Building reusable UI with Power Apps component framework and canvas apps components
Power Apps offers two options to create reusable components:
- Canvas apps components, which is a low-code way of creating reusable controls within Power Apps Studio.
- Power Apps component framework, which is a pro-developer way of building reusable controls using HTML, Typescript, and CSS.
Canvas apps components are powerful and can be used to fulfill most UI requirements for your app. You should consider them first, because the cost to build and maintain them can be lower in most cases than Power Apps component framework.
The following image shows examples of canvas app components.
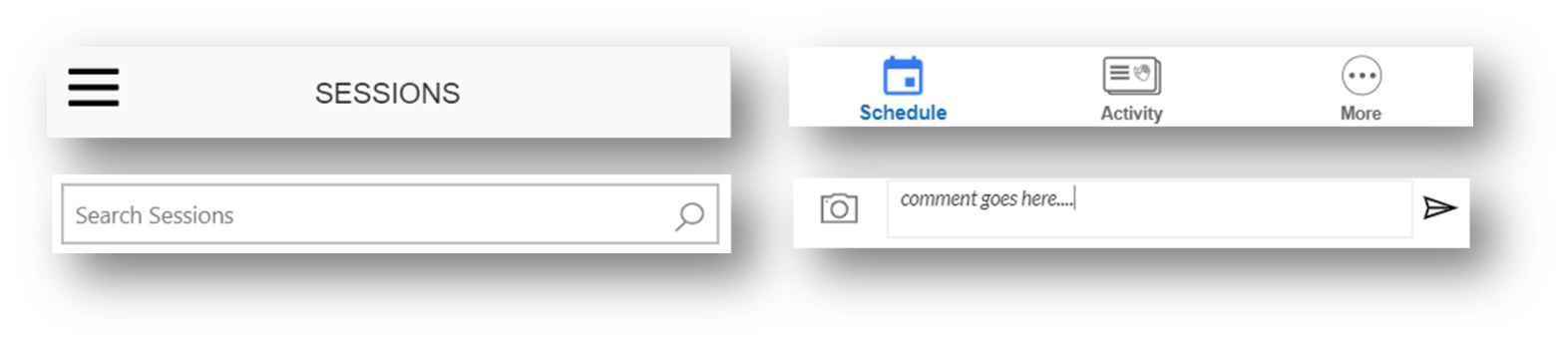
Canvas apps components can be packaged within component libraries, which are containers that makes it easy to reuse components across many apps. Component libraries make it easy to search and discover components, publish changes, and notify app makers when component updates are available.
For more advanced scenarios, Power Apps component framework offers access to a rich set of framework APIs that expose many capabilities like component lifecycle management, contextual data, and metadata. For scenarios that require access to device features—like camera, microphone—building a code component by using Power Apps component framework will be the only option. Code components created with Power Apps component framework can be used in canvas apps, model-driven apps, and Power Apps portals.
To see real-world use of Power Apps component framework, view this video on how Chevron built a digitally enhanced well-planning tool to help with the design of a well that's 35,000 feet deep (nearly 7 miles under the earth): Video: Real World Stories: Global energy companies power digital transformation with Microsoft Power Platform. This digital tool uses Power Apps component framework to enhance the app experience.
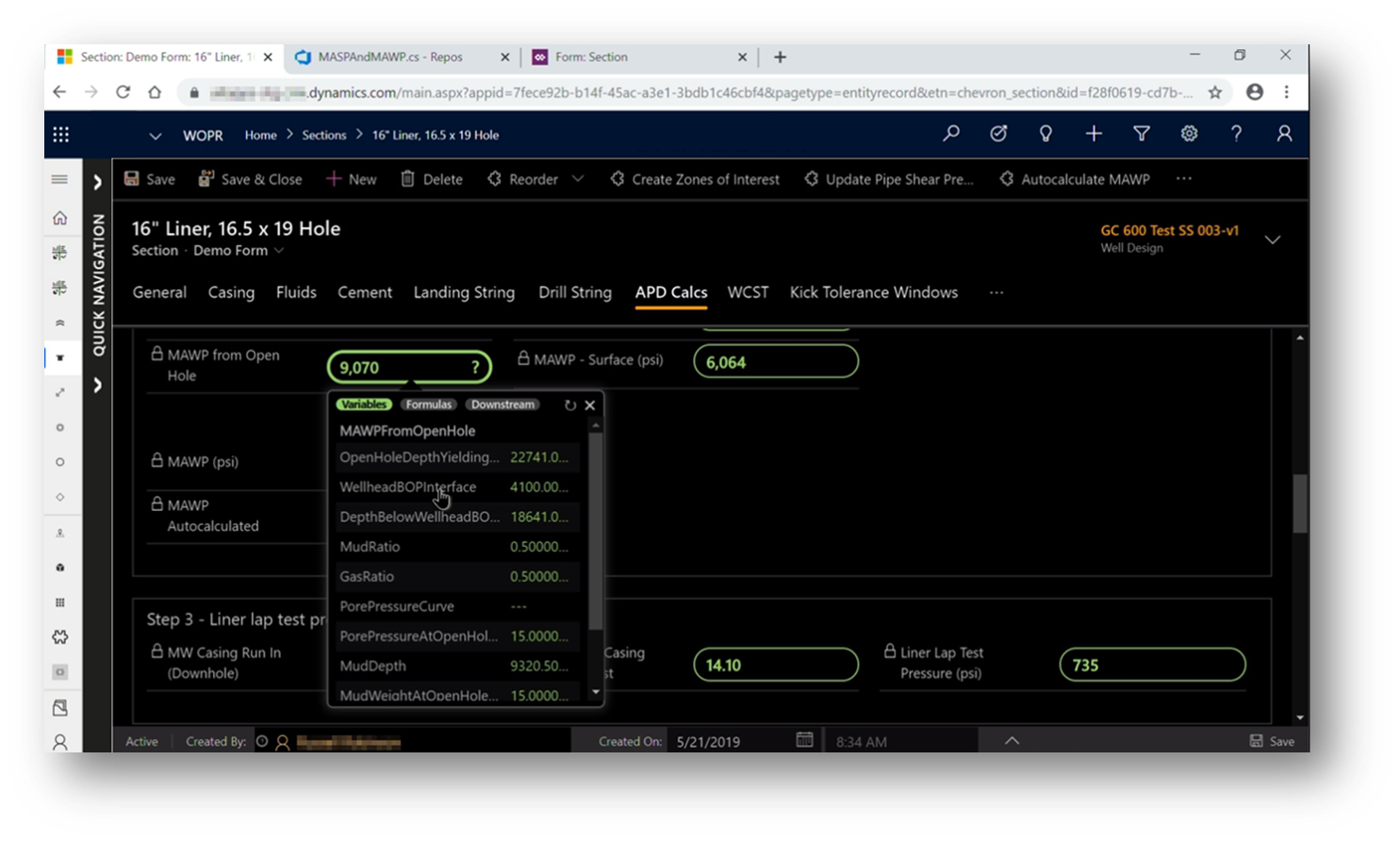
The code component shows an advanced input field with a dropdown containing additional information that helps users understand the formulas used to obtain the value of the input field.