Formazione
Modulo
Eseguire operazioni sulle matrici usando i metodi helper in C# - Training
Usare i metodi helper di C# per eseguire operazioni di inversione, ridimensionamento, suddivisione e join su matrici.
Questo browser non è più supportato.
Esegui l'aggiornamento a Microsoft Edge per sfruttare i vantaggi di funzionalità più recenti, aggiornamenti della sicurezza e supporto tecnico.
Language-Integrated Query (LINQ) offre funzionalità di query a livello di linguaggio e un'API per le funzioni superiore a C# e Visual Basic, che consentono di scrivere codice dichiarativo espressivo.
Si tratta della sintassi della query a livello di linguaggio:
var linqExperts = from p in programmers
where p.IsNewToLINQ
select new LINQExpert(p);
Dim linqExperts = From p in programmers
Where p.IsNewToLINQ
Select New LINQExpert(p)
Questo è lo stesso esempio usando l'API IEnumerable<T> :
var linqExperts = programmers.Where(p => p.IsNewToLINQ)
.Select(p => new LINQExpert(p));
Dim linqExperts = programmers.Where(Function(p) p.IsNewToLINQ).
Select(Function(p) New LINQExpert(p))
Si supponga di avere un elenco di animali domestici e di volerlo convertire in un dizionario nel quale sia possibile accedere a un animale selezionando direttamente il valore RFID corrispondente.
Questo è il codice imperativo tradizionale:
var petLookup = new Dictionary<int, Pet>();
foreach (var pet in pets)
{
petLookup.Add(pet.RFID, pet);
}
Dim petLookup = New Dictionary(Of Integer, Pet)()
For Each pet in pets
petLookup.Add(pet.RFID, pet)
Next
L'intenzione dietro il codice non è creare un nuovo Dictionary<int, Pet> e aggiungerlo tramite un ciclo, è convertire un elenco esistente in un dizionario! LINQ mantiene l'intenzione mentre il codice imperativo non è.
Si tratta dell'espressione LINQ equivalente:
var petLookup = pets.ToDictionary(pet => pet.RFID);
Dim petLookup = pets.ToDictionary(Function(pet) pet.RFID)
Il codice che usa LINQ è utile perché mette sullo stesso livello scopo e codice in fase di programmazione. Un altro vantaggio del codice è il fatto che sia conciso. È infatti possibile ridurre parti prolisse della codebase di un 1/3 come illustrato in precedenza. Dolce affare, vero?
Per un notevole blocco di software in natura, tutto ruota intorno alla gestione dei dati da un'origine (Database, JSON, XML e così via). Spesso è necessario imparare a conoscere un'API nuova per ogni origine dati, operazione alquanto noiosa. LINQ semplifica questa operazione astraendo elementi comuni di accesso ai dati in una sintassi di query che sembra la stessa indipendentemente dall'origine dati selezionata.
Questo trova tutti gli elementi XML con un valore di attributo specifico:
public static IEnumerable<XElement> FindAllElementsWithAttribute(XElement documentRoot, string elementName,
string attributeName, string value)
{
return from el in documentRoot.Elements(elementName)
where (string)el.Element(attributeName) == value
select el;
}
Public Shared Function FindAllElementsWithAttribute(documentRoot As XElement, elementName As String,
attributeName As String, value As String) As IEnumerable(Of XElement)
Return From el In documentRoot.Elements(elementName)
Where el.Element(attributeName).ToString() = value
Select el
End Function
La scrittura di codice per attraversare manualmente il documento XML per eseguire questa attività sarebbe molto più complessa.
L'interazione con XML non è l'unica cosa che è possibile eseguire con i provider LINQ. LINQ to SQL è un Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) pressoché essenziale per un database del server MSSQL. La libreria Json.NET fornisce un efficiente attraversamento del documento JSON tramite LINQ. Inoltre, se non esiste una libreria che esegue ciò che è necessario, è anche possibile scrivere il proprio provider LINQ!
Perché usare la sintassi delle query? Questa è una domanda che spesso si presenta. Dopo tutto, il codice seguente:
var filteredItems = myItems.Where(item => item.Foo);
Dim filteredItems = myItems.Where(Function(item) item.Foo)
è molto più breve rispetto alla seguente:
var filteredItems = from item in myItems
where item.Foo
select item;
Dim filteredItems = From item In myItems
Where item.Foo
Select item
La sintassi dell'API non è solo un modo più conciso per eseguire la sintassi della query?
No. La sintassi di query consente l'uso della clausola let grazie alla quale è possibile introdurre e associare una variabile nell'ambito dell'espressione, usandola nelle parti successive dell'espressione. La riproduzione dello stesso codice con solo la sintassi dell'API può essere eseguita, ma probabilmente porterà al codice difficile da leggere.
Una domanda sorge spontanea. È consigliabile usare solo la sintassi di query?
La risposta a questa domanda è sì se:
La risposta a questa domanda è no se...
Per un elenco completo di esempi di LINQ, vedere 101 LINQ Samples (101 esempi di LINQ).
Gli esempi seguenti sono una rapida dimostrazione di alcuni dei pezzi essenziali di LINQ. Questo non è in alcun modo completo, poiché LINQ offre più funzionalità rispetto a ciò che viene presentato qui.
// Filtering a list.
var germanShepherds = dogs.Where(dog => dog.Breed == DogBreed.GermanShepherd);
// Using the query syntax.
var queryGermanShepherds = from dog in dogs
where dog.Breed == DogBreed.GermanShepherd
select dog;
// Mapping a list from type A to type B.
var cats = dogs.Select(dog => dog.TurnIntoACat());
// Using the query syntax.
var queryCats = from dog in dogs
select dog.TurnIntoACat();
// Summing the lengths of a set of strings.
int seed = 0;
int sumOfStrings = strings.Aggregate(seed, (s1, s2) => s1.Length + s2.Length);
' Filtering a list.
Dim germanShepherds = dogs.Where(Function(dog) dog.Breed = DogBreed.GermanShepherd)
' Using the query syntax.
Dim queryGermanShepherds = From dog In dogs
Where dog.Breed = DogBreed.GermanShepherd
Select dog
' Mapping a list from type A to type B.
Dim cats = dogs.Select(Function(dog) dog.TurnIntoACat())
' Using the query syntax.
Dim queryCats = From dog In dogs
Select dog.TurnIntoACat()
' Summing the lengths of a set of strings.
Dim seed As Integer = 0
Dim sumOfStrings As Integer = strings.Aggregate(seed, Function(s1, s2) s1.Length + s2.Length)
// Transforms the list of kennels into a list of all their dogs.
var allDogsFromKennels = kennels.SelectMany(kennel => kennel.Dogs);
' Transforms the list of kennels into a list of all their dogs.
Dim allDogsFromKennels = kennels.SelectMany(Function(kennel) kennel.Dogs)
public class DogHairLengthComparer : IEqualityComparer<Dog>
{
public bool Equals(Dog a, Dog b)
{
if (a == null && b == null)
{
return true;
}
else if ((a == null && b != null) ||
(a != null && b == null))
{
return false;
}
else
{
return a.HairLengthType == b.HairLengthType;
}
}
public int GetHashCode(Dog d)
{
// Default hashcode is enough here, as these are simple objects.
return d.GetHashCode();
}
}
...
// Gets all the short-haired dogs between two different kennels.
var allShortHairedDogs = kennel1.Dogs.Union(kennel2.Dogs, new DogHairLengthComparer());
Public Class DogHairLengthComparer
Inherits IEqualityComparer(Of Dog)
Public Function Equals(a As Dog,b As Dog) As Boolean
If a Is Nothing AndAlso b Is Nothing Then
Return True
ElseIf (a Is Nothing AndAlso b IsNot Nothing) OrElse (a IsNot Nothing AndAlso b Is Nothing) Then
Return False
Else
Return a.HairLengthType = b.HairLengthType
End If
End Function
Public Function GetHashCode(d As Dog) As Integer
' Default hashcode is enough here, as these are simple objects.
Return d.GetHashCode()
End Function
End Class
...
' Gets all the short-haired dogs between two different kennels.
Dim allShortHairedDogs = kennel1.Dogs.Union(kennel2.Dogs, New DogHairLengthComparer())
// Gets the volunteers who spend share time with two humane societies.
var volunteers = humaneSociety1.Volunteers.Intersect(humaneSociety2.Volunteers,
new VolunteerTimeComparer());
' Gets the volunteers who spend share time with two humane societies.
Dim volunteers = humaneSociety1.Volunteers.Intersect(humaneSociety2.Volunteers,
New VolunteerTimeComparer())
// Get driving directions, ordering by if it's toll-free before estimated driving time.
var results = DirectionsProcessor.GetDirections(start, end)
.OrderBy(direction => direction.HasNoTolls)
.ThenBy(direction => direction.EstimatedTime);
' Get driving directions, ordering by if it's toll-free before estimated driving time.
Dim results = DirectionsProcessor.GetDirections(start, end).
OrderBy(Function(direction) direction.HasNoTolls).
ThenBy(Function(direction) direction.EstimatedTime)
Infine, un esempio più avanzato: determinare se i valori delle proprietà di due istanze dello stesso tipo sono uguali. L'esempio è stato preso in prestito e modificato da questo articolo di StackOverflow:
public static bool PublicInstancePropertiesEqual<T>(this T self, T to, params string[] ignore) where T : class
{
if (self == null || to == null)
{
return self == to;
}
// Selects the properties which have unequal values into a sequence of those properties.
var unequalProperties = from property in typeof(T).GetProperties(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance)
where !ignore.Contains(property.Name)
let selfValue = property.GetValue(self, null)
let toValue = property.GetValue(to, null)
where !Equals(selfValue, toValue)
select property;
return !unequalProperties.Any();
}
<System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Extension()>
Public Function PublicInstancePropertiesEqual(Of T As Class)(self As T, [to] As T, ParamArray ignore As String()) As Boolean
If self Is Nothing OrElse [to] Is Nothing Then
Return self Is [to]
End If
' Selects the properties which have unequal values into a sequence of those properties.
Dim unequalProperties = From [property] In GetType(T).GetProperties(BindingFlags.Public Or BindingFlags.Instance)
Where Not ignore.Contains([property].Name)
Let selfValue = [property].GetValue(self, Nothing)
Let toValue = [property].GetValue([to], Nothing)
Where Not Equals(selfValue, toValue) Select [property]
Return Not unequalProperties.Any()
End Function
PLINQ o Parallel LINQ è un motore di esecuzione parallela per le espressioni LINQ. In altre parole, un'espressione LINQ può essere facilmente parallelizzata su un numero qualsiasi di thread. Questa operazione viene eseguita chiamando AsParallel(), che precede l'espressione.
Considerare quanto segue:
public static string GetAllFacebookUserLikesMessage(IEnumerable<FacebookUser> facebookUsers)
{
var seed = default(UInt64);
Func<UInt64, UInt64, UInt64> threadAccumulator = (t1, t2) => t1 + t2;
Func<UInt64, UInt64, UInt64> threadResultAccumulator = (t1, t2) => t1 + t2;
Func<Uint64, string> resultSelector = total => $"Facebook has {total} likes!";
return facebookUsers.AsParallel()
.Aggregate(seed, threadAccumulator, threadResultAccumulator, resultSelector);
}
Public Shared GetAllFacebookUserLikesMessage(facebookUsers As IEnumerable(Of FacebookUser)) As String
{
Dim seed As UInt64 = 0
Dim threadAccumulator As Func(Of UInt64, UInt64, UInt64) = Function(t1, t2) t1 + t2
Dim threadResultAccumulator As Func(Of UInt64, UInt64, UInt64) = Function(t1, t2) t1 + t2
Dim resultSelector As Func(Of Uint64, string) = Function(total) $"Facebook has {total} likes!"
Return facebookUsers.AsParallel().
Aggregate(seed, threadAccumulator, threadResultAccumulator, resultSelector)
}
Questo codice, se necessario, crea un partizione di facebookUsers tra i thread del sistema, somma i like totali su ogni thread in parallelo, somma i risultati calcolati da ogni thread e proietta il risultato in una stringa.
Sotto forma di diagramma:
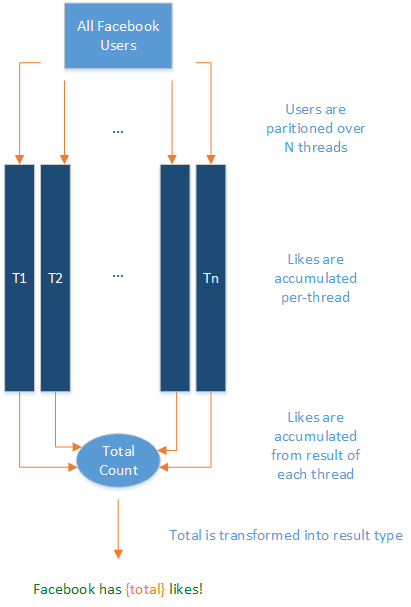
I processi associati a CPU parallelizzabili che possono essere facilmente espressi tramite LINQ (in altre parole, sono funzioni pure e non hanno effetti collaterali) sono un ottimo candidato per PLINQ. Per i processi che hanno un effetto collaterale, valutare l'uso della libreria parallela attività.
Formazione
Modulo
Eseguire operazioni sulle matrici usando i metodi helper in C# - Training
Usare i metodi helper di C# per eseguire operazioni di inversione, ridimensionamento, suddivisione e join su matrici.