Ask Learn
Preview
Ask Learn is an AI assistant that can answer questions, clarify concepts, and define terms using trusted Microsoft documentation.
Please sign in to use Ask Learn.
Sign inThis browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
Microsoft Purview Data Catalog (classic) and Data Health Insights (classic) are no longer taking on new customers and these services, previously Azure Purview, are now in customer support mode.
Managed attributes are user-defined attributes that provide a business or organization level context to an asset. When applied to assets, managed attributes enable data consumers using the data catalog to gain context on the role an asset plays in a business.
Important
Attributes for data assets are referred to by different names, depending on which portal you're using.
This article explains working with Managed attributes in the classic governance portal (although the process for working with data asset attributes in the Microsoft Purview portal is the same).
Managed attribute: A set of user-defined attributes that provide a business or organization level context to an asset. A managed attribute has a name and a value. For example, 'Department' is an attribute name and 'Finance' is its value.
Attribute group: A grouping of managed attributes that allow for easier organization and consumption.
Access managed attributes by following the steps corresponding to the portal you're using:
Select New, then select either New attribute or New attribute group.
To create an attribute group, enter a name and a description.
Managed attributes have a name, attribute group, data type, and associated asset types. They also have a required flag that can only be enabled when created as part of creating a new attribute group. Associated asset types are the data asset types you can apply the attribute to. For example, if you select "Azure SQL Table" for an attribute, it will be applied to Azure SQL Table assets, but not Azure Synapse Dedicated Table assets.
Select Create to save your attribute.
These attributes will be automatically applied to the specified resources without a value. You'll need to apply a value for each asset.
When you create a managed attribute as part of a managed attribute group, you can add the required flag. The required flag means that a value must be provided for this managed attribute. When you edit a data asset, the required attribute must be filled out before you can close the editor.
Important
Once a managed attribute has been created, you'll need to add a value for each of your assets. You can add values to your assets by:
In the managed attribute management experience, managed attributes can't be deleted, only expired. Expired attributes can't be applied to any assets and are, by default, hidden in the user experience. By default, expired managed attributes aren't removed from an asset. If an asset has an expired managed attribute applied, it can only be removed, not edited.
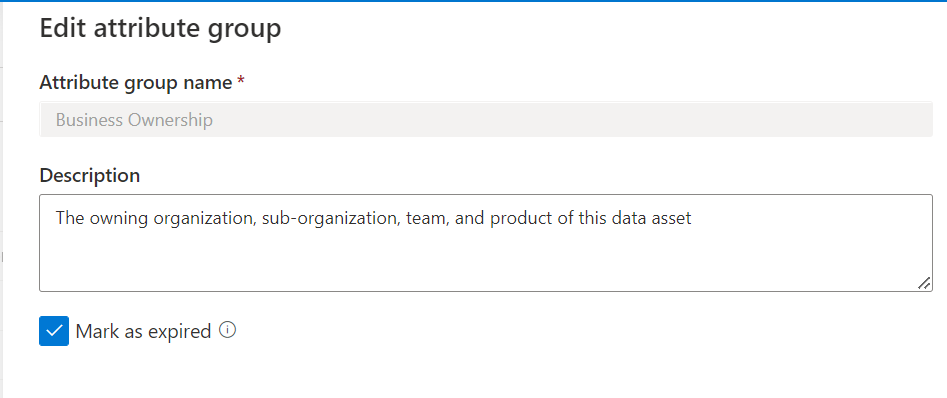
Both attribute groups and individual managed attributes can be expired. To mark an attribute group or managed attribute as expired, select the Edit icon.

Select Mark as expired and confirm your change. Once expired, attribute groups and managed attributes can't be reactivated.
Managed attributes can be programmatically created and applied using the business metadata APIs in Apache Atlas 2.2. For more information, see the Use Atlas 2.2 APIs tutorial.
Once you have created managed attributes, you can refine your data catalog searches using these attributes.
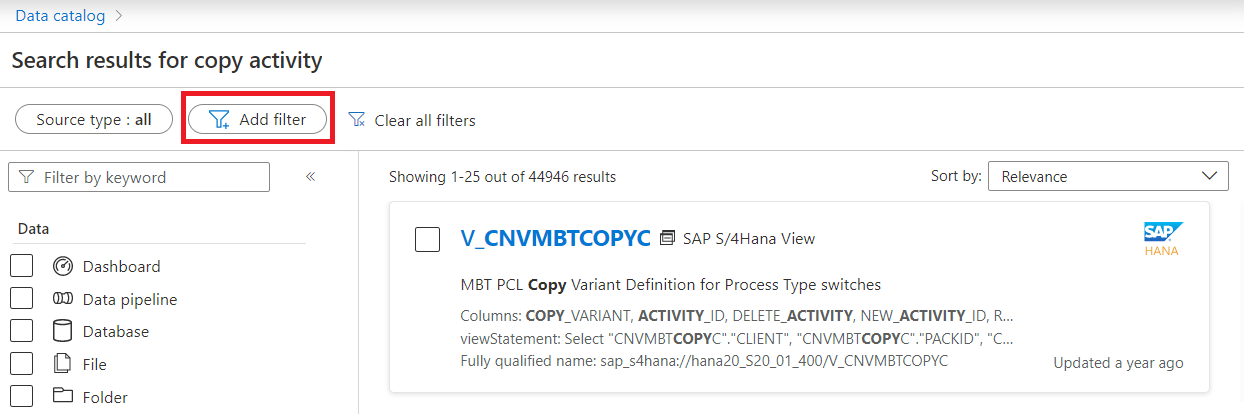
In a data catalog search, to refine by a managed attribute, first select Add filter at the top of the search.
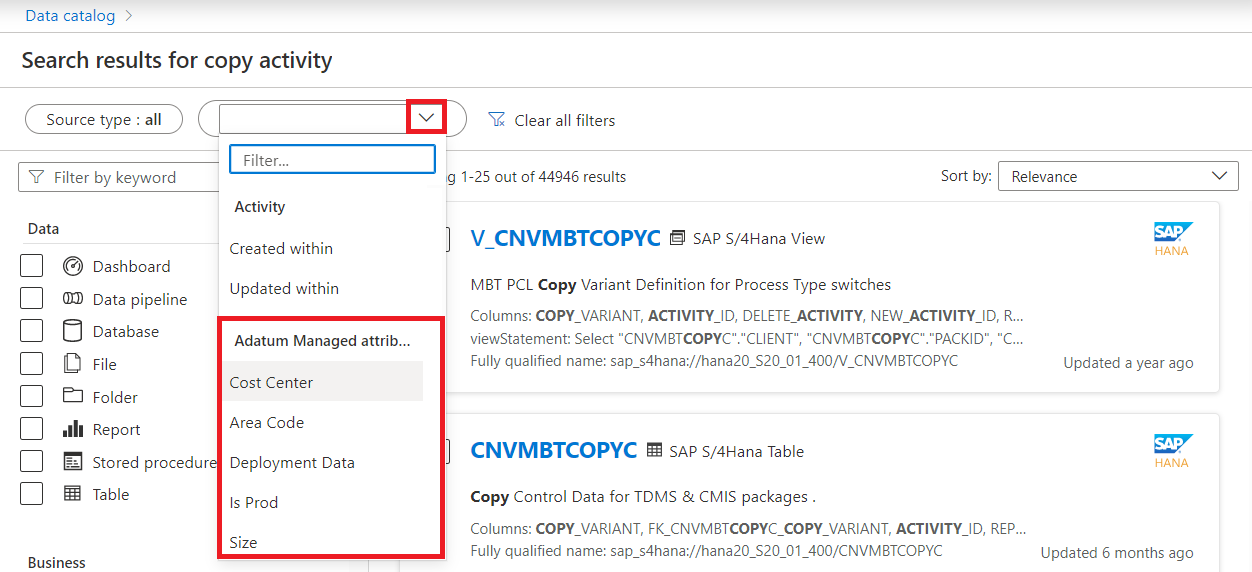
Select the drop-down, scroll to your list of managed attributes, and select one.
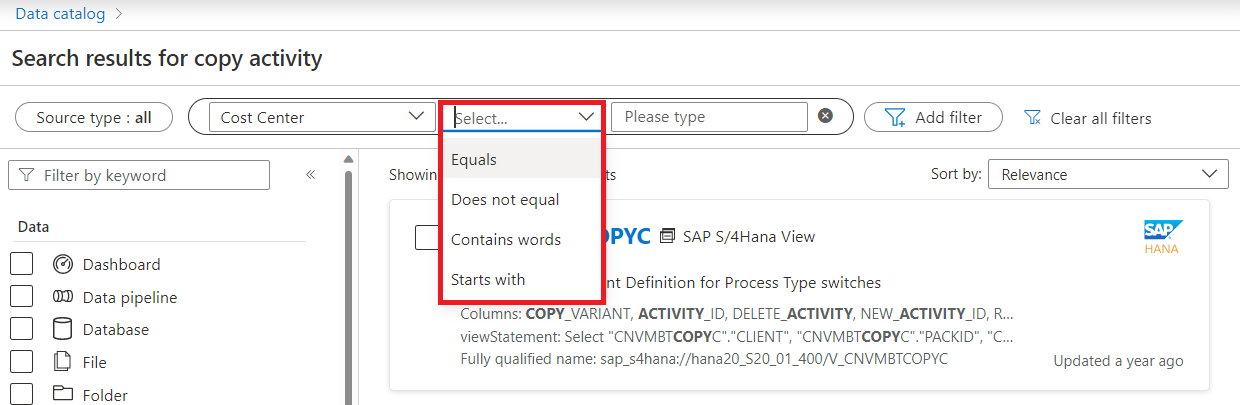
Select your operator, which will be different based on the kinds of values allowed by the attribute. In this example, we've selected Cost Center, which is a text value, so we can compare Cost Center with the text we'll enter.
Enter your values, and the search runs with your new filter.
Use managed attributes to extend the fields available for an asset in the Microsoft Purview Data Catalog. Managed attributes are key-value pairs that add structured metadata to your data catalog. When Microsoft Purview scans data, it adds technical information about the data like data type, classification, etc. If you want to add more fields, you need to define managed attributes.
In the following example, a managed attribute lets me tag tables with the department that publishes them. I use a managed attribute because I want to make sure assets are always tagged in exactly the same way with this information. I also want to filter by the publisher field when I search for data.
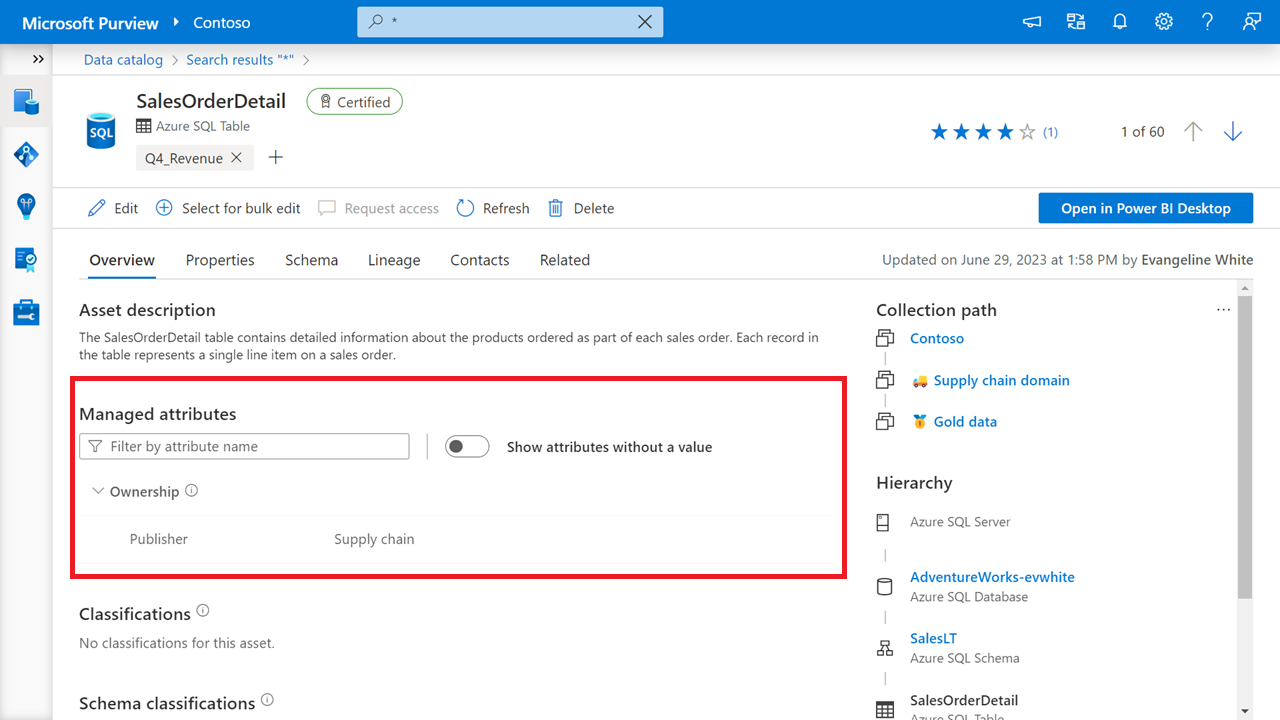
The managed attribute in this example helps people quickly find all data published by the supply chain team, but doesn't help someone understand the definition of a publisher or what it means if supply chain is the publisher of the data. For any information that needs a business explanation, use terms.
Below are the known limitations of the managed attribute feature as it currently exists in Microsoft Purview.
Ask Learn is an AI assistant that can answer questions, clarify concepts, and define terms using trusted Microsoft documentation.
Please sign in to use Ask Learn.
Sign in