Design integrated posture management and workload protection
This unit will provide an overview of the capabilities of Microsoft Defender for cloud, which provides extensive capabilities for integrating posture management and workload protection.
What is Microsoft Defender for Cloud?
Microsoft Defender for Cloud is a cloud-native application protection platform (CNAPP) with a set of security measures and practices designed to protect cloud-based applications from various cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Defender for Cloud combines the capabilities of:
- A development security operations (DevSecOps) solution that unifies security management at the code level across multicloud and multiple-pipeline environments
- A cloud security posture management (CSPM) solution that surfaces actions that you can take to prevent breaches
- A cloud workload protection platform (CWPP) with specific protections for servers, containers, storage, databases, and other workloads
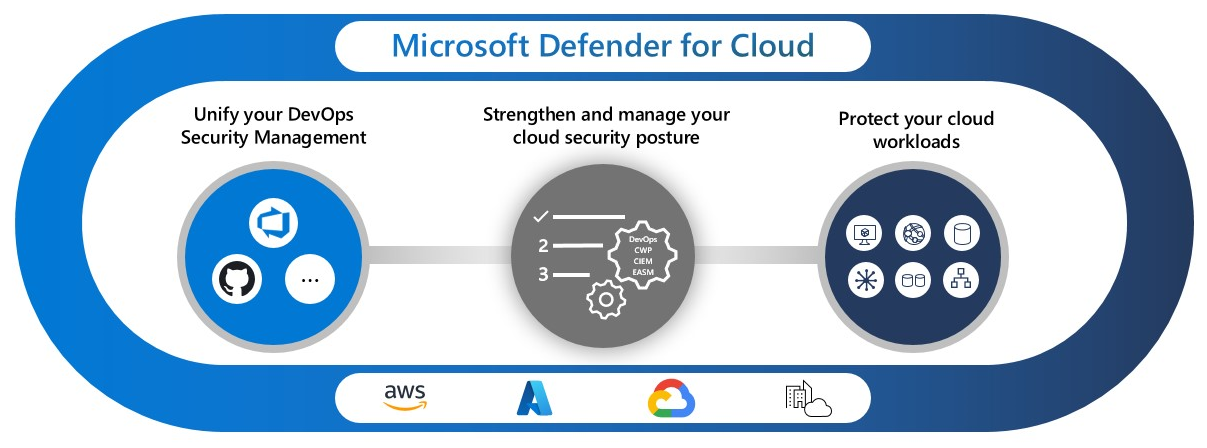
Secure cloud applications
Defender for Cloud helps you to incorporate good security practices early during the software development process, or DevSecOps. You can protect your code management environments and your code pipelines, and get insights into your development environment security posture from a single location. Defender for Cloud currently includes Defender for DevOps.
Today’s applications require security awareness at the code, infrastructure, and runtime levels to make sure that deployed applications are hardened against attacks.
| Capability | What problem does it solve? | Get started | Defender plan and pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code pipeline insights | Empowers security teams with the ability to protect applications and resources from code to cloud across multi-pipeline environments, including GitHub and Azure DevOps. Findings from Defender for DevOps, such as IaC misconfigurations and exposed secrets, can then be correlated with other contextual cloud security insights to prioritize remediation in code. | Connect Azure DevOps and GitHub repositories to Defender for Cloud | Defender for DevOps |
Improve your security posture
The security of your cloud and on-premises resources depends on proper configuration and deployment. Defender for Cloud recommendations identify the steps that you can take to secure your environment.
Defender for Cloud includes Foundational CSPM (Free) capabilities for free. You can also enable advanced CSPM capabilities by enabling paid Defender plans.
| Capability | What problem does it solve? | Get started | Defender plan and pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Centralized policy management | Define the security conditions that you want to maintain across your environment. The policy translates to recommendations that identify resource configurations that violate your security policy. The Microsoft cloud security benchmark is a built-in standard that applies security principles with detailed technical implementation guidance for Azure, for other cloud providers (such as AWS and GCP), and for other Microsoft clouds. | Customize security a policy | Foundational CSPM (Free) |
| Secure score | Summarize your security posture based on the security recommendations. As you remediate recommendations, your secure score improves. | Track your secure score | Foundational CSPM (Free) |
| Multicloud coverage | Connect to your multicloud environments with agentless methods for CSPM insight and CWP protection. | Connect your Amazon AWS and Google GCP cloud resources to Defender for Cloud | Foundational CSPM (Free) |
| Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) | Use the dashboard to see weaknesses in your security posture. | Enable CSPM tools | Foundational CSPM (Free) |
| Advanced Cloud Security Posture Management | Get advanced tools to identify weaknesses in your security posture, including: - Governance to drive actions to improve your security posture - Regulatory compliance to verify compliance with security standards - Cloud security explorer to build a comprehensive view of your environment |
Enable CSPM tools | Defender CSPM |
| Attack path analysis | Model traffic on your network to identify potential risks before you implement changes to your environment. | Build queries to analyze paths | Defender CSPM |
| Cloud Security Explorer | A map of your cloud environment that lets you build queries to find security risks. | Build queries to find security risks | Defender CSPM |
| Security governance | Drive security improvements through your organization by assigning tasks to resource owners and tracking progress in aligning your security state with your security policy. | Define governance rules | Defender CSPM |
| Microsoft Entra Permissions Management | Provide comprehensive visibility and control over permissions for any identity and any resource in Azure, AWS, and GCP. | Review your Permission Creep Index (CPI) | Defender CSPM |
Protect cloud workloads
Proactive security principles require that you implement security practices that protect your workloads from threats. Cloud workload protections (CWP) surface workload-specific recommendations that lead you to the right security controls to protect your workloads.
When your environment is threatened, security alerts right away indicate the nature and severity of the threat so you can plan your response. After you identify a threat in your environment, you need to quickly respond to limit the risk to your resources.
| Capability | What problem does it solve? | Get started | Defender plan and pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protect cloud servers | Provide server protections through Microsoft Defender for Endpoint or extended protection with just-in-time network access, file integrity monitoring, vulnerability assessment, and more. | Secure your multicloud and on-premises servers | Defender for Servers |
| Identify threats to your storage resources | Detect unusual and potentially harmful attempts to access or exploit your storage accounts using advanced threat detection capabilities and Microsoft Threat Intelligence data to provide contextual security alerts. | Protect your cloud storage resources | Defender for Storage |
| Protect cloud databases | Protect your entire database estate with attack detection and threat response for the most popular database types in Azure to protect the database engines and data types, according to their attack surface and security risks. | Deploy specialized protections for cloud and on-premises databases | - Defender for Azure SQL Databases - Defender for SQL servers on machines - Defender for Open-source relational databases - Defender for Azure Cosmos DB |
| Protect containers | Secure your containers so you can improve, monitor, and maintain the security of your clusters, containers, and their applications with environment hardening, vulnerability assessments, and run-time protection. | Find security risks in your containers | Defender for Containers |
| Infrastructure service insights | Diagnose weaknesses in your application infrastructure that can leave your environment susceptible to attack. | - Identify attacks targeting applications running over App Service - Detect attempts to exploit Key Vault accounts - Get alerted on suspicious Resource Manager operations - Expose anomalous DNS activities |
- Defender for App Service - Defender for Key Vault - Defender for Resource Manager - Defender for DNS |
| Security alerts | Get informed of real-time events that threaten the security of your environment. Alerts are categorized and assigned severity levels to indicate proper responses. | Manage security alerts | Any workload protection Defender plan |
| Security incidents | Correlate alerts to identify attack patterns and integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), Security Orchestration Automated Response (SOAR), and IT Service Management (ITSM) solutions to respond to threats and limit the risk to your resources. | Export alerts to SIEM, SOAR, or ITSM systems | Any workload protection Defender plan |
Defender for Cloud planning and operations
The key areas to consider when planning to use Defender for Cloud are:
- Security Roles and Access Controls
- Security Policies and Recommendations
- Data Collection and Storage
- Onboarding non-Azure resources
- Ongoing Security Monitoring
- Incident Response
Security Roles and Access Controls
Defender for Cloud uses Azure role-based access control (Azure Role-based access control), which provides built-in roles that can be assigned to users, groups, and services in Azure. When a user opens Defender for Cloud, they only see information related to resources they have access to. Which means the user is assigned the role of Owner, Contributor, or Reader to the subscription or resource group that a resource belongs to. In addition to these roles, there are two roles specific to Defender for Cloud:
Security reader: a user that belongs to this role is able to view only Defender for Cloud configurations, which include recommendations, alerts, policy, and health, but it won't be able to make changes.
Security admin: same as security reader but it can also update the security policy, dismiss recommendations and alerts.
When planning access control using Azure Role-based access control for Defender for Cloud, make sure you understand who in your organization needs access to Defender for Cloud the tasks they'll perform. Then you can configure Azure Role-based access control properly.
Security Policies and Recommendations
Defender for Cloud automatically creates a default security policy for each of your Azure subscriptions. You can edit the policy in Defender for Cloud or use Azure Policy to create new definitions, define more policies, and assign policies across management groups. Management groups can represent the entire organization or a business unit within the organization. You can monitor policy compliance across these management groups.
Before configuring security policies, review each of the security recommendations:
- See if these policies are appropriate for your various subscriptions and resource groups.
- Understand what actions address the security recommendations.
- Determine who in your organization is responsible for monitoring and remediating new recommendations.
Data Collection and Storage
Defender for Cloud uses the Log Analytics agent and the Azure Monitor Agent to collect security data from your virtual machines. Data collected from this agent is stored in your Log Analytics workspaces.
Agent
When automatic provisioning is enabled in the security policy, the data collection agent is installed on all supported Azure VMs and any new supported VMs that are created. If the VM or computer already has the Log Analytics agent installed, Defender for Cloud uses the current installed agent. The agent's process is designed to be non-invasive and have minimal effect on VM performance.
If at some point you want to disable Data Collection, you can turn it off in the security policy. However, because the Log Analytics agent may be used by other Azure management and monitoring services, the agent won't be uninstalled automatically when you turn off data collection in Defender for Cloud. You can manually uninstall the agent if needed.
Workspace
A workspace is an Azure resource that serves as a container for data. You or other members of your organization might use multiple workspaces to manage different sets of data that is collected from all or portions of your IT infrastructure.
Data collected from the Log Analytics agent can be stored in an existing Log Analytics workspace associated with your Azure subscription or a new workspace.
In the Azure portal, you can browse to see a list of your Log Analytics workspaces, including any created by Defender for Cloud. A related resource group is created for new workspaces. Resources are created according to this naming convention:
- Workspace: DefaultWorkspace-[subscription-ID]-[geo]
- Resource Group: DefaultResourceGroup-[geo]
For workspaces created by Defender for Cloud, data is retained for 30 days. For existing workspaces, retention is based on the workspace pricing tier. If you want, you can also use an existing workspace.
If your agent reports to a workspace other than the default workspace, any Defender for Cloud Defender plans that you've enabled on the subscription should also be enabled on the workspace.
Onboarding non-Azure resources
Defender for Cloud can monitor the security posture of your non-Azure computers but you need to first onboard these resources. Read Onboard non-Azure computers for more information on how to onboard non-Azure resources. VMs can be onboarded using Azure Arc, or the Azure portal.
Ongoing Security Monitoring
After initial configuration and application of Defender for Cloud recommendations, the next step is considering Defender for Cloud operational processes.
The Defender for Cloud Overview provides a unified view of security across all your Azure resources and any non-Azure resources you've connected.
When you first opt in to use Defender for Cloud for your current Azure environment, make sure that you review all recommendations, which can be done in the Recommendations page.
Plan to visit the threat intelligence option as part of your daily security operations. There you can identify security threats against the environment, such as identify if a particular computer is part of a botnet.
Monitoring for new or changed resources
Most Azure environments are dynamic, with resources regularly being created, spun up or down, reconfigured, and changed. Defender for Cloud helps ensure that you have visibility into the security state of these new resources.
When you add new resources (VMs, SQL DBs) to your Azure environment, Defender for Cloud automatically discovers these resources and begins to monitor their security, including PaaS web roles and worker roles. If Data Collection is enabled in the Security Policy, more monitoring capabilities are enabled automatically for your virtual machines.
You should also regularly monitor existing resources for configuration changes that could have created security risks, drift from recommended baselines, and security alerts.
Hardening access and applications
As part of your security operations, you should also adopt preventative measures to restrict access to VMs, and control the applications that are running on VMs. By locking down inbound traffic to your Azure VMs, you're reducing the exposure to attacks, and at the same time providing easy access to connect to VMs when needed. Use just-in-time VM access feature to hardening access to your VMs.
You can use adaptive application controls to limit which applications can run on your VMs located in Azure. Among other benefits, adaptive application controls help harden your VMs against malware. With the help of machine learning, Defender for Cloud analyzes processes running in the VM to help you create allowlist rules.
Incident Response
Defender for Cloud detects and alerts you to threats as they occur. Organizations should monitor for new security alerts and take action as needed to investigate further or remediate the attack.
Although we can't create your Incident Response plan, we'll use Microsoft Azure Security Response in the Cloud lifecycle as the foundation for incident response stages. The stages of incident response in the cloud lifecycle are:
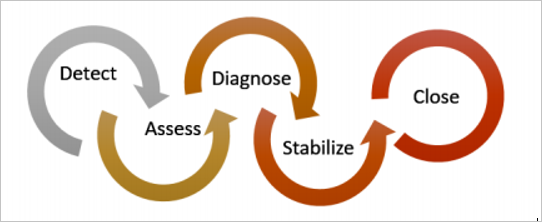
You can use Defender for Cloud alerts during the following stages:
- Detect: identify a suspicious activity in one or more resources.
- Assess: perform the initial assessment to obtain more information about the suspicious activity.
- Diagnose: use the remediation steps to conduct the technical procedure to address the issue.
Each Security Alert provides information that can be used to better understand the nature of the attack and suggest possible mitigations. Some alerts also provide links to either more information or to other sources of information within Azure. You can use the information provided for further research and to begin mitigation, and you can also search security-related data that is stored in your workspace.
Once you identify the compromised system, you can run a workflow automation that was previously created. Workflow automations are a collection of procedures that can be executed from Defender for Cloud once triggered by an alert.