Get access on behalf of a user
To call Microsoft Graph, an app must obtain an access token from the Microsoft identity platform. This access token includes information about whether the app is authorized to access Microsoft Graph on behalf of a signed-in user or with its own identity. This article provides guidance on how an app can access Microsoft Graph on behalf of a user, also called delegated access.
This article details the raw HTTP requests involved for an app to get access on behalf of a user using a popular flow called the OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant flow. Alternatively, you can avoid writing raw HTTP requests and use a Microsoft-built or supported authentication library that handles many of these details for you and helps you to get access tokens and call Microsoft Graph. For more information, see Use the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL).
In this article, you complete the following steps in using the OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant flow:
- Request authorization.
- Request an access token.
- Use the access token to call Microsoft Graph.
- [Optional] Use the refresh token to renew an expired access token.
Before proceeding with the steps in this article:
- Understand the authentication and authorization concepts in the Microsoft identity platform. For more information, see Authentication and authorization basics.
- Register the app with Microsoft Entra ID. For more information, see Register an application with the Microsoft identity platform. Save the following values from the app registration:
- The application ID (referred to as Object ID on the Microsoft Entra admin center).
- A client secret (application password), a certificate, or a federated identity credential. This property isn't needed for public clients like native, mobile, and single page applications.
- A redirect URI for the app to receive token responses from Microsoft Entra ID.
The first step in the authorization code flow is for the user to authorize the app to act on their behalf.
In the flow, the app redirects the user to the Microsoft identity platform /authorize endpoint. Through this endpoint, Microsoft Entra ID signs the user in and requests their consent for the permissions that the app requests. After consent is obtained, Microsoft Entra ID returns an authorization code to the app. The app can then redeem this code at the Microsoft identity platform /token endpoint for an access token.
The following example shows a request to the /authorize endpoint.
In the request URL, you call the /authorize endpoint and specify the required and recommended properties as query parameters.
In the following example, the app requests the User.Read and Mail.Read Microsoft Graph permissions, which allow the app to read the profile and mail of the signed-in user respectively. The offline_access permission is a standard OIDC scope that's requested so that the app can get a refresh token. The app can use the refresh token to get a new access token when the current one expires.
// Line breaks for legibility only
GET https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/authorize?
client_id=11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111
&response_type=code
&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fmyapp%2F
&response_mode=query
&scope=offline_access%20user.read%20mail.read
&state=12345 HTTP/1.1
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| tenant | Required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. The allowed values are: common for both Microsoft accounts and work or school accounts organizations for work or school accounts only consumers for Microsoft accounts only For more information, see protocol basics. |
| client_id | Required | The Application (client) ID that the registration portal assigned the app. Also referred to as appId in the Microsoft Graph application and service principal object. |
| response_type | Required | Must include code for the OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow. |
| redirect_uri | Recommended | The redirect URI of the app, where authentication responses are sent to and received by the app. It must exactly match one of the redirect URIs you registered in the app registration portal, except it must be URL encoded. For native and mobile apps, you should use the default value of https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient. |
| scope | Required | A space-separated list of the Microsoft Graph permissions that you want the user to consent to. These permissions can include resource permissions, such as User.Read and Mail.Read, and OIDC scopes, such as offline_access, which indicates that the app needs a refresh token for long-lived access to resources. |
| response_mode | Recommended | Specifies the method that should be used to send the resulting token back to the app. Can be query or form_post. |
| state | Recommended | A value included in the request that's also returned in the token response. It can be a string of any content that you wish. A randomly generated unique value is typically used for preventing cross-site request forgery attacks. This property is also used to encode information about the user's state in the app before the authentication request occurred, such as the page or view they were on. |
After the app sends the authorization request, the user is asked to enter their credentials to authenticate with Microsoft. The Microsoft identity platform v2.0 endpoint ensures that the user has consented to the permissions indicated in the scope query parameter. If there's any permission that the user or administrator hasn't consented to, they're asked to consent to the required permissions. For more information about the Microsoft Entra consent experience, see Application consent experience and Introduction to permissions and consent.
The following screenshot is an example of the consent dialog box presented for a Microsoft account user.
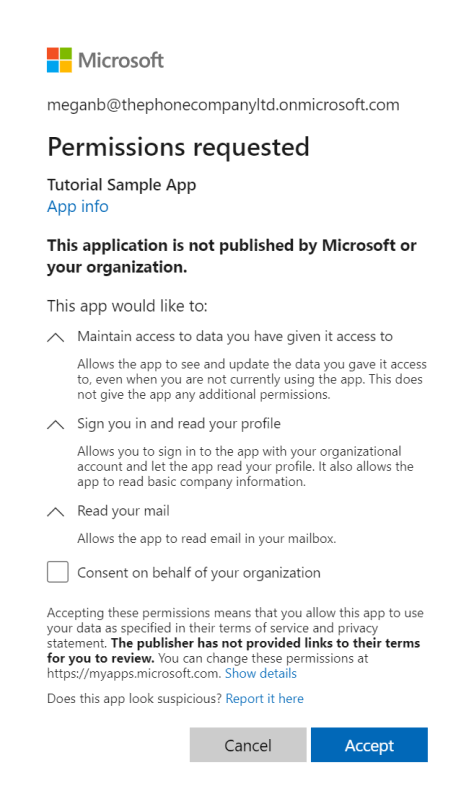
If the user consents to the permissions the app requested, the response contains the authorization code in the code parameter. Here's an example of a successful response to the previous request. Because the response_mode parameter in the request was set to query, the response is returned in the query string of the redirect URL.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
https://localhost/myapp/?code=M0ab92efe-b6fd-df08-87dc-2c6500a7f84d&state=12345&session_state=fe1540c3-a69a-469a-9fa3-8a2470936421#
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| code | The authorization code that the app requested. The app uses the authorization code to request an access token for the target resource. Authorization codes are short lived, typically they expire after about 10 minutes. |
| state | If a state parameter is included in the request, the same value should appear in the response. The app should verify that the state values in the request and response are identical. This check helps to detect Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) attacks against the client. |
| session_state | A unique value that identifies the current user session. This value is a GUID, but should be treated as an opaque value that is passed without examination. |
The app uses the authorization code received in the previous step to request an access token by sending a POST request to the /token endpoint.
// Line breaks for legibility only
POST /{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/token HTTP/1.1
Host: https://login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111
&scope=user.read%20mail.read
&code=OAAABAAAAiL9Kn2Z27UubvWFPbm0gLWQJVzCTE9UkP3pSx1aXxUjq3n8b2JRLk4OxVXr...
&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fmyapp%2F
&grant_type=authorization_code
&client_secret=HF8Q~Krjqh4r... // NOTE: Only required for web apps
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| tenant | Required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. The allowed values are: common for both Microsoft accounts and work or school accounts organizations for work or school accounts only consumers for Microsoft accounts only For more information, see protocol basics. |
| client_id | Required | The Application (client) ID that the registration portal assigned the app. Also referred to as appId in the Microsoft Graph application and service principal object. |
| grant_type | Required | Must be authorization_code for the authorization code flow. |
| scope | Required | A space-separated list of scopes. The scopes that your app requests in this leg must be equivalent to or a subset of the scopes that it requested in the authorization leg in Step 2. If the scopes specified in this request span multiple resource servers, then the v2.0 endpoint returns a token for the resource specified in the first scope. |
| code | Required | The authorization code that you acquired in the authorization leg in Step 2. |
| redirect_uri | Required | The same redirect URI value that was used to acquire the authorization code in Step 2. |
| client_secret | Required for web apps | The client secret that you created in the app registration portal for your app. It shouldn't be used in a native app, because client secrets can't be reliably stored on devices. It's required for web apps and web APIs, which have the ability to store the client_secret securely on the server side. |
The access token contains a list of the permissions that the access token is good for in the scope parameter. The response is similar to the following sample.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-type: application/json
{
"token_type": "Bearer",
"scope": "Mail.Read User.Read",
"expires_in": 3736,
"ext_expires_in": 3736,
"access_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Ik5HVEZ2ZEstZnl0aEV1Q...",
"refresh_token": "AwABAAAAvPM1KaPlrEqdFSBzjqfTGAMxZGUTdM0t4B4..."
}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| token_type | Indicates the token type value. The only type that Microsoft Entra ID supports is Bearer. |
| scope | A space separated list of the Microsoft Graph permissions that the access token is valid for. |
| expires_in | How long the access token is valid (in seconds). |
| ext_expires_in | Indicates an extended lifetime for the access token (in seconds) and used to support resiliency when the token issuance service isn't responding. |
| access_token | The requested access token. The app can use this token to call Microsoft Graph. |
| refresh_token | An OAuth 2.0 refresh token. The app can use this token to acquire additional access tokens after the current access token expires. Refresh tokens are long-lived, and can be used to retain access to resources for extended periods of time. A refresh token will only be returned if offline_access was included as a scope parameter. For details, see the v2.0 token reference. |
After you have an access token, the app uses it to call Microsoft Graph by attaching the access token as a Bearer token to the Authorization header in an HTTP request. The following request gets the profile of the signed-in user.
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/me HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiO ... 0X2tnSQLEANnSPHY0gKcgw
Host: graph.microsoft.com
A successful response looks similar to the following (some response headers have been removed).
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json;odata.metadata=minimal;odata.streaming=true;IEEE754Compatible=false;charset=utf-8
request-id: f45d08c0-6901-473a-90f5-7867287de97f
client-request-id: f45d08c0-6901-473a-90f5-7867287de97f
OData-Version: 4.0
Duration: 727.0022
Date: Thu, 20 Apr 2017 05:21:18 GMT
Content-Length: 407
{
"@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/v1.0/$metadata#users/$entity",
"businessPhones": [
"425-555-0100"
],
"displayName": "MOD Administrator",
"givenName": "MOD",
"jobTitle": null,
"mail": "admin@contoso.com",
"mobilePhone": "425-555-0101",
"officeLocation": null,
"preferredLanguage": "en-US",
"surname": "Administrator",
"userPrincipalName": "admin@contoso.com",
"id": "10a08e2e-3ea2-4ce0-80cb-d5fdd4b05ea6"
}
Access tokens are short lived, and the app must refresh them after they expire to continue accessing resources. The app does so by submitting another POST request to the /token endpoint, this time:
- Providing the
refresh_tokeninstead of the code in the request body - Specifying
refresh_tokenas the grant_type, instead ofauthorization_code.
// Line breaks for legibility only
POST /{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/token HTTP/1.1
Host: https://login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=11111111-1111-1111-1111-111111111111
&scope=user.read%20mail.read
&refresh_token=OAAABAAAAiL9Kn2Z27UubvWFPbm0gLWQJVzCTE9UkP3pSx1aXxUjq...
&grant_type=refresh_token
&client_secret=jXoM3iz... // NOTE: Only required for web apps
| Parameter | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| tenant | Required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. The allowed values are: common for both Microsoft accounts and work or school accounts organizations for work or school accounts only consumers for Microsoft accounts only For more information, see protocol basics. |
| client_id | Required | The Application (client) ID that the registration portal assigned your app. Also referred to as appId in the Microsoft Graph application and service principal object. |
| grant_type | Required | Must be refresh_token. |
| scope | Optional | A space-separated list of permissions (scopes). The permissions that your app requests must be equivalent to or a subset of the permissions that it requested in the original authorization code request in Step 2. |
| refresh_token | Required | The refresh_token that your app acquired during the token request in Step 3. |
| client_secret | Required for web apps | The client secret that you created in the app registration portal for your app. Don't use the secret in a native app, because client_secrets can't be reliably stored on devices. It's required for web apps and web APIs, which have the ability to store the client_secret securely on the server side. |
A successful token response looks similar to the following.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-type: application/json
{
"access_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Ik5HVEZ2ZEstZnl0aEV1Q...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3599,
"scope": "Mail.Read User.Read",
"refresh_token": "AwABAAAAvPM1KaPlrEqdFSBzjqfTGAMxZGUTdM0t4B4...",
}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| access_token | The requested access token. The app can use this token in calls to Microsoft Graph. |
| token_type | Indicates the token type value. The only type that Microsoft Entra ID supports is Bearer. |
| expires_in | How long the access token is valid (in seconds). |
| scope | The permissions (scopes) that the access_token is valid for. |
| refresh_token | A new OAuth 2.0 refresh token. Replace the old refresh token with this newly acquired refresh token to ensure your refresh tokens remain valid for as long as possible. |
In this article, you walked through the low-level protocol details that are required only when manually crafting and issuing raw HTTP requests to execute the authorization code flow. In production apps, use a Microsoft-built or supported authentication library, such as the Microsoft Authentication Library (MSAL), to get security tokens and call protected web APIs such as Microsoft Graph. Also, explore how to choose a Microsoft Graph authentication provider based on scenario.
MSAL and other supported authentication libraries simplify the process for you by handling details such as validation, cookie handling, token caching, and secure connections, allowing you to focus on the functionality of your application.
Microsoft has built and maintains a wide selection of code samples that demonstrate usage of supported authentication libraries with the Microsoft identity platform. To access these code samples, see the Microsoft identity platform code samples.
- Explore Microsoft Graph tutorials for code samples that are built using different SDKs to create basic applications that authenticate and access data in delegated scenarios.
- Choose from code samples that are built using different SDKs and maintained by Microsoft to run custom apps that use supported authentication libraries, sign-in users, and call Microsoft Graph. See Microsoft Graph tutorials.