Not
Bu sayfaya erişim yetkilendirme gerektiriyor. Oturum açmayı veya dizinleri değiştirmeyi deneyebilirsiniz.
Bu sayfaya erişim yetkilendirme gerektiriyor. Dizinleri değiştirmeyi deneyebilirsiniz.
Not
Bu tasarım kılavuzu Windows 7 için oluşturulmuştur ve Windows'un daha yeni sürümleri için güncelleştirilmemiştir. Kılavuzun çoğu ilke olarak hala geçerlidir, ancak sunu ve örnekler geçerli tasarım kılavuzumuzu yansıtmaz.
Denetimler, kullanıcılarınızın uygulamanızın ana pencere alanında etkileşimde bulunduğu kullanıcı arabirimi öğeleridir. Windows tabanlı, masaüstü uygulamalarındaki denetimlerin görsel örneklerine bakın ve her denetim için yönergelere bağlantılar alın.
| Örnekler |
|---|
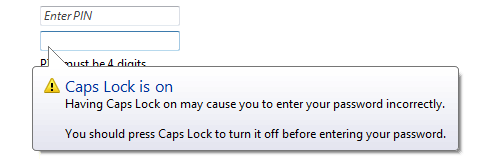
Balonlar kullanıcıları bir denetimdeki kritik olmayan bir sorun veya özel koşul hakkında bilgilendirin. |

Onay kutuları kullanıcıların iki veya daha fazla farklı seçenek arasında karar vermelerine olanak tanır. |
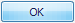
Komut düğmeleri kullanıcıların hemen eylem gerçekleştirmesine olanak sağlar. |
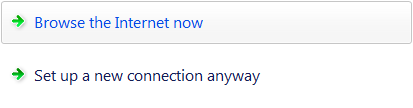
Komut bağlantıları kullanıcıların birbirini dışlayan, ilgili seçenekler arasından seçim yapmasına olanak tanır. |
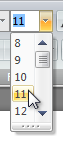
Açılan listeler ve birleşik giriş kutuları kullanıcıların birbirini dışlayan değerler listesinden seçim yapmasına olanak tanır. |
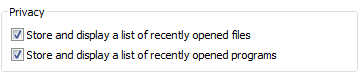
Grup kutuları kullanıcıların bir dizi ilgili denetim arasındaki ilişkileri görmesine olanak sağlar. |
Bağlantılar kullanıcıların başka bir sayfaya, pencereye veya Yardım konusuna gitmesine izin verir; tanımı görüntüleme; bir komut başlatın; veya bir seçenek belirleyin. |
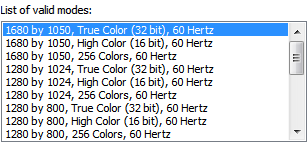
liste kutularını kullanıcıların her zaman görünür olan bir listede sunulan değer kümesinden seçimlerini sağlamasına olanak sağlar. Tek seçimli liste kutusuyla, kullanıcılar birbirini dışlayan değerler listesinden bir öğe seçer. Birden çok seçimli liste kutusuyla, kullanıcılar değer listesinden sıfır veya daha fazla öğe seçer. |
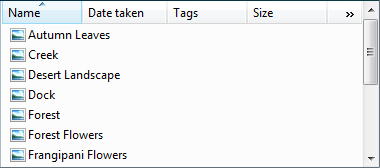
Liste görünümleri kullanıcıların tek seçim veya birden çok seçim kullanarak veri nesneleri koleksiyonunu görüntülemesine ve bunlarla etkileşim kurmasına olanak sağlar. |
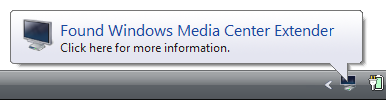
Bildirimleri kullanıcıları geçerli kullanıcı etkinliğiyle ilgili olmayan olaylar hakkında bilgilendirin. |
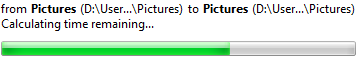
İlerleme çubukları kullanıcıların uzun bir işlemin ilerleme durumunu izlemesine olanak tanır. |

Aşamalı açıklama denetimleri kullanıcıların veriler, seçenekler veya komutlar gibi ek bilgileri göstermesine veya gizlemesine olanak sağlar. |
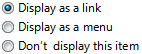
Radyo düğmeleri kullanıcıların birbirini dışlayan, ilgili seçenekler arasından seçim yapmasına olanak tanır. |
arama kutusu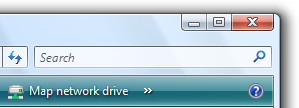 search box search boxArama kutuları kullanıcılara belirli nesneleri veya metni hızla bulmaları için bir yol sağlar. |
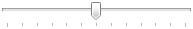
Kaydırıcılar kullanıcıların sürekli bir değer aralığı arasından seçim yapmalarına olanak sağlar. |
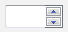
Döndürme denetimleri kullanıcıların ilişkili sayısal metin kutusundaki değeri artımlı olarak değiştirmesine olanak sağlar. |
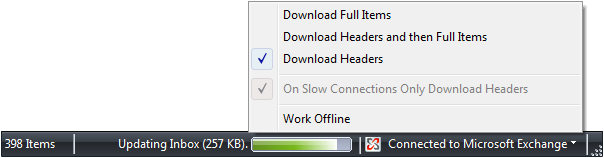
Durum çubukları geçerli pencerenin durumu, arka plan görevleri veya diğer bağlamsal bilgiler hakkındaki bilgileri görüntüler. |

Sekmeler kullanıcılara ayrı etiketli sayfalarda ilgili bilgileri sunar. |
metin kutusu text box text boxMetin kutularını kullanıcıların metin veya sayısal değer görüntülemesine, girmesine veya düzenlemesine olanak sağlar. |
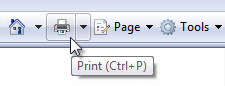
Araç İpuçları etiketlenmemiş bir denetimi etiketler. |
Bilgi ipuçları kullanıcının işaret ettiği bir nesneyi açıklar. |
ağaç görünümü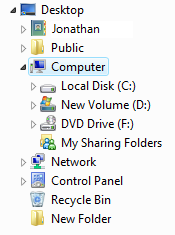 treeview treeviewAğaç görünümleri kullanıcıların tek seçim veya birden çok seçim kullanarak hiyerarşik olarak düzenlenmiş bir nesne koleksiyonunu görüntülemesine ve bunlarla etkileşim kurmasına olanak sağlar. |