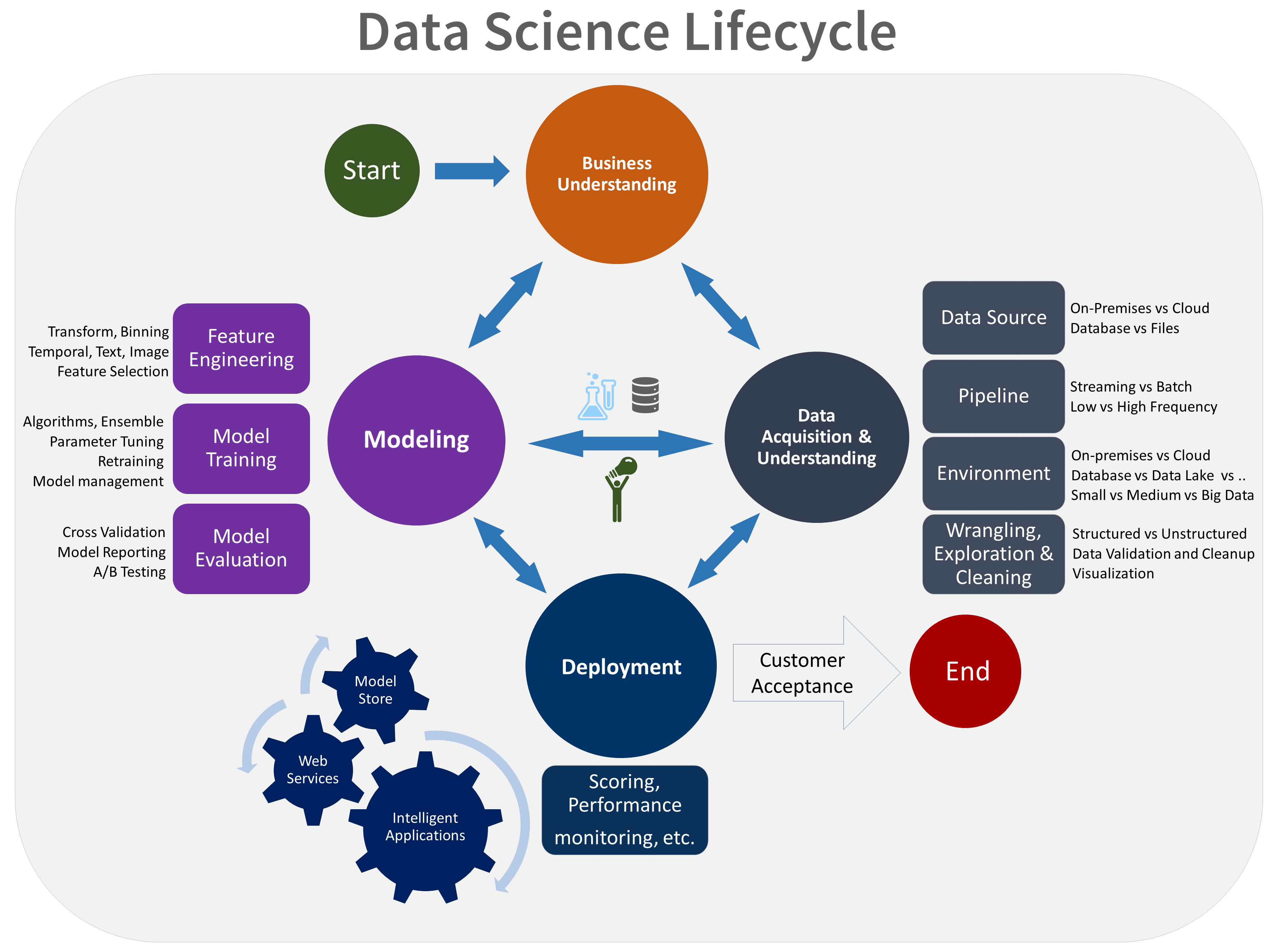
The TDSP lifecycle consists of five major stages that your team performs iteratively. These stages include:
Here's a visual representation of the TDSP lifecycle:
For more information about the goals, tasks, and documentation artifacts for each stage, see The TDSP lifecycle.
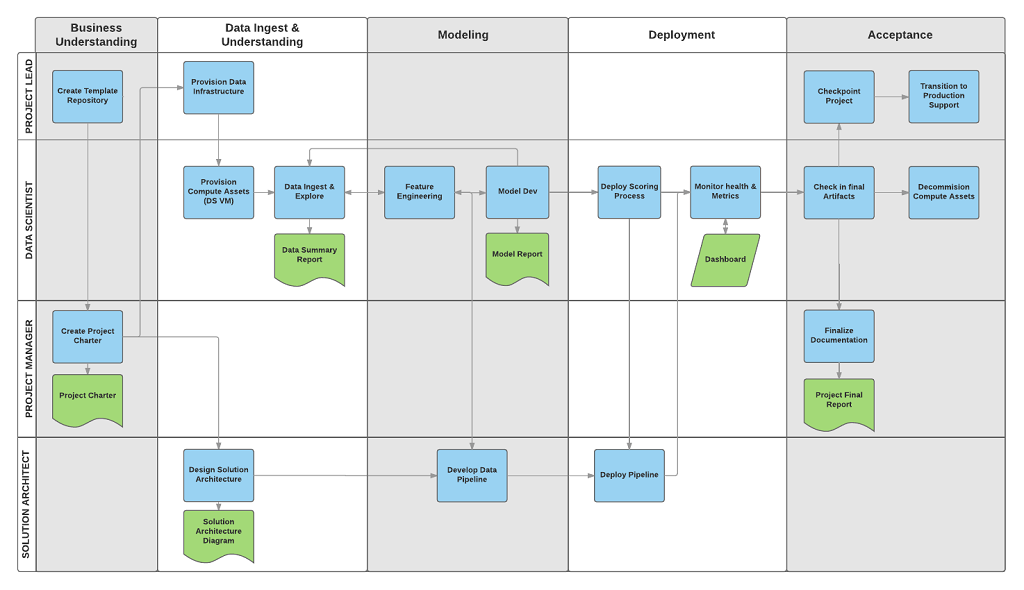
These tasks and artifacts align with project roles, such as:
- Solution architect
- Project manager
- Data engineer
- Data scientist
- Application developer
- Project lead
The following diagram shows the tasks (in blue) and artifacts (in green) that correspond to each stage of the lifecycle depicted on the horizontal axis and for the roles depicted on the vertical axis.
Standardized project structure
Your team can use the Azure infrastructure to organize your data science assets.
Azure Machine Learning supports the open-source MLflow. We recommend that you use MLflow for data science and AI project management. MLflow is designed to manage the complete machine learning lifecycle. It trains and serves models on different platforms, so that you can use a consistent set of tools regardless of where your experiments run. You can use MLflow locally on your computer, on a remote compute target, on a virtual machine, or on a machine learning compute instance.
MLflow consists of several key functionalities:
Track experiments: You can use MLflow to keep track of experiments, including parameters, code versions, metrics, and output files. This feature helps you compare different runs and efficiently manage the experimentation process.
Package code: It provides a standardized format for packaging machine learning code, which includes dependencies and configurations. This packaging makes it easier to reproduce runs and share code with others.
Manage models: MLflow provides functionalities to manage and version models. It supports various machine learning frameworks so that you can store, version, and serve models.
Serve and deploy models: MLflow integrates model serving and deployment capabilities so that you can easily deploy models in diverse environments.
Register models: You can manage the lifecycle of a model, which includes versioning, stage transitions, and annotations. You can use MLflow to maintain a centralized model store in a collaborative environment.
Use an API and UI: Inside Azure, MLflow is bundled within the Machine Learning API version 2, so you can interact with the system programmatically. You can use the Azure portal to interact with a UI.
MLflow simplifies and standardizes the process of machine learning development, from experimentation to deployment.
Machine Learning integrates with Git repositories, so that you can use Git-compatible services, such as GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Azure DevOps, or another Git-compatible service. In addition to the assets that are already tracked in Machine Learning, your team can develop their own taxonomy within their Git-compatible service to store other project data, such as:
- Documentation
- Project data: such as, the final project report
- Data report: such as, the data dictionary or data quality reports
- Model: such as, model reports
- Code
- Data preparation
- Model development
- Operationalization, which includes security and compliance
Infrastructure and resources
The TDSP provides recommendations for how to manage shared analytics and storage infrastructure in the following categories:
- Cloud file systems to store datasets
- Cloud databases
- Big data clusters that use SQL or Spark
- AI and machine learning services
Cloud file systems to store datasets
Cloud file systems are crucial to the TDSP for several reasons:
Centralized data storage: Cloud file systems provide a centralized location to store datasets, which is essential for collaboration among data science team members. Centralization ensures that all team members can access the most current data, and reduces the risk of working with outdated or inconsistent datasets.
Scalability: Cloud file systems can handle large volumes of data, which is common in data science projects. The file systems provide scalable storage solutions that grow with the needs of the project. They enable teams to store and process massive datasets without worrying about hardware limitations.
Accessibility: With cloud file systems, you can access data from anywhere with an internet connection. This access is important for distributed teams or when team members need to work remotely. Cloud file systems facilitate seamless collaboration and ensure that data is always accessible.
Security and compliance: Cloud providers often implement robust security measures, which include encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards and regulations. Strong security measures can protect sensitive data and help your team meet legal and regulatory requirements.
Version control: Cloud file systems often include version control features, that teams can use to track changes to datasets over time. Version control is crucial to maintain the integrity of the data and to reproduce the results in data science projects. It also helps you audit and troubleshoot any problems that arise.
Integration with tools: Cloud file systems can integrate seamlessly with various data science tools and platforms. Tool integration supports easier data ingestion, data processing, and data analysis. For example, Azure Storage integrates well with Machine Learning, Azure Databricks, and other data science tools.
Collaboration and sharing: Cloud file systems make it easy to share datasets with other team members or stakeholders. These systems support collaborative features such as shared folders and permissions management. Collaboration features facilitate teamwork and ensure that the right people have access to the data they need.
Cost efficiency: Cloud file systems can be more cost-effective than maintaining on-premises storage solutions. Cloud providers have flexible pricing models that include pay-as-you-go options, which can help manage costs based on the actual usage and storage requirements of your data science project.
Disaster recovery: Cloud file systems typically include features for data backup and disaster recovery. These features help safeguard data against hardware failures, accidental deletions, and other disasters. It provides peace of mind and supports continuity in data science operations.
Automation and workflow integration: Cloud storage systems can integrate into automated workflows, which enable seamless data transfer between different stages of the data science process. Automation can help improve efficiency and reduce the required manual effort to manage data.
Recommended Azure resources for cloud file systems
- Azure Blob Storage - Comprehensive documentation on Azure Blob Storage, which is a scalable object storage service for unstructured data.
- Azure Data Lake Storage - Information on Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2, designed for big data analytics and supports large-scale datasets.
- Azure Files - Details on Azure Files, which provides fully managed file shares in the cloud.
In summary, cloud file systems are crucial to the TDSP as they provide scalable, secure, and accessible storage solutions that support the entire data lifecycle. Cloud file systems enable seamless data integration from various sources, which supports comprehensive data acquisition and understanding. Data scientists can use cloud file systems to efficiently store, manage, and access large datasets. This functionality is essential for training and deploying machine learning models. These systems also enhance collaboration by enabling team members to share and work on data simultaneously in a unified environment. Cloud file systems provide robust security features that help protect data and make it compliant with regulatory requirements, which is vital for maintaining data integrity and trust.
Cloud databases
Cloud databases play a critical role in the TDSP for several reasons:
Scalability: Cloud databases provide scalable solutions that can easily grow to meet the increasing data needs of a project. Scalability is crucial for data science projects that frequently handle large and intricate datasets. Cloud databases can handle varying workloads without the need for manual intervention or hardware upgrades.
Performance optimization: Developers optimize cloud databases for performance by using capabilities such as automatic indexing, query optimization, and load balancing. These features help ensure that data retrieval and processing are fast and efficient, which is crucial for data science tasks that require real-time or near-real-time data access.
Accessibility and collaboration: Teams can access stored data in cloud databases from any location. This accessibility fosters collaboration among team members who might be geographically dispersed. Accessibility and collaboration are important for distributed teams or people who work remotely. Cloud databases support multi-user environments that enable simultaneous access and collaboration.
Integration with data science tools: Cloud databases seamlessly integrate with various data science tools and platforms. For example, Azure cloud databases integrate well with Machine Learning, Power BI, and other data analytics tools. This integration streamlines the data pipeline, from ingestion and storage to analysis and visualization.
Security and compliance: Cloud providers implement robust security measures that include data encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards and regulations. Security measures protect sensitive data and help your team meet legal and regulatory requirements. Security features are vital for maintaining data integrity and privacy.
Cost efficiency: Cloud databases often operate on a pay-as-you-go model, which can be more cost-effective than maintaining on-premises database systems. This pricing flexibility enables organizations to manage their budgets effectively and pay only for the storage and compute resources that they use.
Automatic backups and disaster recovery: Cloud databases provide automatic backup and disaster recovery solutions. These solutions help prevent data loss if there are hardware failures, accidental deletions, or other disasters. Reliability is crucial for maintaining data continuity and integrity in data science projects.
Real-time data processing: Many cloud databases support real-time data processing and analytics, which is essential for data science tasks that require the most current information. This capability helps data scientists make timely decisions based on the most recent available data.
Data integration: Cloud databases can easily integrate with other data sources, databases, data lakes, and external data feeds. Integration helps data scientists combine data from multiple sources and provides a comprehensive view and more sophisticated analysis.
Flexibility and variety: Cloud databases come in various forms, such as relational databases, NoSQL databases, and data warehouses. This variety lets data science teams choose the best type of database for their specific needs, whether they require structured data storage, unstructured data handling, or large-scale data analytics.
Support for advanced analytics: Cloud databases often come with built-in support for advanced analytics and machine learning. For example, Azure SQL Database provides built-in machine learning services. These services help data scientists perform advanced analytics directly within the database environment.
Recommended Azure resources for cloud databases
- Azure SQL Database - Documentation on Azure SQL Database, a fully managed relational database service.
- Azure Cosmos DB - Information on Azure Cosmos DB, a globally distributed, multi-model database service.
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Guide to Azure Database for PostgreSQL, a managed database service for app development and deployment.
- Azure Database for MySQL - Details on Azure Database for MySQL, a managed service for MySQL databases.
In summary, cloud databases are crucial for TDSP because they provide scalable, reliable, and efficient data storage and management solutions that support data-driven projects. They facilitate seamless data integration, which helps data scientists ingest, preprocess, and analyze large datasets from various sources. Cloud databases enable rapid querying and data processing, which is essential to develop, test, and deploy machine learning models. Also, cloud databases enhance collaboration by providing a centralized platform for team members to access and work with data simultaneously. Lastly, cloud databases provide advanced security features and compliance support to keep data protected and compliant with regulatory standards, which is critical for maintaining data integrity and trust.
Big data clusters that use SQL or Spark
Big data clusters, such as those that use SQL or Spark, are fundamental to the TDSP for several reasons:
Handling large volumes of data: Big data clusters are designed to handle large volumes of data efficiently. Data science projects often involve massive datasets that exceed the capacity of traditional databases. SQL-based big data clusters and Spark can manage and process this data at scale.
Distributed computing: Big data clusters use distributed computing to spread data and computational tasks across multiple nodes. The parallel processing capability significantly accelerates data processing and analysis tasks, which is essential to obtain timely insights in data science projects.
Scalability: Big data clusters provide high scalability, both horizontally by adding more nodes and vertically by increasing the power of existing nodes. Scalability helps ensure that the data infrastructure grows with the needs of the project by handling increasing data sizes and complexity.
Integration with data science tools: Big data clusters integrate well with various data science tools and platforms. For example, Spark integrates seamlessly with Hadoop, and SQL clusters work with various data analysis tools. Integration facilitates a smooth workflow from data ingestion to analysis and visualization.
Advanced analytics: Big data clusters support advanced analytics and machine learning. For example, Spark provides the following built-in libraries:
- Machine learning, MLlib
- Graph processing, GraphX
- Stream processing, Spark Streaming
These capabilities help data scientists perform complex analytics directly within the cluster.
Real-time data processing: Big data clusters, especially the ones that use Spark, support real-time data processing. This capability is crucial for projects that require up-to-the-minute data analysis and decision-making. Real-time processing helps in scenarios like fraud detection, real-time recommendations, and dynamic pricing.
Data transformation and extract, transform, load (ETL): Big data clusters are ideal for data transformation and ETL processes. They can efficiently handle complex data transformations, cleaning, and aggregation tasks, which are often necessary before data can be analyzed.
Cost efficiency: Big data clusters can be cost-effective, especially when you use cloud-based solutions like Azure Databricks and other cloud services. These services provide flexible pricing models that include pay-as-you-go, which can be more economical than maintaining on-premises big data infrastructure.
Fault tolerance: Big data clusters are designed with fault tolerance in mind. They replicate data across nodes to help ensure that the system remains operational even if some nodes fail. This reliability is critical for maintaining data integrity and availability in data science projects.
Data lake integration: Big data clusters often integrate seamlessly with data lakes, which enable data scientists to access and analyze diverse data sources in a unified manner. Integration fosters more comprehensive analyses by supporting a combination of structured and unstructured data.
SQL-based processing: For data scientists that are familiar with SQL, big data clusters that work with SQL queries, such as Spark SQL or SQL on Hadoop, provide a familiar interface to query and analyze big data. This ease of use can accelerate the analysis process and make it more accessible to a broader range of users.
Collaboration and sharing: Big data clusters support collaborative environments where multiple data scientists and analysts can work together on the same datasets. They provide features to share code, notebooks, and results that foster teamwork and knowledge sharing.
Security and compliance: Big data clusters provide robust security features, such as data encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards. The security features protect sensitive data and help your team meet regulatory requirements.
Recommended Azure resources for big data clusters
- Apache Spark in Machine Learning: Machine Learning integration with Azure Synapse Analytics provides easy access to distributed computation resources through the Apache Spark framework.
- Azure Synapse Analytics: Comprehensive documentation for Azure Synapse Analytics, which integrates big data and data warehousing.
In summary, big data clusters, whether SQL or Spark, are crucial for the TDSP, because they provide the computational power and scalability necessary to efficiently handle vast amounts of data. Big data clusters enable data scientists to perform complex queries and advanced analytics on large datasets that facilitate deep insights, and accurate model development. When you use distributed computing, these clusters enable rapid data processing and analysis, which accelerates the overall data science workflow. Big data clusters also support seamless integration with various data sources and tools, which enhances the ability to ingest, process, and analyze data from multiple environments. Big data clusters also promote collaboration and reproducibility by providing a unified platform where teams can effectively share resources, workflows, and results.
AI and machine learning services
AI and machine learning (ML) services are integral to the TDSP for several reasons:
Advanced analytics: AI and ML services enable advanced analytics. Data scientists can use advanced analytics to uncover complex patterns, make predictions, and generate insights that aren't possible with traditional analytical methods. These advanced capabilities are crucial for creating high-impact data science solutions.
Automation of repetitive tasks: AI and ML services can automate repetitive tasks, such as data cleaning, feature engineering, and model training. Automation saves time and helps data scientists focus on more strategic aspects of the project, which improves overall productivity.
Improved accuracy and performance: ML models can improve the accuracy and performance of predictions and analyses by learning from data. These models can continuously improve as they become exposed to more data, which leads to better decision-making and more reliable results.
Scalability: AI and ML services provided by cloud platforms, such as Machine Learning, are highly scalable. They can handle large volumes of data and complex computations, which help data science teams scale their solutions to meet growing demands without worrying about underlying infrastructure limitations.
Integration with other tools: AI and ML services integrate seamlessly with other tools and services within the Microsoft ecosystem, such as Azure Data Lake, Azure Databricks, and Power BI. Integration supports a streamlined workflow from data ingestion and processing to model deployment and visualization.
Model deployment and management: AI and ML services provide robust tools for deploying and managing machine learning models in production. Features such as version control, monitoring, and automated retraining help ensure that models remain accurate and effective over time. This approach simplifies the maintenance of ML solutions.
Real-time processing: AI and ML services support real-time data processing and decision-making. Real-time processing is essential for applications that require immediate insights and actions, such as fraud detection, dynamic pricing, and recommendation systems.
Customizability and flexibility: AI and ML services provide a range of customizable options, from prebuilt models and APIs to frameworks for building custom models from scratch. This flexibility helps data science teams tailor solutions to specific business needs and use cases.
Access to cutting-edge algorithms: AI and ML services provide data scientists with access to cutting-edge algorithms and technologies developed by leading researchers. Access ensures that the team can use the latest advancements in AI and ML for their projects.
Collaboration and sharing: AI and ML platforms support collaborative development environments, where multiple team members can work together on the same project, share code, and reproduce experiments. Collaboration enhances teamwork and helps ensure consistency in model development.
Cost efficiency: AI and ML services on the cloud can be more cost-effective than building and maintaining on-premises solutions. Cloud providers have flexible pricing models that include pay-as-you-go options, which can reduce costs and optimize resource usage.
Enhanced security and compliance: AI and ML services come with robust security features, which include data encryption, secure access controls, and compliance with industry standards and regulations. These features help protect your data and models and meet legal and regulatory requirements.
Pre-built models and APIs: Many AI and ML services provide prebuilt models and APIs for common tasks such as natural language processing, image recognition, and anomaly detection. The prebuilt solutions can accelerate development and deployment and help teams quickly integrate AI capabilities into their applications.
Experimentation and prototyping: AI and ML platforms provide environments for rapid experimentation and prototyping. Data scientists can quickly test different algorithms, parameters, and datasets to find the best solution. Experimentation and prototyping support an iterative approach to model development.
Recommended Azure resources for AI and ML services
Machine Learning is the main resource that we recommend for data science application and TDSP. Also, Azure provides AI services that have ready-to-use AI models for specific applications.
- Machine Learning: The main documentation page for Machine Learning that covers setup, model training, deployment, and so on.
- Azure AI services: Information on AI services that provide prebuilt AI models for vision, speech, language, and decision-making tasks.
In summary, AI and ML services are crucial for the TDSP, because they provide powerful tools and frameworks that streamline the development, training, and deployment of machine learning models. These services automate complex tasks such as algorithm selection and hyperparameter tuning, which greatly accelerates the model development process. These services also provide scalable infrastructure that help data scientists efficiently handle large datasets and computationally intensive tasks. AI and ML tools integrate seamlessly with other Azure services and enhance data ingestion, preprocessing, and model deployment. Integration helps ensure a smooth end-to-end workflow. Also, these services foster collaboration and reproducibility. Teams can share insights and effectively experiment with results and models while they maintain high standards of security and compliance.
Responsible AI
With AI or ML solutions, Microsoft promotes responsible AI tools within its AI and ML solutions. These tools support the Microsoft Responsible AI Standard. Your workload must still individually address AI-related harms.
Peer-reviewed citations
The TDSP is a well-established methodology that teams use across Microsoft engagements. The TDSP is documented and studied in peer-reviewed literature. The citations provide an opportunity to investigate the TDSP features and applications. For more information and a list of citations, see The TDSP lifecycle.