Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies To: # OData client v7.12.1 supported OData Client V7.12.1
OData Client V7.12.1
OData Client v7.12.1 introduced support for grouping and aggregation. Grouping and aggregation allows us to summarize data for display or analysis. We achieve this by collapsing multiple rows of data into single rows based on some criteria and then computing aggregations like average, sum, min, max, count, etc. In this page, we look at how this feature is implemented in OData client.
Sample Data
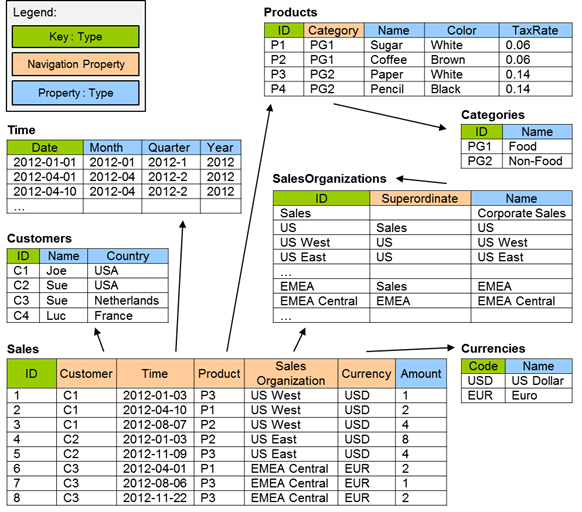
The following sample data from OASIS OData Extension for Data Aggregation Version 4.0 site will be used to illustrate the scenarios supported by this feature.
Simple Aggregation
The standard LINQ aggregation methods include Average, Sum, Min, and Max. We support overloads of these methods that accept two parameters; a sequence of values - source: IQueryable<TSource>, and a projection function to apply to each element - selector.
These methods are translated into the corresponding OData URL.
Standard LINQ Aggregation Methods Examples
Return average of sale amounts
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Average(d1 => d1.Amount)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount)Result: 3.0
Return sum of sale amounts
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Sum(d1 => d1.Amount)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Amount with sum as SumAmount)Result: 24.0
Return minimum sale amount
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Min(d1 => d1.Amount)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Amount with min as MinAmount)Result: 1.0
Return maximum sale amount
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Max(d1 => d1.Amount)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Amount with max as MaxAmount)Result: 8.0
Return average sale product tax rate - where Product is a navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Max(d1 => d1.Product.TaxRate)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Product/TaxRate with average as AverageProduct_TaxRate)Result: 0.1
Return sum sale product tax rate - where Product is a navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Sum(d1 => d1.Product.TaxRate)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Product/TaxRate with sum as SumProduct_TaxRate)Result: 0.8
Return minimum sale product tax rate - where Product is a navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Min(d1 => d1.Product.TaxRate)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Product/TaxRate with min as MinProduct_TaxRate)Result: 0.06
Return maximum sale product tax rate - where Product is a navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Max(d1 => d1.Product.TaxRate)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Product/TaxRate with max as MaxProduct_TaxRate)Result: 0.14
In addition to the 4 aggregation methods described in the section above, we also support a custom CountDistinct method that returns the total number of distinct values in the specified property. This custom method was introduced to eliminate the need for writing an expression of the following form to achieve the same: dataServiceContext.Sales.Select(d1 => d1.Product).Distinct().Count().
CountDistinct Examples
CountDistinct targeting structural property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.CountDistinct(d1 => d1.ProductId)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(ProductId with countdistinct as CountDistinctProductId)Result: 3
CountDistinct targeting navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.CountDistinct(d1 => d1.Product.Color)Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Product/Color with countdistinct as CountDistinctProductColor)Result: 2
We can restrict the set of data to be aggregated by using the Where method. In this case however, the Where method is translated into a filter transformation, not a $filter query option.
Filter Transformation Example
Return average USD sale amounts
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Where(d1 => d1.CurrencyCode == "USD").Average(d2 => d2.Amount)
Translation:
/Sales?$apply=filter(CurrencyCode eq 'USD')/aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount)
Result: 3.8
Grouping and Aggregation
There are 8 overloads of the GroupBy method defined in the System.Linq library. Our starting point in implementing support for grouping and aggregation is the following overload:
GroupBy<TSource, TKey, TResult>(
IQueryable<TSource>,
Expression<Func<TSource, TKey>>,
Expression<Func<TKey, IEnumerable<TSource>, TResult>>)
This overloads accepts 3 parameters:
source- anIQueryable<T>whose elements to groupkeySelector- a function to extract the key for each elementresultSelector- a function to create a result value for each group
We translate a GroupBy expression based on the above overload into the relevant OData URL.
Grouping and Aggregation Examples:
Group by constant
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => 1, (d2, d3) => new { AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount)Group by single property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => d1.ProductId, (d2, d3) => new { ProductId = d2, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((ProductId), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount))Group by single navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => d1.Product.Category.Id, (d2, d3) => new { CategoryId = d2, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((Product/Category/Id), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount))Group by multiple properties
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new { d1.ProductId, d1.CurrencyCode }, (d2, d3) => new { d2.ProductId, d2.CategoryCode, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((ProductId,CurrencyCode), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount))Group by multiple navigation properties
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new { d1.Product.CategoryId, d1.Customer.Country ), (d2, d3) => new { d2.CategoryId, d2.Country, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((Product/CategoryId,Customer/Country), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount))Aggregating navigation property
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => d1.Customer.Country, (d2, d3) => new { Country = d2, MinTaxRate = d3.Min(d4 => d4.Product.TaxRate), MaxTaxRate = d3.Max(d4 => d4.Product.TaxRate) });Translation:
/Sales?$groupby((Customer/Country), aggregate(Product/TaxRate with min as MinTaxRate, Product/TaxRate with max as MaxTaxRate))Group and count
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new { d1.ProductId, d1.Customer.Country }, (d2, d3) => new { d2.ProductId, d2.Country, NumberOfProductsSoldByCountry = d3.Count() });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((ProductId,Customer/Country), aggregate($count as NumberOfProductsSoldByCountry))Group and count distinct
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => d1.Customer.Country, (d2, d3) => new { d2.Country, DistinctNumberOfProductsSoldByCountry = d3.CountDistinct( d4 => d4.Product.Name) });Translation:
Sales?$apply=groupby((Customer/Country), aggregate(Product/Name with countdistinct as DistinctNumberOfProductsSoldByCountry))Member initialization in the result selector
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new { d1.ProductId, d1.Customer.Country }, (d2, d3) => new GroupedResult { ProductId = d2.ProductId, Country = d2.Country, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount), MinAmount = d3.Min(d4 => d4.Amount), MaxAmount = d3.Max(d4 => d4.Amount), NumberOfProductsSoldByCountry = d3.Count(), DistinctNumberOfProductsSoldByCountry = d3.CountDistinct( d4 => d4.Product.Name) });where
GroupedResultis a class defined as follows:class GroupedResult { public string ProductId { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } public decimal AverageAmount { get; set; } public decimal SumAmount { get; set; } public decimal MinAmount { get; set; } public decimal MaxAmount { get; set; } public int NumberOfProductsSoldByCountry { get; set; } public int DistinctNumberOfProductsSoldByCountry { get; set; } }Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((ProductId,Customer/Country), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount, Amount with min as MinAmount,Amount with max as MaxAmount, $count as NumberOfProductsSoldByCountry, Product/Name with countdistinct as DistinctNumberOfProductsSoldByCountry))Member initialization in the key selector
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new GroupingKey { CategoryId = d1.Product.CategoryId, Country = d1.Customer.Country }, (d2, d3) => new { d2.CategoryId, d2.Country, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });where
GroupingKeyis a class defined as follows:class GroupingKey { public string CategoryId { get; set; } public string Country { get; set; } }Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((Product/CategoryId,Customer/Country), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount))Mixed constructor and member initialization in the result selector
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new { d1.Time.Year, CategoryName = d1.Product.Category.Name }, (d2, d3) = new GroupedResult(d2.Year, d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount)) { CategoryName = d2.CategoryName, SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });where
GroupedResultis a class defined as:class GroupedResult { public int Year { get; } public string CategoryName { get; set; } public decimal AverageAmount { get; } public decimal SumAmount { get; set; } }Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((Time/Year,Product/Category/Name), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount)Support for known primitive types' member access and method calls
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.GroupBy( d1 => new { d1.Time.Year, CategoryName = d1.Product.Category.Name, d1.CurrencyCode }, (d2, d3) => new { FoobarLength = "foobar".Length, TenStr = 10.ToString(), YearStr = d2.Year.ToString(), CategoryNameLength = d2.CategoryName.Length, d2.CurrencyCode, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount).ToString(), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount), MinAmount = d3.Min(d4 => d4.Amount).ToString() });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=groupby((Time/Year,Product/Category/Name,CurrencyCode), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount, Amount with sum as SumAmount,Amount with min as MinAmount)Filter before grouping
Expression:
dataServiceContext.Sales.Where(d1 => d1.CurrencyCode == "USD").GroupBy( d1 => d1.ProductId, (d2, d3) => new { ProductId = d2, AverageAmount = d3.Average(d4 => d4.Amount), SumAmount = d3.Sum(d4 => d4.Amount) });Translation:
/Sales?$apply=filter(CurrencyCode eq 'USD')/groupby((ProductId), aggregate(Amount with average as AverageAmount,Amount with sum as SumAmount))