Remarque
L’accès à cette page nécessite une autorisation. Vous pouvez essayer de vous connecter ou de modifier des répertoires.
L’accès à cette page nécessite une autorisation. Vous pouvez essayer de modifier des répertoires.
Lorsqu’un visuel a une hiérarchie, vous pouvez autoriser les utilisateurs à utiliser la fonctionnalité d’exploration Power BI pour afficher plus de détails.
Pour en savoir plus sur la fonction d'exploration de Power BI, consultez la page Mode Exploration dans le service Power BI. Pour permettre au visuel d’activer ou de désactiver la fonctionnalité d’extraction de manière dynamique, consultez Contrôle d’exploration dynamique.
Activer la prise en charge de l’exploration dans le visuel
Pour prendre en charge les actions d'exploration dans votre visuel, ajoutez un nouveau champ capabilities.jsonnommédrill-down. Ce champ possède une propriété appelée roles qui contient le nom du dataRole sur lequel vous souhaitez activer les actions de recherche.
"drilldown": {
"roles": [
"category"
]
}
Remarque
Le dataRole d’exploration doit être de type Grouping.
La propriété max des conditions de dataRole doit avoir la valeur 1.
Une fois que vous avez ajouté le rôle au champ d’exploration des détails, les utilisateurs peuvent faire glisser plusieurs champs dans le rôle de données.
Par exemple :
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Category",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"drilldown": {
"roles": [
"category"
]
},
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": {
"in": "category"
}
},
"values": {
"select": [
{
"bind": {
"to": "value"
}
}
]
}
}
}
]
}
Créer un visuel avec prise en charge de l’exploration
Pour créer un visuel avec prise en charge de l’exploration, exécutez la commande suivante :
pbiviz new testDrillDown -t default
Pour créer un exemple de visuel par défaut, appliquez l’exemple de ci-dessus de capabilities.json au visuel nouvellement créé.
Créez la propriété pour le conteneur div qui contiendra les éléments HTML du visuel :
"use strict";
import "core-js/stable";
import "./../style/visual.less";
// imports
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// visual properties
// ...
private div: HTMLDivElement; // <== NEW PROPERTY
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
// ...
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// update method body
// ...
}
/**
* Returns properties pane formatting model content hierarchies, properties and latest formatting values, Then populate properties pane.
* This method is called once each time we open the properties pane or when the user edits any format property.
*/
public getFormattingModel(): powerbi.visuals.FormattingModel {
return this.formattingSettingsService.buildFormattingModel(this.formattingSettings);
}
}
Mettez à jour le constructeur du visuel :
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// visual properties
// ...
private div: HTMLDivElement;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.updateCount = 0;
if (document) {
const new_p: HTMLElement = document.createElement("p");
new_p.appendChild(document.createTextNode("Update count:"));
const new_em: HTMLElement = document.createElement("em");
this.textNode = document.createTextNode(this.updateCount.toString());
new_em.appendChild(this.textNode);
new_p.appendChild(new_em);
this.div = document.createElement("div"); // <== CREATE DIV ELEMENT
this.target.appendChild(new_p);
}
}
}
Pour créer des button, mettez à jour la méthode du visuel update :
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// ...
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const categoricalDataView: DataViewCategorical = dataView.categorical;
// don't create elements if no data
if (!options.dataViews[0].categorical ||
!options.dataViews[0].categorical.categories) {
return
}
// to display current level of hierarchy
if (typeof this.textNode !== undefined) {
this.textNode.textContent = categoricalDataView.categories[categoricalDataView.categories.length - 1].source.displayName.toString();
}
// remove old elements
// for better performance use D3js pattern:
// https://d3js.org/#enter-exit
while (this.div.firstChild) {
this.div.removeChild(this.div.firstChild);
}
// create buttons for each category value
categoricalDataView.categories[categoricalDataView.categories.length - 1].values.forEach( (category: powerbi.PrimitiveValue, index: number) => {
let button = document.createElement("button");
button.innerText = category.toString();
this.div.appendChild(button);
})
}
// ...
Appliquez des styles simples dans .\style\visual.less :
button {
margin: 5px;
min-width: 50px;
min-height: 50px;
}
Préparez des exemples de données pour tester le visuel :
| H1 | H2 | H3 | VALUES |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | A1 | A11 | 1 |
| A | A1 | A12 | 2 |
| A | A2 | A21 | 3 |
| A | A2 | A22 | 4 |
| A | A3 | A31 | 5 |
| A | A3 | A32 | 6 |
| B | B1 | B11 | 7 |
| B | B1 | B12 | 8 |
| B | B2 | B21 | 9 |
| B | B2 | B22 | 10 |
| B | B3 | B31 | 11 |
| B | B3 | B32 | 12 |
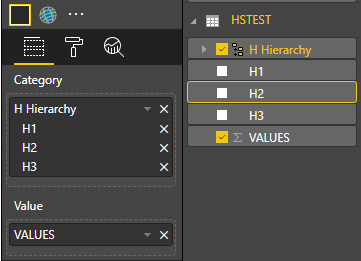
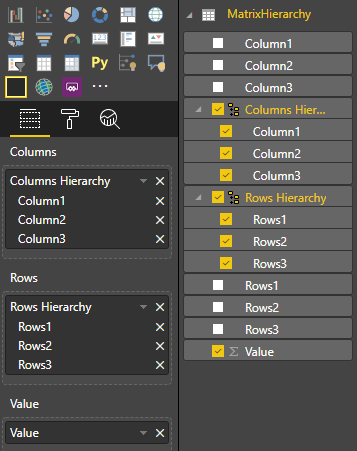
Créez ensuite une hiérarchie dans Power BI Desktop :
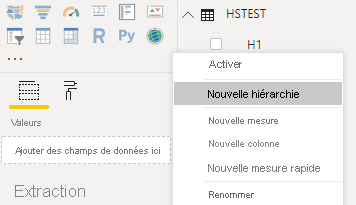
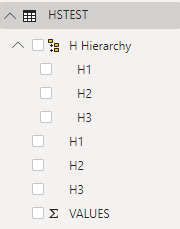
Ajoutez toutes les colonnes de catégorie (H1, H2, H3) à la nouvelle hiérarchie :
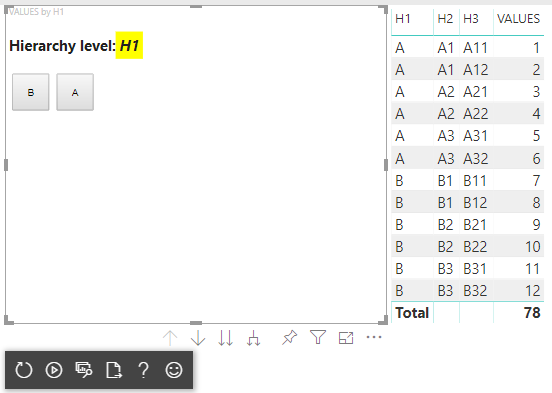
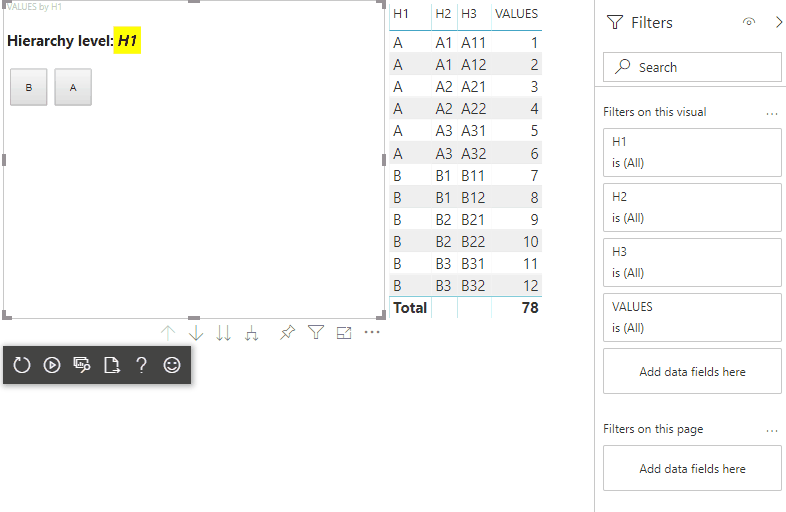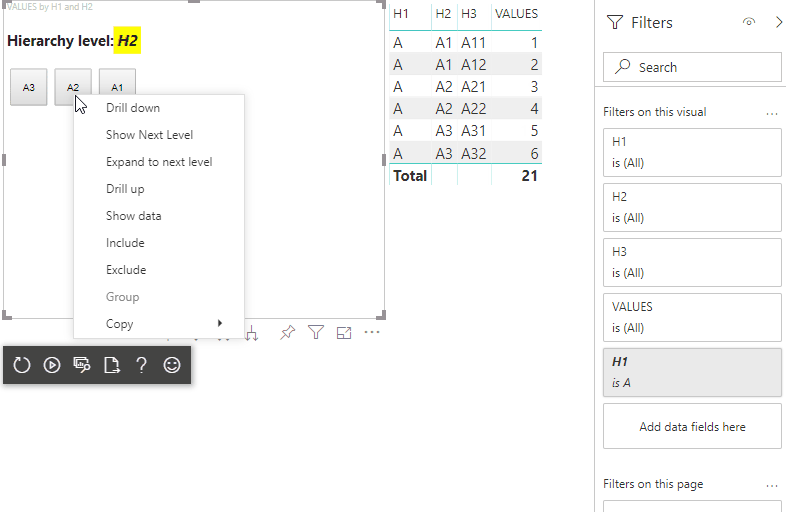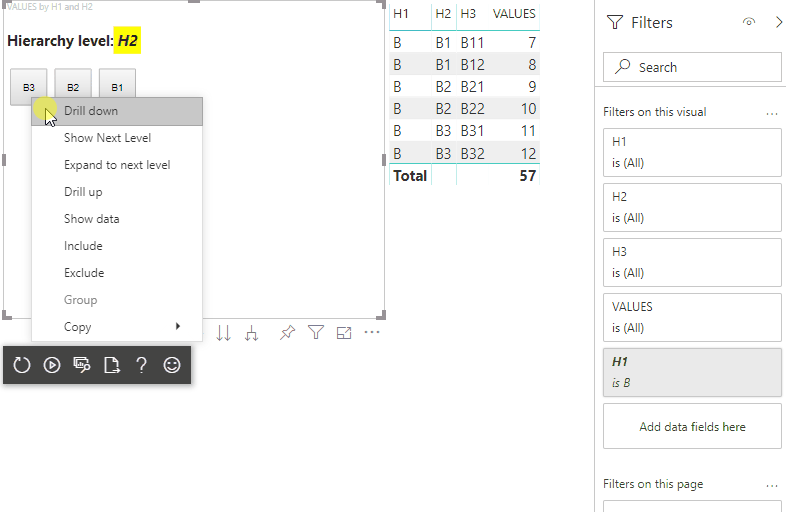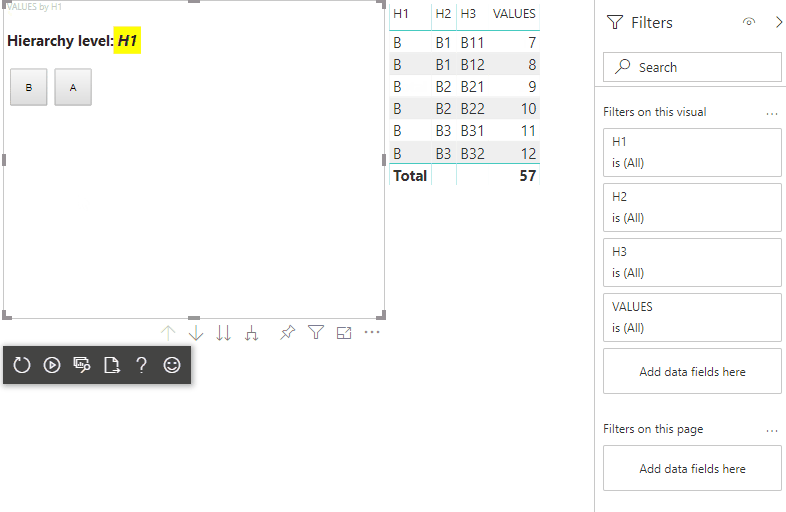
Après ces étapes, vous devez obtenir le visuel suivant :
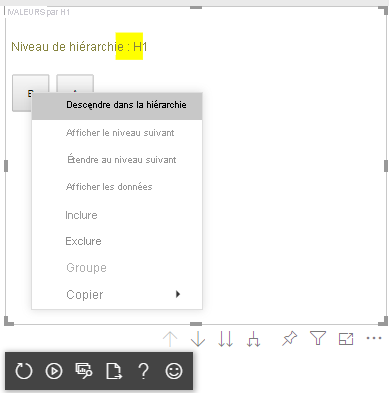
Ajouter un menu contextuel aux éléments visuels
Pour ajouter un menu contextuel aux boutons du visuel :
Enregistrez l’objet host dans les propriétés du visuel et appelez la méthode createSelectionManager au gestionnaire de sélection pour afficher un menu contextuel à l’aide de l’API Visuels Power BI.
"use strict";
import "core-js/stable";
import "./../style/visual.less";
// default imports
import IVisualHost = powerbi.extensibility.visual.IVisualHost;
import ISelectionManager = powerbi.extensibility.ISelectionManager;
import ISelectionId = powerbi.visuals.ISelectionId;
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// visual properties
// ...
private div: HTMLDivElement;
private host: IVisualHost; // <== NEW PROPERTY
private selectionManager: ISelectionManager; // <== NEW PROPERTY
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
// save the host in the visuals properties
this.host = options.host;
// create selection manager
this.selectionManager = this.host.createSelectionManager();
// ...
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// update method body
// ...
}
// ...
}
Remplacez le corps du rappel de fonction forEach par :
categoricalDataView.categories[categoricalDataView.categories.length - 1].values.forEach( (category: powerbi.PrimitiveValue, index: number) => {
// create selectionID for each category value
let selectionID: ISelectionId = this.host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withCategory(categoricalDataView.categories[0], index)
.createSelectionId();
let button = document.createElement("button");
button.innerText = category.toString();
// add event listener to click event
button.addEventListener("click", (event) => {
// call select method in the selection manager
this.selectionManager.select(selectionID);
});
button.addEventListener("contextmenu", (event) => {
// call showContextMenu method to display context menu on the visual
this.selectionManager.showContextMenu(selectionID, {
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
event.preventDefault();
});
this.div.appendChild(button);
});
Appliquez des données au visuel :
À l’étape finale, vous devez obtenir un visuel avec les sélections et le menu contextuel :
Ajouter la prise en charge de l’exploration pour le mappage de vues de données de matrices
Pour tester le visuel avec des mappages de vues de données de matrice, commencez par préparer des exemples de données :
| Ligne 1 | Ligne 2 | Ligne 3 | Colonne 1 | Colonne 2 | Colonne 3 | Valeurs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R11 | R111 | C1 | C11 | C111 | 1 |
| R1 | R11 | R112 | C1 | C11 | C112 | 2 |
| R1 | R11 | R113 | C1 | C11 | C113 | 3 |
| R1 | R12 | R121 | C1 | C12 | C121 | 4 |
| R1 | R12 | R122 | C1 | C12 | C122 | 5 |
| R1 | R12 | R123 | C1 | C12 | C123 | 6 |
| R1 | R13 | R131 | C1 | C13 | C131 | 7 |
| R1 | R13 | R132 | C1 | C13 | C132 | 8 |
| R1 | R13 | R133 | C1 | C13 | C133 | 9 |
| R2 | R21 | R211 | C2 | C21 | C211 | 10 |
| R2 | R21 | R212 | C2 | C21 | C212 | 11 |
| R2 | R21 | R213 | C2 | C21 | C213 | 12 |
| R2 | R22 | R221 | C2 | C22 | C221 | 13 |
| R2 | R22 | R222 | C2 | C22 | C222 | 14 |
| R2 | R22 | R223 | C2 | C22 | C223 | 16 |
| R2 | R23 | R231 | C2 | C23 | C231 | 17 |
| R2 | R23 | R232 | C2 | C23 | C232 | 18 |
| R2 | R23 | R233 | C2 | C23 | C233 | 19 |
Appliquez ensuite le mappage de vue de données suivant au visuel :
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Columns",
"name": "columns",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Rows",
"name": "rows",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"drilldown": {
"roles": [
"columns",
"rows"
]
},
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"matrix": {
"columns": {
"for": {
"in": "columns"
}
},
"rows": {
"for": {
"in": "rows"
}
},
"values": {
"for": {
"in": "value"
}
}
}
}
]
}
Appliquez des données au visuel :
Importez les interfaces nécessaires pour traiter les mappages de vues de données de matrices :
// ...
import DataViewMatrix = powerbi.DataViewMatrix;
import DataViewMatrixNode = powerbi.DataViewMatrixNode;
import DataViewHierarchyLevel = powerbi.DataViewHierarchyLevel;
// ...
Créez deux propriétés pour deux éléments div de lignes et de colonnes :
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// ...
private rowsDiv: HTMLDivElement;
private colsDiv: HTMLDivElement;
// ...
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
// ...
// Create div elements and append to main div of the visual
this.rowsDiv = document.createElement("div");
this.target.appendChild(this.rowsDiv);
this.colsDiv = document.createElement("div");
this.target.appendChild(this.colsDiv);
}
// ...
}
Vérifiez les données avant de restituer les éléments et affichez le niveau actuel de la hiérarchie :
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// ...
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// constructor body
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const matrixDataView: DataViewMatrix = dataView.matrix;
// if the visual doesn't receive the data no reason to continue rendering
if (!matrixDataView ||
!matrixDataView.columns ||
!matrixDataView.rows ) {
return
}
// to display current level of hierarchy
if (typeof this.textNode !== undefined) {
this.textNode.textContent = categoricalDataView.categories[categoricalDataView.categories.length - 1].source.displayName.toString();
}
// ...
}
// ...
}
Créez une fonction treeWalker pour parcourir la hiérarchie :
export class Visual implements IVisual {
// ...
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
// if the visual doesn't receive the data no reason to continue rendering
if (!matrixDataView ||
!matrixDataView.columns ||
!matrixDataView.rows ) {
return
}
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
if (matrixNode.children) {
// ...
// traversing child nodes
matrixNode.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, levels, childDiv));
}
}
// traversing rows
const rowRoot: DataViewMatrixNode = matrixDataView.rows.root;
rowRoot.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, matrixDataView.rows.levels, this.rowsDiv));
// traversing columns
const colRoot = matrixDataView.columns.root;
colRoot.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, matrixDataView.columns.levels, this.colsDiv));
}
// ...
}
Générez les sélections pour les points de données.
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// generate selectionID for each node of matrix
const selectionID: ISelectionID = this.host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withMatrixNode(matrixNode, levels)
.createSelectionId();
// ...
if (matrixNode.children) {
// ...
// traversing child nodes
matrixNode.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, levels, childDiv));
}
}
Créez un élément div pour chaque niveau de hiérarchie :
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// generate selectionID for each node of matrix
const selectionID: ISelectionID = this.host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withMatrixNode(matrixNode, levels)
.createSelectionId();
// ...
if (matrixNode.children) {
// create div element for level
const childDiv = document.createElement("div");
// add to current div
div.appendChild(childDiv);
// create paragraph element to display next
const p = document.createElement("p");
// display level name on paragraph element
const level = levels[matrixNode.level];
p.innerText = level.sources[level.sources.length - 1].displayName;
// add paragraph element to created child div
childDiv.appendChild(p);
// traversing child nodes
matrixNode.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, levels, childDiv));
}
}
Créez des buttons pour interagir avec le visuel et affichez le menu contextuel pour les points de données de matrice :
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// generate selectionID for each node of matrix
const selectionID: ISelectionID = this.host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withMatrixNode(matrixNode, levels)
.createSelectionId();
// create button element
let button = document.createElement("button");
// display node value/name of the button's text
button.innerText = matrixNode.value.toString();
// add event listener on click
button.addEventListener("click", (event) => {
// call select method in the selection manager
this.selectionManager.select(selectionID);
});
// display context menu on click
button.addEventListener("contextmenu", (event) => {
// call showContextMenu method to display context menu on the visual
this.selectionManager.showContextMenu(selectionID, {
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
event.preventDefault();
});
div.appendChild(button);
if (matrixNode.children) {
// ...
}
}
Effacez les éléments div avant de réafficher les éléments :
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
}
// remove old elements
// to better performance use D3js pattern:
// https://d3js.org/#enter-exit
while (this.rowsDiv.firstChild) {
this.rowsDiv.removeChild(this.rowsDiv.firstChild);
}
// create label for row elements
const prow = document.createElement("p");
prow.innerText = "Rows";
this.rowsDiv.appendChild(prow);
while (this.colsDiv.firstChild) {
this.colsDiv.removeChild(this.colsDiv.firstChild);
}
// create label for columns elements
const pcol = document.createElement("p");
pcol.innerText = "Columns";
this.colsDiv.appendChild(pcol);
// render elements for rows
const rowRoot: DataViewMatrixNode = matrixDataView.rows.root;
rowRoot.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, matrixDataView.rows.levels, this.rowsDiv));
// render elements for columns
const colRoot = matrixDataView.columns.root;
colRoot.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, index, matrixDataView.columns.levels, this.colsDiv));
}
Enfin, vous devez obtenir un visuel avec le menu contextuel :
