CoreMidi Namespace
Important
Some information relates to prerelease product that may be substantially modified before it’s released. Microsoft makes no warranties, express or implied, with respect to the information provided here.
The CoreMidi namespace provides classes for interacting with the MIDI subsystem.
|
IOError |
Provides data for the IOError event. |
| Midi |
Global methods and constants for using CoreMidi. |
|
Midi. |
Notification posted by the Midi class. |
|
Midi |
|
|
Midi |
|
|
Midi |
|
|
Midi |
Main entry point to use MIDI in MacOS X and iOS. |
|
Midi |
Represents a MIDI device (typically they represent a hardware device, but virtual devices also exist). Devices can contain one or more entities. |
|
Midi |
|
|
Midi |
Endpoints represent an individual source or destination on the MIDI stream. |
|
Midi |
A MidiObject that represents a sub-component of a MidiDevice. |
|
Midi |
Exception raised by Midi methods. |
|
Midi |
A connection to a MIDI network host, using a MidiNetworkSession. |
|
Midi |
A remote MIDI host. |
|
Midi |
A singleton class that maintains the MidiNetworkConnections between various MIDI entities. |
|
Midi |
Base class for the MidiClient, MidiPort, MidiEntity, MidiDevice and MidiEndpoint classes. |
|
Midi |
Encapsulates a series of MIDI events. |
|
Midi |
Provides data for the MessageReceived and E:CoreMidi.MidiPacketsEventArgs.MessageReceived events. |
|
Midi |
Input and Output ports. |
|
Midi |
Manages MIDI play-through connections. |
|
Midi |
MIDI transformations and routings. |
|
Object |
Provides data for the ObjectRemoved and E:CoreMidi.ObjectAddedOrRemovedEventArgs.ObjectRemoved events. |
|
Object |
Provides data for the PropertyChanged event. |
|
Midi |
|
|
Midi |
Represents a transformation of a MIDI control. |
|
Midi |
Source or Destination of a MidiThruConnection. |
|
Midi |
Object that defines how a MIDI event is transformed. |
|
Midi |
MIDI Value map. |
|
Midi |
Errors raised by the CoreMIDI stack. |
|
Midi |
An enumeration whose values specify which hosts are eligible to connect to a MIDI network session. |
|
Midi |
MIDI Control Transformation Type. |
|
Midi |
MIDI transform types. |
CoreMIDI is an API that talks to the MIDI server on iOS and OSX which in turn interacts with MIDI devices connected to your Mac or iOS device.
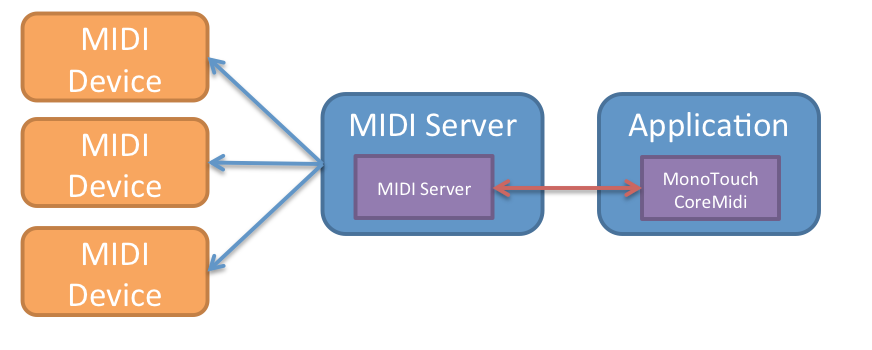
When using CoreMIDI, you will run into various classes that deal with different parts of the MIDI stack, the following graphic illustrates the relationships:
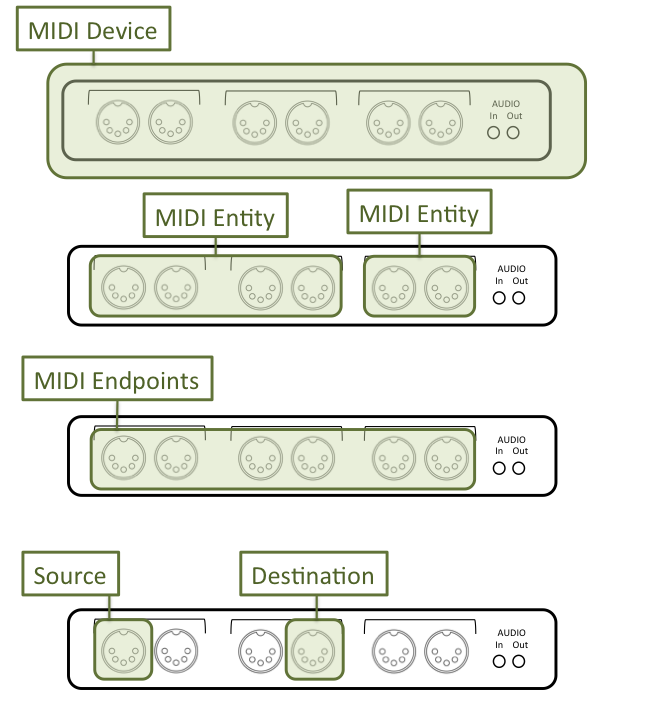
The MIDI device itself is represented by the MidiDevice class. Devices can contain one or more entities (MidiEntity). For example a MIDI device could contain two independent MIDI tone generators. Each Entity contains a series of endpoints which are either sources or destintions. Both MIDI sources and MIDI destinations are encapsulated by the MidiEntity class.
To start with MIDI, you will need to create a MidiClient object. This object is the gateway between your application and the MIDI server process. You subscribe to the events that this object raises to track devices being added, removed and to changes in their properties and setup configuration.
You also use the MidiClient to create input ports and output ports. The input ports raise the MessageReceived event when new MIDI data is available and you can use the Packets property in the arguments received to get the data out
See the MidiClient class for an example of how to set things up.
To use networked MIDI connections, you need to enable the network session and set its connection policy, like this:
var session = MidiNetworkSession.DefaultSession;
session.Enabled = true;
session.ConnectionPolicy = MidiNetworkConnectionPolicy.Anyone;
To connect to a remote MIDI network host you use the MidiNetworkHost, like this:
var host = MidiNetworkHost.Create ("My Session", "myhost.xamarin.com", 5004);
var connection = MidiNetworkConnection.FromHost (host);