การฝึกอบรม
โมดูล
Implement Windows Server File Server high availability - Training
Implement Windows Server File Server high availability
เบราว์เซอร์นี้ไม่ได้รับการสนับสนุนอีกต่อไป
อัปเกรดเป็น Microsoft Edge เพื่อใช้ประโยชน์จากคุณลักษณะล่าสุด เช่น การอัปเดตความปลอดภัยและการสนับสนุนด้านเทคนิค
Block cloning instructs the file system to copy a range of file bytes on behalf of an application, where the destination file may be the same as, or different from, the source file. Traditional copy operations, unfortunately, are expensive since they trigger expensive read and writes to the underlying physical data.
Block cloning in ReFS, however, performs copies as a low-cost metadata operation rather than reading from and writing to file data. Because ReFS enables multiple files to share the same logical clusters (physical locations on a volume), copy operations only need to remap a region of a file to a separate physical location, converting an expensive, physical operation to a quick, logical one. This allows copies to complete faster and generate less I/O to the underlying storage. This improvement also benefits virtualization workloads, as .vhdx checkpoint merge operations are dramatically accelerated when using block clone operations. Additionally, because multiple files can share the same logical clusters, identical data isn't physically stored multiple times, improving storage capacity.
Block cloning on ReFS converts a file data operation into a metadata operation. In order to make this optimization, ReFS introduces reference counts into its metadata for copied regions. This reference count records the number of distinct file regions that reference the same physical regions. This allows multiple files to share the same physical data:
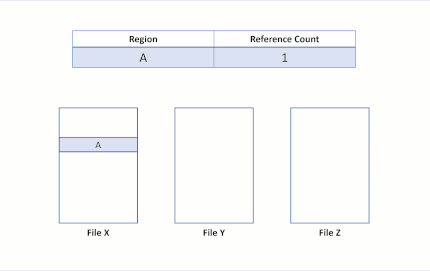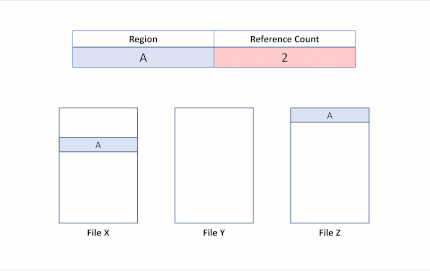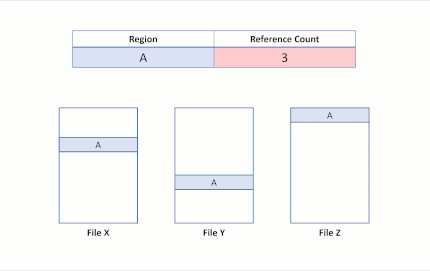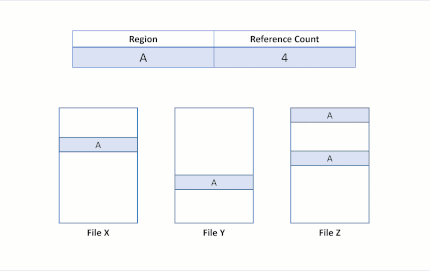
By keeping a reference count for each logical cluster, ReFS doesn't break the isolation between files: writes to shared regions trigger an allocate-on-write mechanism, where ReFS allocates a new region for the incoming write. This mechanism preserves the integrity of the shared logical clusters.
Suppose there are two files, X and Y, where each file is composed of three regions, and each region maps to separate logical clusters.
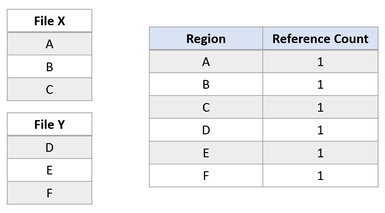
Now suppose an application issues a block clone operation from File X to File Y, for regions A and B to be copied at the offset of region E. The following file system state would result:
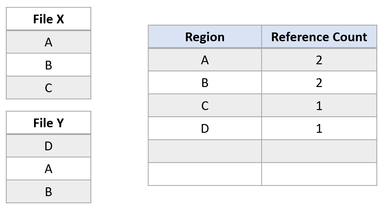
This file system state reveals a successful duplication of the block cloned region. Because ReFS performs this copy operation by only updating VCN to LCN mappings, no physical data was read, nor was the physical data in File Y overwritten. File X and Y now share logical clusters, reflected by the reference counts in the table. Because no data was physically copied, ReFS reduces capacity consumption on the volume.
Now suppose the application attempts to overwrite region A in File X. ReFS duplicates the shared region, update the reference counts appropriately, and perform the incoming write to the newly duplicated region. This ensures that isolation between the files is preserved.
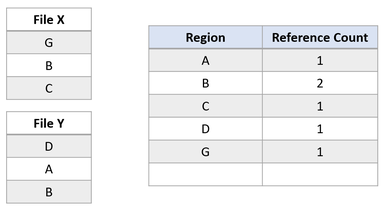
After the modifying write, region B is still shared by both files. If region A was larger than a cluster, only the modified cluster would have been duplicated, and the remaining portion would have remained shared.
การฝึกอบรม
โมดูล
Implement Windows Server File Server high availability - Training
Implement Windows Server File Server high availability