Notitie
Preview-functies zijn niet bedoeld voor productiegebruik en bieden mogelijk beperkte functionaliteit. Deze functies zijn beschikbaar voorafgaand aan een officiële release, zodat klanten vroeg toegang kunnen krijgen en feedback kunnen geven.
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is een allesomvattende benadering voor het beheren van de levenscyclus van applicaties, van het eerste concept tot en met de ontwikkeling, het testen, de implementatie en het voortdurende onderhoud. In de context van Power Platform zorgt het integreren van geautomatiseerde tests met Test Engine in uw ALM-proces ervoor dat applicaties in elke ontwikkelingsfase grondig worden getest, wat resulteert in releases van hogere kwaliteit.
Testautomatisering in ALM begrijpen
Testautomatisering speelt een cruciale rol in het ALM-proces door:
-
kwaliteit garanderen - Controleren of applicaties functioneren zoals verwacht vóór de implementatie
-
Risico's verminderen - Problemen vroegtijdig signaleren voordat ze de productieomgeving bereiken
-
Continue integratie mogelijk maken - Ondersteuning van geautomatiseerde buildverificatietests
-
Het faciliteren van gecontroleerde implementaties - Het toevoegen van kwaliteitspoorten aan releasepijplijnen
Met Power Apps Test Engine kunt u geautomatiseerd testen integreren in uw bestaande Power Platform ALM-workflows, ongeacht welke CI/CD-tools u gebruikt.
Levenscyclus van testautomatisering
De Test Engine ondersteunt een volledige testlevenscyclus die integreert met uw ALM-processen:
-
Ontwikkeling - Maak en voer lokaal tests uit tijdens de app-ontwikkeling
-
Bouwvalidatie - Voer tests uit als onderdeel van geautomatiseerde bouwverificatie
-
Release gates - gebruik testresultaten als kwaliteitspoorten voor gecontroleerde implementaties
-
productieverificatie - Valideer kritieke functionaliteit in productieomgevingen
Aan de slag met testautomatisering in ALM
Aan de slag met het integreren van Test Engine in uw ALM-processen:
-
Maak uw testplan - Ontwerp YAML-testplannen voor uw Power Platform oplossingen
-
Voer tests lokaal uit - Controleer of tests werken in uw ontwikkelomgeving
-
Authenticatie instellen - Configureer de juiste authenticatie voor uw lokale uitvoerings- en pijplijnomgevingen
-
Integreer met uw pijplijn - Verbind Test Engine met uw bestaande ALM-pijplijn
-
Implementeer kwaliteitspoorten - gebruik testresultaten om de promotie van oplossingen te controleren
Tip
Begin met kritische gebruikersreizen en breid uw geautomatiseerde testdekking geleidelijk uit naarmate u meer vertrouwd raakt met Test Engine.
Broncodeversie van Test Engine (optioneel)
Als u de broncodeversie van Test Engine gebruikt, hebt u ook het volgende nodig:
Integratieopties
Test Engine integreert naadloos met verschillende ALM-tools en -processen
U kunt een lokale editor zoals Visual Studio Code gebruiken om de YAML bestanden te bewerken en zo de Test Engine-tests te ontwerpen. Om de tests lokaal uit te voeren:
- Zorg ervoor dat u Microsoft Power Platform CLI hebt geïnstalleerd
- Als u broncodebeheerintegratie gebruikt, kloont u uw project naar uw lokale machine
- Gebruik de pac-testrun om uw test uit te voeren
- Bekijk de resultaten van de geslaagde/gezakte test
De Azure CLI is essentieel voor het verkrijgen van toegangstokens waarmee verbinding kan worden gemaakt Dataverse. Lokaal kunt u gebruik maken van:
az login --allow-no-subscriptions
U kunt Test Engine eenvoudig integreren met de ingebouwde pipelines van Power Platform voor een native, geïntegreerde ervaring:
U kunt de uitvoering van geautomatiseerde tests activeren wanneer u een aangepaste pijplijnhost gebruikt: ...
- Maak een Power Automate cloudflow die wordt geactiveerd op basis van pijplijngebeurtenissen
- Maak verbinding met uw CI/CD-systeem om de tests uit te voeren
- Testresultaten verwerken en de pijplijnstatus bijwerken
Het volgende diagram toont een voorbeeld van dit integratiepatroon:
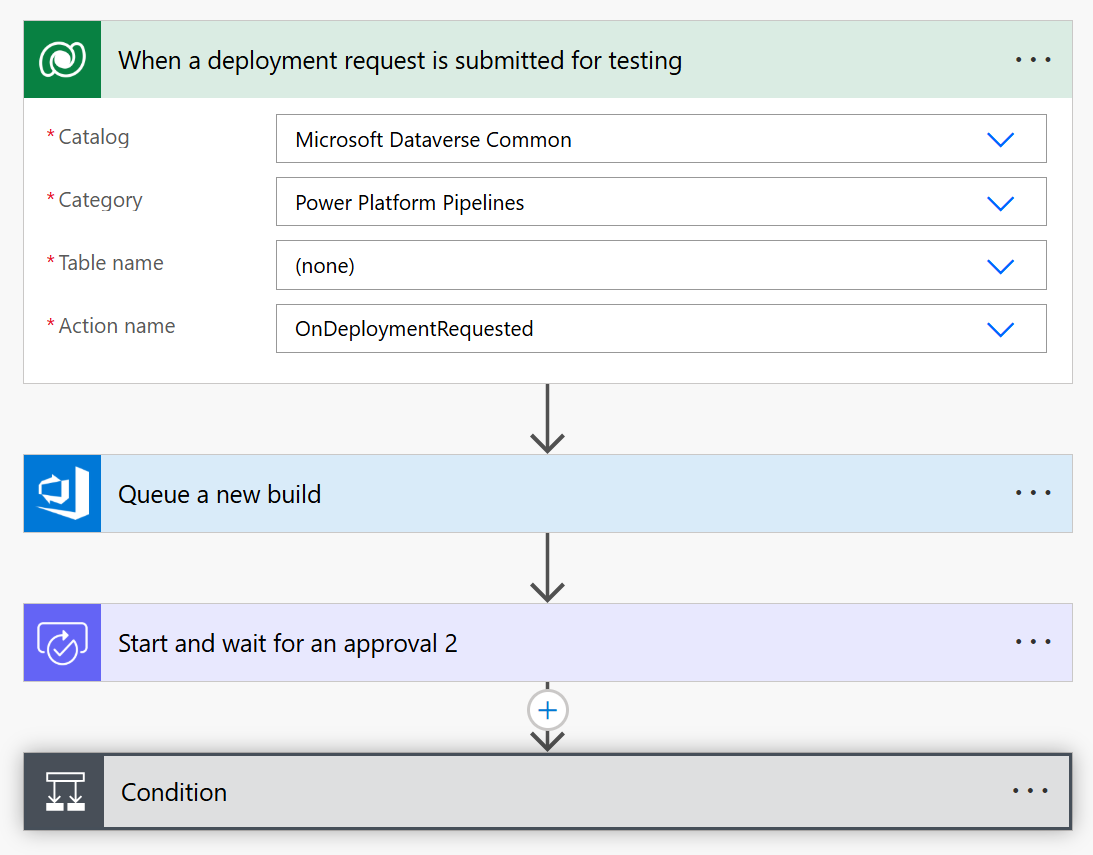
Deze stroom maakt gebruik van:
Aangepaste CI/CD-integratie met Power Automate
Voor organisaties met bestaande CI/CD-tools integreert Test Engine met aangepaste pijplijnen via de functie Power Automate Custom Host Power Platform . Met de Custom Host-aanpak kunt u:
- Definieer een aangepaste pijplijnhost die uw geautomatiseerde tests uitvoert
- Maak cloudstromen die automatisch worden geactiveerd door implementatiegebeurtenissen Power Automate
- Voer opdrachten rechtstreeks uit vanuit cloudstromen om tests uit te voeren die zijn opgeslagen in broncodebeheer
pac test run
- Maak verbinding met uw favoriete CI/CD-systeem (Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, enz.)
- Implementeer goedkeuringsworkflows op basis van testresultaten
- Implementatiestatus bijwerken op basis van de testresultaten
Dankzij deze integratie kunt u uw bestaande CI/CD-investeringen behouden en tegelijkertijd de mogelijkheden van Test Engine toevoegen aan uw ALM-proces. De Custom Host fungeert als een brug tussen de native ALM-functies van Power Platform en uw externe testinfrastructuur.
U kunt uw Power Platform Pipeline uitbreiden met aangepaste host of de pac test run opdracht rechtstreeks integreren in om uw buildscripts uit te voeren.
Hier is een voorbeeld van een Azure DevOps pipeline YAML-bestand dat laat zien hoe u Power Apps Test Engine-tests instelt en uitvoert:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
variables:
- group: PowerPlatformTestVariables # Create a variable group with these variables
# Required variables in the variable group:
# ClientId - Service Principal App ID
# ClientSecret - Service Principal Secret (mark as secret)
# TenantId - Microsoft Entra Tenant ID
# EnvironmentUrl - Power Platform Environment URL
# EnvironmentId - Power Platform Environment ID
steps:
# Download the test plan file from secure files
- task: DownloadSecureFile@1
name: testPlan
displayName: 'Download Test Plan File'
inputs:
secureFile: 'testplan.te.yaml' # Upload your test plan to Secure Files in Azure DevOps
# Install Power Platform CLI
- task: PowerShell@2
displayName: 'Install Power Platform CLI'
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
Write-Host "Installing Power Platform CLI..."
$pacUrl = "https://aka.ms/PowerAppsCLI"
$pacZip = "$env:TEMP\pac.zip"
$pacDestination = "$env:TEMP\pac"
# Create the destination folder if it doesn't exist
if (-not (Test-Path $pacDestination)) {
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $pacDestination -Force | Out-Null
}
# Download PAC CLI
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $pacUrl -OutFile $pacZip
# Extract PAC CLI
Expand-Archive -Path $pacZip -DestinationPath $pacDestination -Force
# Add PAC CLI to PATH
$env:PATH = "$pacDestination;$env:PATH"
# Verify installation
pac help
# Install Azure CLI and authenticate with service principal
- task: PowerShell@2
displayName: 'Install Azure CLI and Authenticate'
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
Write-Host "Installing Azure CLI..."
$azureCliUrl = "https://aka.ms/installazurecliwindows"
$azureCliInstaller = "$env:TEMP\AzureCLI.msi"
# Download Azure CLI installer
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $azureCliUrl -OutFile $azureCliInstaller
# Install Azure CLI silently
Start-Process -FilePath msiexec.exe -Args "/i $azureCliInstaller /quiet /norestart" -Wait
# Reload PATH to include Azure CLI
$env:PATH = [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "Machine") + ";" + [System.Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "User")
# Authenticate with service principal
Write-Host "Authenticating with Azure CLI..."
az login --service-principal -u "$(ClientId)" -p "$(ClientSecret)" --tenant "$(TenantId)" --allow-no-subscriptions
# Authenticate PAC CLI with service principal
- task: PowerShell@2
displayName: 'Authenticate PAC CLI'
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
Write-Host "Authenticating PAC CLI..."
# Create authentication profile
pac auth create --name TestEngineAuth --url "$(EnvironmentUrl)" --applicationId "$(ClientId)" --clientSecret "$(ClientSecret)" --tenant "$(TenantId)"
# Select the authentication profile
pac auth select --name TestEngineAuth
# Run the tests
- task: PowerShell@2
displayName: 'Execute Test Engine Tests'
inputs:
targetType: 'inline'
script: |
Write-Host "Running Test Engine tests..."
# Create output directory
$outputDir = "$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\TestResults"
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $outputDir -Force | Out-Null
# Run the tests
pac test run `
--test-plan-file "$(testPlan.secureFilePath)" `
--environment-id "$(EnvironmentId)" `
--tenant "$(TenantId)" `
--logConsole info `
--trx `
--outputDirectory $outputDir
if ($LASTEXITCODE -ne 0) {
Write-Error "Test execution failed with exit code $LASTEXITCODE"
exit $LASTEXITCODE
}
# Publish test results
- task: PublishTestResults@2
displayName: 'Publish Test Results'
inputs:
testResultsFormat: 'VSTest'
testResultsFiles: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\TestResults\*.trx'
mergeTestResults: true
testRunTitle: 'Power Apps Test Engine Results'
condition: always() # Ensure results are published even if tests fail
# Publish test artifacts
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
displayName: 'Publish Test Artifacts'
inputs:
PathtoPublish: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)\TestResults'
ArtifactName: 'TestArtifacts'
publishLocation: 'Container'
condition: always()
Referentiecomponenten
De volgende referentieonderdelen kunnen nuttig zijn bij het bouwen van uw automatiseringstestpijplijn.
Hier is een voorbeeld van een GitHub Actions-workflow die hetzelfde testuitvoeringsproces uitvoert:
name: Test Engine Execution
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
workflow_dispatch: # Allow manual triggering
jobs:
test:
runs-on: windows-latest
env:
TENANT_ID: ${{ secrets.TENANT_ID }}
CLIENT_ID: ${{ secrets.CLIENT_ID }}
CLIENT_SECRET: ${{ secrets.CLIENT_SECRET }}
ENVIRONMENT_URL: ${{ secrets.ENVIRONMENT_URL }}
ENVIRONMENT_ID: ${{ secrets.ENVIRONMENT_ID }}
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Power Platform CLI
run: |
Write-Host "Installing Power Platform CLI..."
$pacUrl = "https://aka.ms/PowerAppsCLI"
$pacZip = "$env:TEMP\pac.zip"
$pacDestination = "$env:TEMP\pac"
# Create the destination folder if it doesn't exist
if (-not (Test-Path $pacDestination)) {
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $pacDestination -Force | Out-Null
}
# Download PAC CLI
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $pacUrl -OutFile $pacZip
# Extract PAC CLI
Expand-Archive -Path $pacZip -DestinationPath $pacDestination -Force
# Add PAC CLI to PATH
$env:PATH = "$pacDestination;$env:PATH"
echo "$pacDestination" >> $env:GITHUB_PATH
# Verify installation
pac help
- name: Install Azure CLI
run: |
Write-Host "Installing Azure CLI..."
$ProgressPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://aka.ms/installazurecliwindows -OutFile .\AzureCLI.msi
Start-Process msiexec.exe -Wait -ArgumentList '/I AzureCLI.msi /quiet'
rm .\AzureCLI.msi
- name: Azure CLI Authentication
run: |
Write-Host "Authenticating with Azure CLI..."
az login --service-principal -u "$env:CLIENT_ID" -p "$env:CLIENT_SECRET" --tenant "$env:TENANT_ID" --allow-no-subscriptions
- name: PAC CLI Authentication
run: |
Write-Host "Authenticating PAC CLI..."
# Create authentication profile
pac auth create --name TestEngineAuth --url "$env:ENVIRONMENT_URL" --applicationId "$env:CLIENT_ID" --clientSecret "$env:CLIENT_SECRET" --tenant "$env:TENANT_ID"
# Select the authentication profile
pac auth select --name TestEngineAuth
- name: Run Test Engine tests
run: |
Write-Host "Running Test Engine tests..."
# Create output directory
$outputDir = "./TestResults"
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $outputDir -Force | Out-Null
# Run the tests
pac test run `
--test-plan-file "./TestPlan/testplan.te.yaml" `
--environment-id "$env:ENVIRONMENT_ID" `
--tenant "$env:TENANT_ID" `
--logConsole info `
--trx `
--outputDirectory $outputDir
if ($LASTEXITCODE -ne 0) {
Write-Error "Test execution failed with exit code $LASTEXITCODE"
exit $LASTEXITCODE
}
- name: Upload test results
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
if: always()
with:
name: test-results
path: ./TestResults
- name: Publish Test Results
uses: EnricoMi/publish-unit-test-result-action@v2
if: always()
with:
files: ./TestResults/**/*.trx
Verwante artikelen
Leer meer over de syntaxis van Test Engine YAML
Authenticatie instellen voor uw tests
Testcanvas-toepassingen, modelgestuurde toepassingen of Dataverse extensies
Begrijp Power Platform ALM
