Tutorial: Get started with .NET for Apache Spark
This tutorial teaches you how to run a .NET for Apache Spark app using .NET Core on Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Prepare your environment for .NET for Apache Spark
- Write your first .NET for Apache Spark application
- Build and run your .NET for Apache Spark application
Warning
.NET for Apache Spark targets an out-of-support version of .NET (.NET Core 3.1). For more information, see the .NET Support Policy.
Before you begin writing your app, you need to set up some prerequisite dependencies. If you can run dotnet, java, spark-shell from your command line environment, then your environment is already prepared and you can skip to the next section. If you cannot run any or all of the commands, do the following steps.
To start building .NET apps, you need to download and install the .NET SDK (Software Development Kit).
Download and install the .NET Core SDK. Installing the SDK adds the dotnet toolchain to your PATH.
Once you've installed the .NET Core SDK, open a new command prompt or terminal and run dotnet.
If the command runs and prints out information about how to use dotnet, can move to the next step. If you receive a 'dotnet' is not recognized as an internal or external command error, make sure you opened a new command prompt or terminal before running the command.
Install Java 8.1 for Windows and macOS, or OpenJDK 8 for Ubuntu.
Select the appropriate version for your operating system. For example, select jdk-8u201-windows-x64.exe for a Windows x64 machine (as shown below) or jdk-8u231-macosx-x64.dmg for macOS. Then, use the command java to verify the installation.

Apache Spark is downloaded as a compressed .tgz file. Use an extraction program, like 7-Zip or WinZip, to extract the file.
Download and install Apache Spark. You'll need to select from version 2.3.* or 2.4.0, 2.4.1, 2.4.3, 2.4.4, 2.4.5, 2.4.6, 2.4.7, 3.0.0, 3.0.1, 3.0.2, 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.2.0, or 3.2.1 (.NET for Apache Spark is not compatible with other versions of Apache Spark). See the .NET Spark Release Notes for more information on compatible versions.
The commands used in the following steps assume you have downloaded and installed Apache Spark 3.0.1. If you wish to use a different version, replace 3.0.1 with the appropriate version number. Then, extract the .tar file and the Apache Spark files.
To extract the nested .tar file:
- Locate the spark-3.0.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tgz file that you downloaded.
- Right click on the file and select 7-Zip -> Extract here.
- spark-3.0.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tar is created alongside the .tgz file you downloaded.
To extract the Apache Spark files:
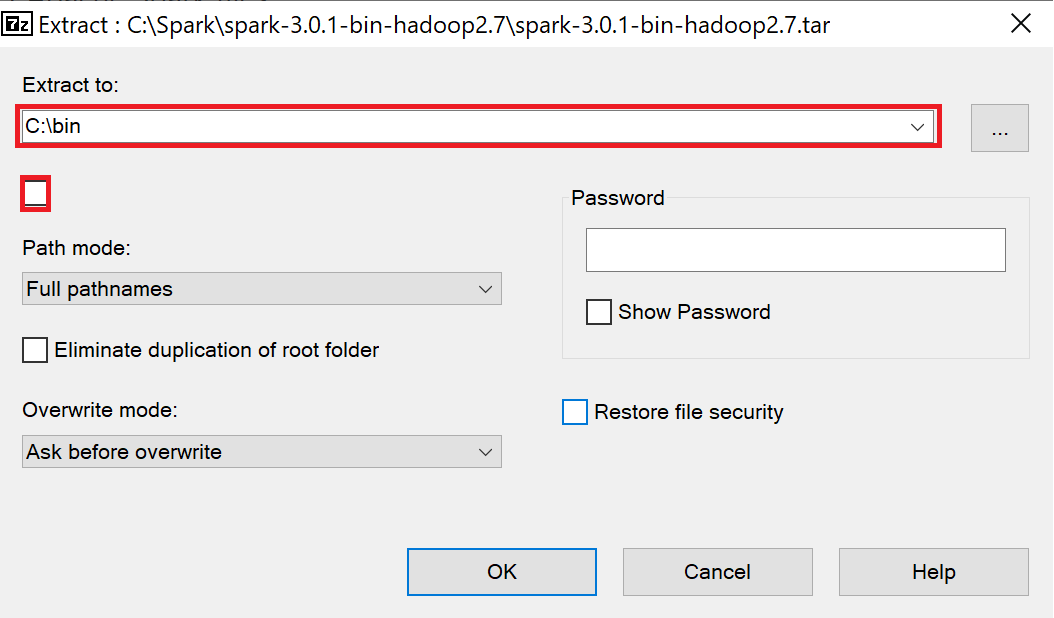
- Right-click on spark-3.0.1-bin-hadoop2.7.tar and select 7-Zip -> Extract files...
- Enter C:\bin in the Extract to field.
- Uncheck the checkbox below the Extract to field.
- Select OK.
- The Apache Spark files are extracted to C:\bin\spark-3.0.1-bin-hadoop2.7\
Run the following commands to set the environment variables used to locate Apache Spark. On Windows, make sure to run the command prompt in administrator mode.
export SPARK_HOME=~/bin/spark-3.0.1-bin-hadoop2.7/
export PATH="$SPARK_HOME/bin:$PATH"
source ~/.bashrc
Once you've installed everything and set your environment variables, open a new command prompt or terminal and run the following command:
spark-submit --version
If the command runs and prints version information, you can move to the next step.
If you receive a 'spark-submit' is not recognized as an internal or external command error, make sure you opened a new command prompt.
Download the Microsoft.Spark.Worker release from the .NET for Apache Spark GitHub. For example if you're on a Windows machine and plan to use .NET Core, download the Windows x64 netcoreapp3.1 release.
To extract the Microsoft.Spark.Worker:
- Locate the Microsoft.Spark.Worker.netcoreapp3.1.win-x64-1.0.0.zip file that you downloaded.
- Right-click and select 7-Zip -> Extract files....
- Enter C:\bin in the Extract to field.
- Uncheck the checkbox below the Extract to field.
- Select OK.
.NET for Apache Spark requires WinUtils to be installed alongside Apache Spark. Download winutils.exe. Then, copy WinUtils into C:\bin\spark-3.0.1-bin-hadoop2.7\bin.
Note
If you are using a different version of Hadoop, which is annotated at the end of your Spark install folder name, select the version of WinUtils that's compatible with your version of Hadoop.
Run one of the following commands to set the DOTNET_WORKER_DIR environment variable, which is used by .NET apps to locate .NET for Apache Spark worker binaries. Make sure to replace <PATH-DOTNET_WORKER_DIR> with the directory where you downloaded and extracted the Microsoft.Spark.Worker. On Windows, make sure to run the command prompt in administrator mode.
Finally, double-check that you can run dotnet, java, spark-shell from your command line before you move to the next section.
In your command prompt or terminal, run the following commands to create a new console application:
dotnet new console -o MySparkApp
cd MySparkApp
The dotnet command creates a new application of type console for you. The -o parameter creates a directory named MySparkApp where your app is stored and populates it with the required files. The cd MySparkApp command changes the directory to the app directory you created.
To use .NET for Apache Spark in an app, install the Microsoft.Spark package. In your command prompt or terminal, run the following command:
dotnet add package Microsoft.Spark
Note
This tutorial uses the latest version of the Microsoft.Spark NuGet package unless otherwise specified.
Open Program.cs in Visual Studio Code, or any text editor, and replace all of the code with the following:
using Microsoft.Spark.Sql;
using static Microsoft.Spark.Sql.Functions;
namespace MySparkApp
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Create Spark session
SparkSession spark =
SparkSession
.Builder()
.AppName("word_count_sample")
.GetOrCreate();
// Create initial DataFrame
string filePath = args[0];
DataFrame dataFrame = spark.Read().Text(filePath);
//Count words
DataFrame words =
dataFrame
.Select(Split(Col("value")," ").Alias("words"))
.Select(Explode(Col("words")).Alias("word"))
.GroupBy("word")
.Count()
.OrderBy(Col("count").Desc());
// Display results
words.Show();
// Stop Spark session
spark.Stop();
}
}
}
SparkSession is the entrypoint of Apache Spark applications, which manages the context and information of your application. Using the Text method, the text data from the file specified by the filePath is read into a DataFrame. A DataFrame is a way of organizing data into a set of named columns. Then, a series of transformations is applied to split the sentences in the file, group each of the words, count them and order them in descending order. The result of these operations is stored in another DataFrame. Note that at this point, no operations have taken place because .NET for Apache Spark lazily evaluates the data. It's not until the Show method is called to display the contents of the words transformed DataFrame to the console that the operations defined in the lines above execute. Once you no longer need the Spark session, use the Stop method to stop your session.
Your app processes a file containing lines of text. Create a file called input.txt file in your MySparkApp directory, containing the following text:
Hello World
This .NET app uses .NET for Apache Spark
This .NET app counts words with Apache Spark
Save the changes and close the file.
Run the following command to build your application:
dotnet build
Navigate to your build output directory and use the spark-submit command to submit your application to run on Apache Spark. Make sure to replace <version> with the version of your .NET worker and <path-of-input.txt> with the path of your input.txt file is stored.
spark-submit \
--class org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner \
--master local \
microsoft-spark-3-0_2.12-<version>.jar \
dotnet MySparkApp.dll <path-of-input.txt>
Note
This command assumes you have downloaded Apache Spark and added it to your PATH environment variable to be able to use spark-submit. Otherwise, you'd have to use the full path (for example, C:\bin\apache-spark\bin\spark-submit or ~/spark/bin/spark-submit).
When your app runs, the word count data of the input.txt file is written to the console.
+------+-----+
| word|count|
+------+-----+
| .NET| 3|
|Apache| 2|
| app| 2|
| This| 2|
| Spark| 2|
| World| 1|
|counts| 1|
| for| 1|
| words| 1|
| with| 1|
| Hello| 1|
| uses| 1|
+------+-----+
Congratulations! You successfully authored and ran a .NET for Apache Spark app.
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Prepare your environment for .NET for Apache Spark
- Write your first .NET for Apache Spark application
- Build and run your .NET for Apache Spark application
To see a video explaining the steps above, check out the .NET for Apache Spark 101 video series.
Check out the resources page to learn more.