@Pizarro, Diego , Thank you for your question.
From the FQDN of the AKS cluster shared in the question : k8s-poc-dns-6b1e0b5d.17f625e8-fe68-4847-87d1-ee47d4bcb285.privatelink.eastus.azmk8s.io we can see that it contains privatelink. Now what this means is that the AKS cluster in question is a private AKS cluster.
In a private cluster, the control plane or API server has internal IP addresses that are defined in the RFC1918 - Address Allocation for Private Internet document. By using a private cluster, you can ensure network traffic between your API server and your node pools remains on the private network only.
The control plane or API server is in an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)-managed Azure subscription. A customer's cluster or node pool is in the customer's subscription. The server and the cluster or node pool can communicate with each other through the Azure Private Link service in the API server virtual network and a private endpoint that's exposed in the subnet of the customer's AKS cluster.
Options for connecting to the private cluster
The API server endpoint has no public IP address. To manage the API server, you'll need to use a VM that has access to the AKS cluster's Azure Virtual Network (VNet). There are several options for establishing network connectivity to the private cluster.
Create a VM in the same Azure Virtual Network (VNet) as the AKS cluster.
Use a VM in a separate network and set up Virtual network peering. See the section below for more information on this option.
Use an Express Route or VPN connection.
Use the AKS Run Command feature.
AKS Run Command (Preview)
Today when you need to access a private cluster, you must do so within the cluster virtual network or a peered network or client machine. This usually requires your machine to be connected via VPN or Express Route to the cluster virtual network or a jumpbox to be created in the cluster virtual network. AKS run command allows you to remotely invoke commands in an AKS cluster through the AKS API. This feature provides an API that allows you to, for example, execute just-in-time commands from a remote laptop for a private cluster. This can greatly assist with quick just-in-time access to a private cluster when the client machine is not on the cluster private network while still retaining and enforcing the same RBAC controls and private API server.
Register the RunCommandPreview preview feature
To use the new Run Command API, you must enable the RunCommandPreview feature flag on your subscription.
Register the RunCommandPreview feature flag by using the az feature register command, as shown in the following example:
az feature register --namespace "Microsoft.ContainerService" --name "RunCommandPreview"
It takes a few minutes for the status to show Registered. Verify the registration status by using the [az feature list][az-feature-list] command:
az feature list -o table --query "[?contains(name, 'Microsoft.ContainerService/RunCommandPreview')].{Name:name,State:properties.state}"
When ready, refresh the registration of the Microsoft.ContainerService resource provider by using the [az provider register][az-provider-register] command:
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.ContainerService
Use AKS Run Command
Simple command
az aks command invoke -g <resourceGroup> -n <clusterName> -c "kubectl get pods -n kube-system"
Deploy a manifest by attaching the specific file
az aks command invoke -g <resourceGroup> -n <clusterName> -c "kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml -n default" -f deployment.yaml
Deploy a manifest by attaching a whole folder
az aks command invoke -g <resourceGroup> -n <clusterName> -c "kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml -n default" -f .
Perform a Helm install and pass the specific values manifest
az aks command invoke -g <resourceGroup> -n <clusterName> -c "helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami && helm repo update && helm install my-release -f values.yaml bitnami/nginx" -f values.yaml
Or you can connect to a Virtual Machine in a virtual network which is in the same virtual network as the AKS cluster or in a peered virtual network and run az aks get-credentials -g $ResourceGroupName -n $AKSClusterName and continue to use your kubectl commands.
Virtual network peering
To use virtual network peering, you need to set up a link between virtual network and the private DNS zone as shown below.
- Go to the node resource group in the Azure portal.
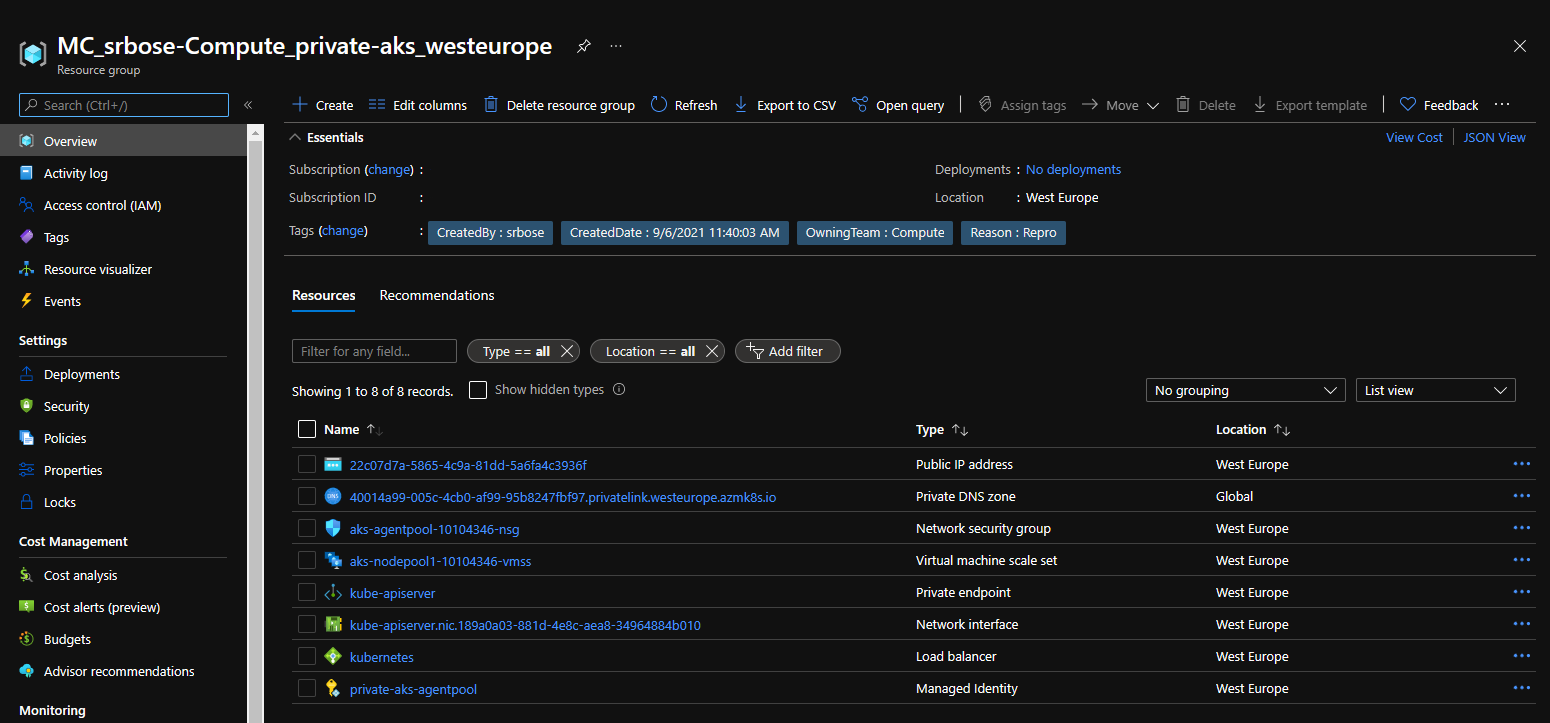
- Select the private DNS zone.
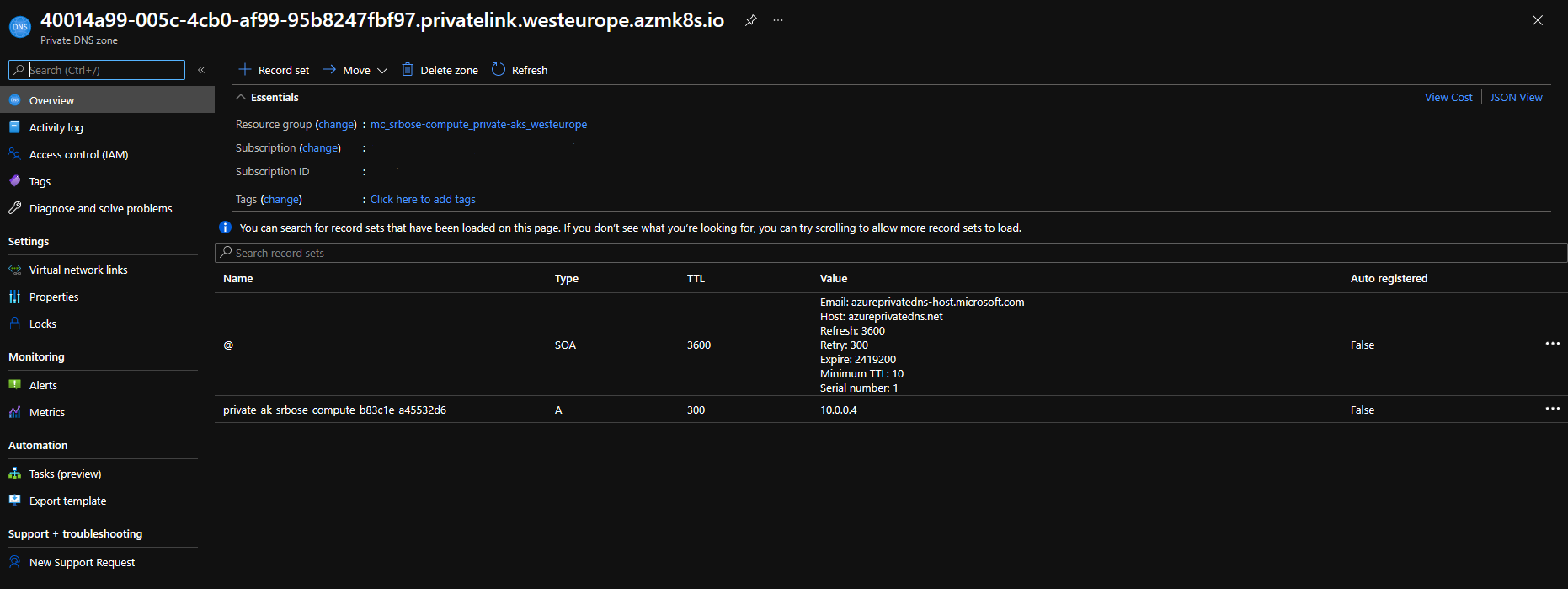
- In the left pane, select the Virtual network link.
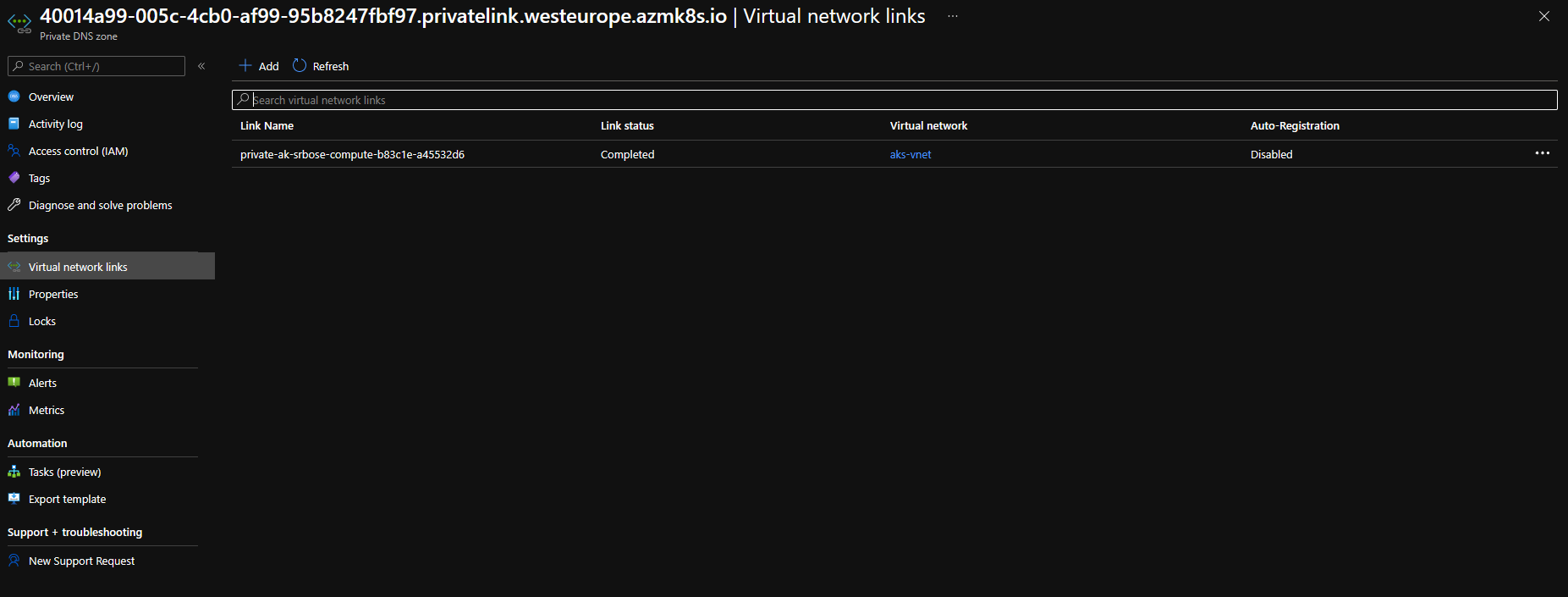
- Create a new link to add the virtual network of the VM to the private DNS zone. It takes a few minutes for the DNS zone link to become available.
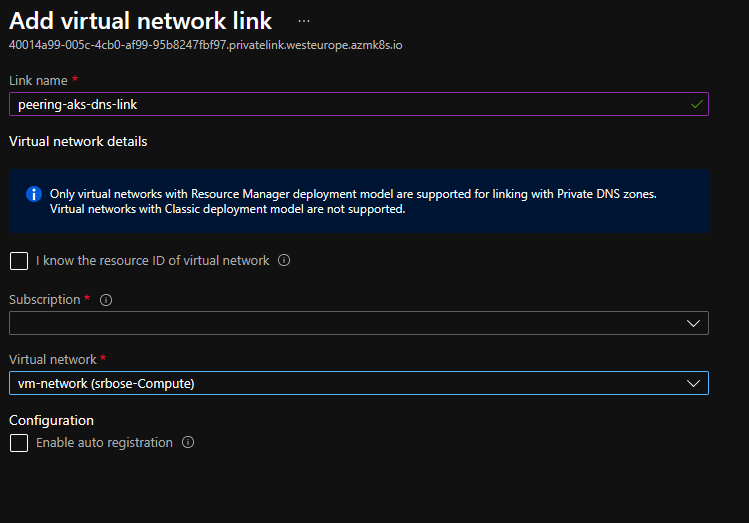
- In the Azure portal, navigate to the resource group that contains your cluster's virtual network.
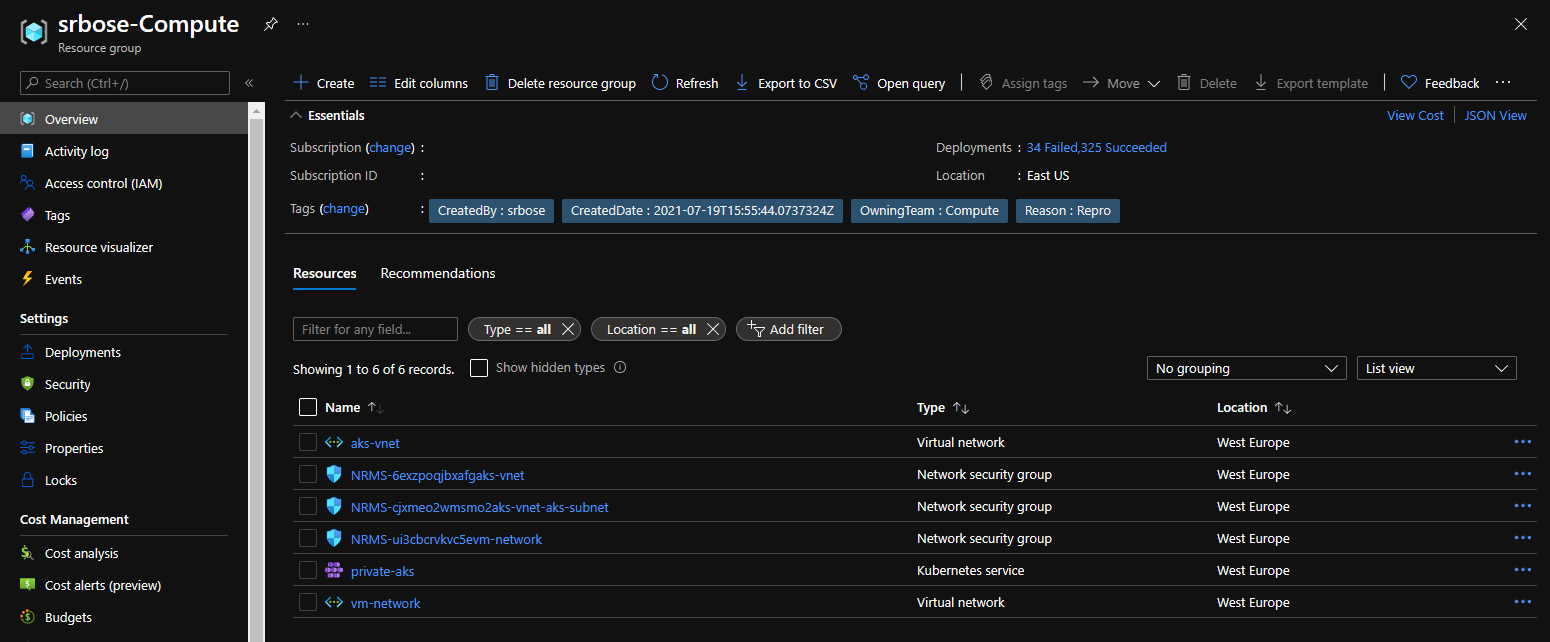
- In the right pane, select the virtual network. The virtual network name is in the form
aks-vnet-*if you are not using an existing virtual network [Reference] with the AKS cluster. (In my case it is an existing virtual network for the AKS cluster named namedaks-vnet) - In the left pane, select Peerings.
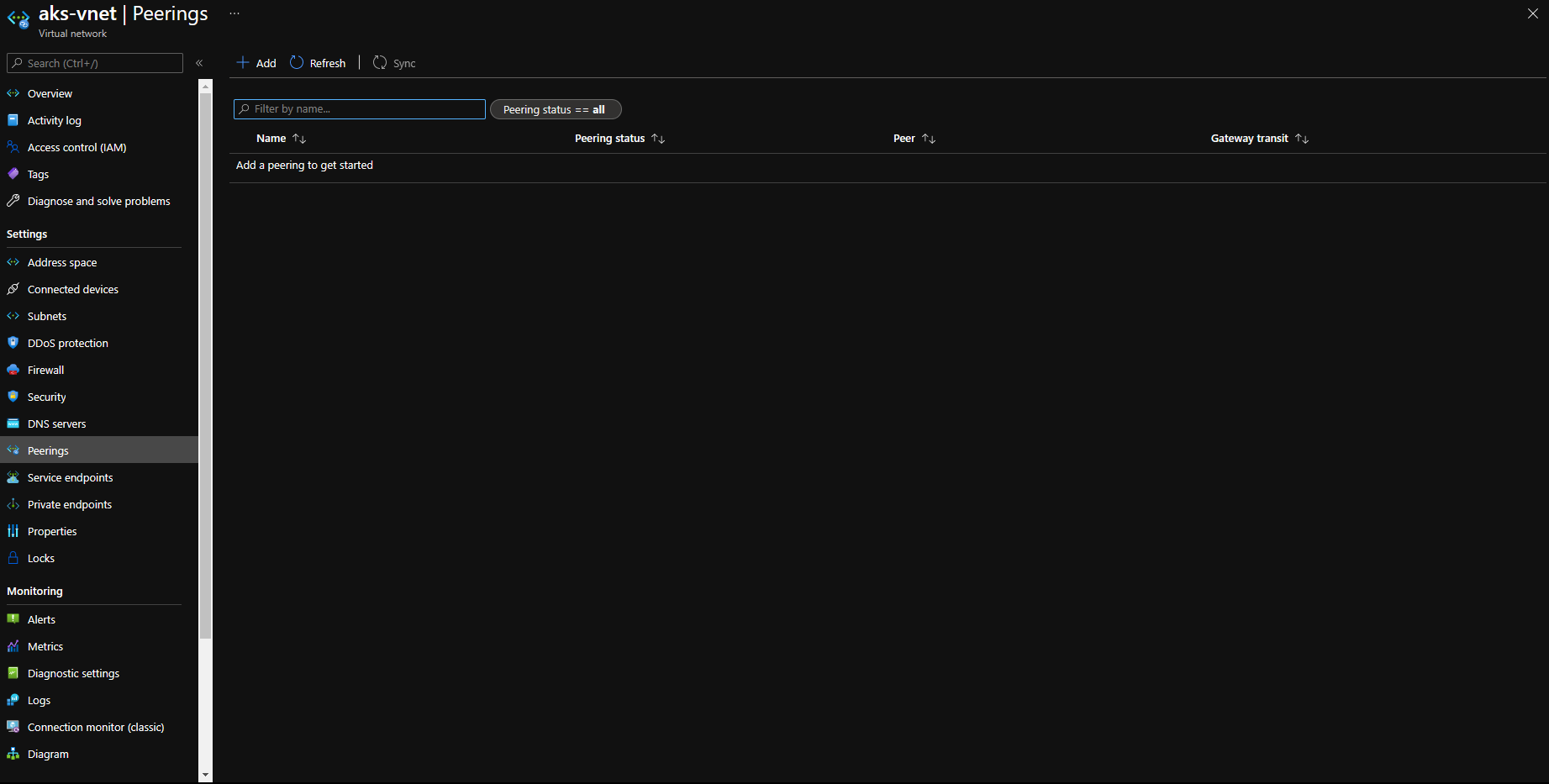
- Select Add, add the virtual network of the VM, and then create the peering.
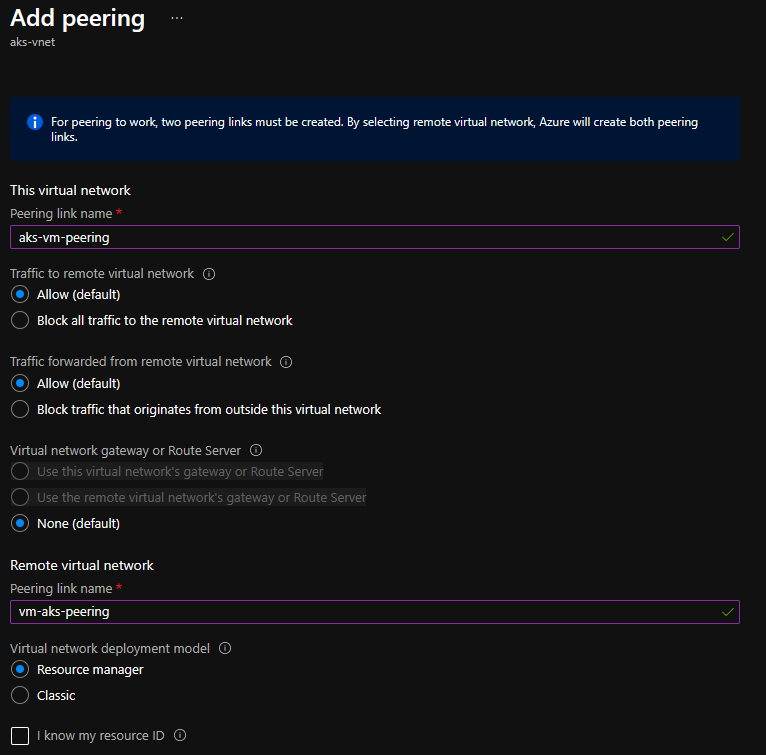
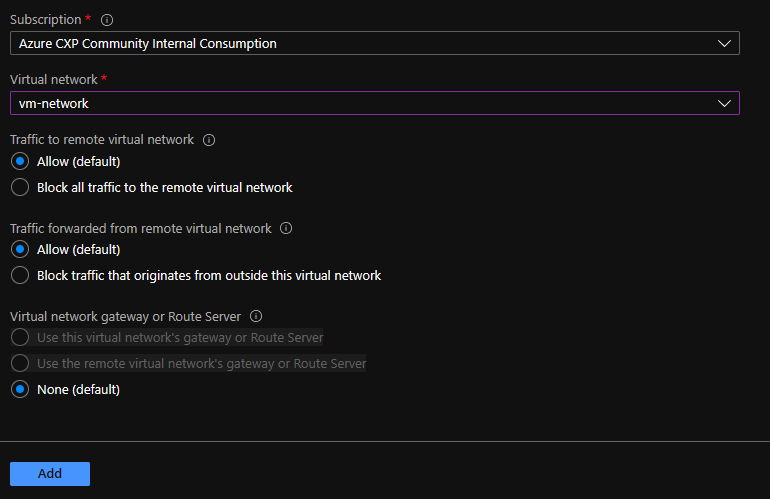 [If the address ranges on the AKS virtual network and the VM's virtual network clash, peering fails. For more information, see Virtual network peering.]
[If the address ranges on the AKS virtual network and the VM's virtual network clash, peering fails. For more information, see Virtual network peering.]
Hope this helps.
Please "Accept as Answer" if it helped, so that it can help others in the community looking for help on similar topics.


 for this AKS PaaS service. This private endpoint will get a non-routable IP and once done add the <private endpoint non-routable IP> + < Server: [ in your .kube/config file]> in your host file : c:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts.
for this AKS PaaS service. This private endpoint will get a non-routable IP and once done add the <private endpoint non-routable IP> + < Server: [ in your .kube/config file]> in your host file : c:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc\hosts.