Security defaults in Microsoft Entra ID
Security defaults make it easier to help protect your organization from identity-related attacks like password spray, replay, and phishing common in today's environments.
Microsoft is making these preconfigured security settings available to everyone, because we know managing security can be difficult. Based on our learnings more than 99.9% of those common identity-related attacks are stopped by using multifactor authentication and blocking legacy authentication. Our goal is to ensure that all organizations have at least a basic level of security enabled at no extra cost.
These basic controls include:
- Requiring all users to register for multifactor authentication
- Requiring administrators to do multifactor authentication
- Requiring users to do multifactor authentication when necessary
- Blocking legacy authentication protocols
- Protecting privileged activities like access to the Azure portal
- Organizations who want to increase their security posture, but don't know how or where to start.
- Organizations using the free tier of Microsoft Entra ID licensing.
- If you're an organization with Microsoft Entra ID P1 or P2 licenses, security defaults are probably not right for you.
- If your organization has complex security requirements, you should consider Conditional Access.
If your tenant was created on or after October 22, 2019, security defaults might be enabled in your tenant. To protect all of our users, security defaults are being rolled out to all new tenants at creation.
To help protect organizations, we're always working to improve the security of Microsoft account services. As part of this protection, customers are periodically notified for the automatic enablement of the security defaults if they:
- Don't have any Conditional Access policies
- Don't have premium licenses
- Aren’t actively using legacy authentication clients
After this setting is enabled, all users in the organization will need to register for multifactor authentication. To avoid confusion, refer to the email you received and alternatively you can disable security defaults after it's enabled.
To configure security defaults in your directory, you must be assigned at least the Security Administrator role. By default the first account in any directory is assigned a higher privileged role known as Global Administrator.
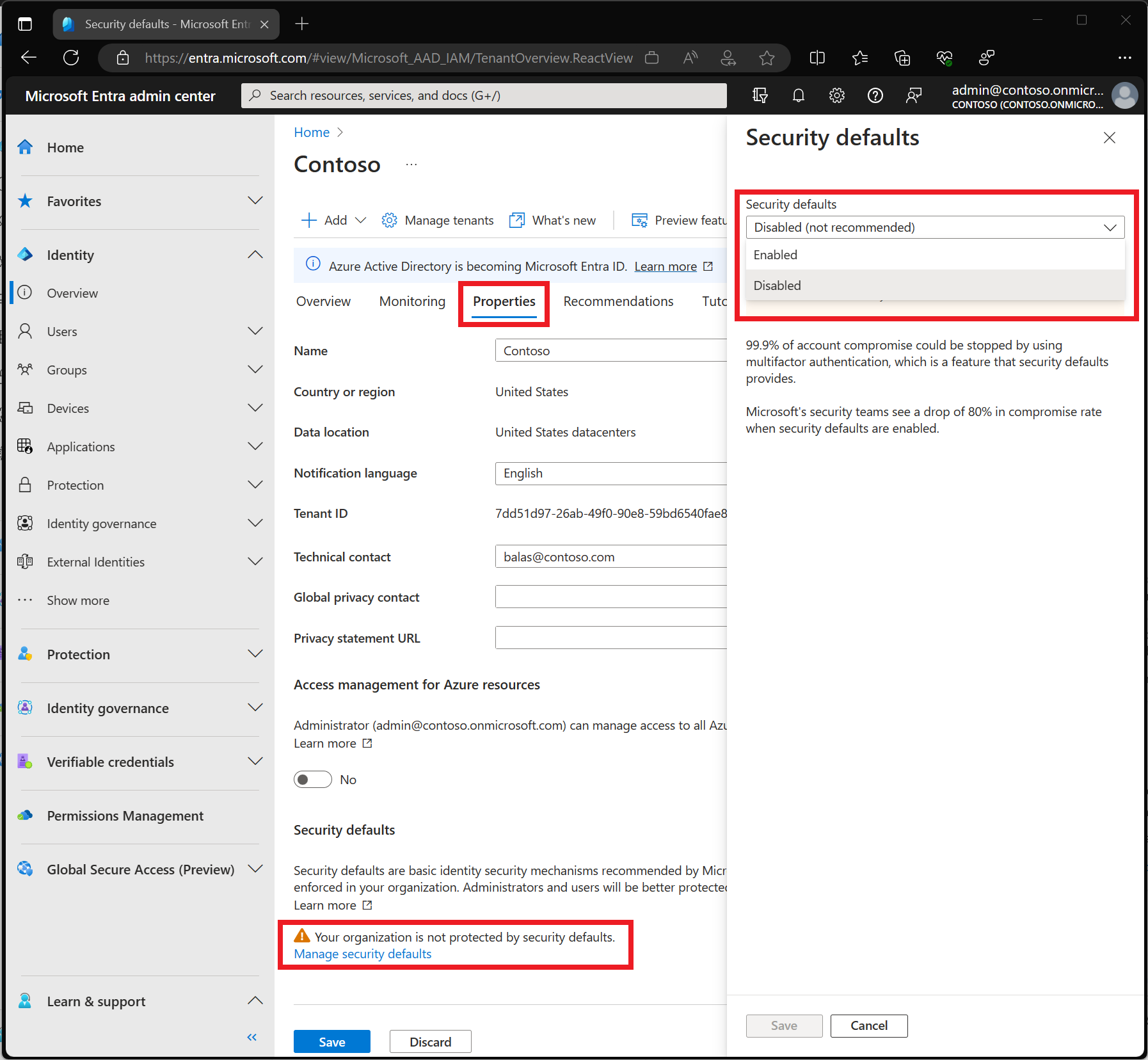
To enable security defaults:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Security Administrator.
- Browse to Identity > Overview > Properties.
- Select Manage security defaults.
- Set Security defaults to Enabled.
- Select Save.
As part of enabling security defaults, administrators should revoke all existing tokens to require all users to register for multifactor authentication. This revocation event forces previously authenticated users to authenticate and register for multifactor authentication. This task can be accomplished using the Revoke-AzureADUserAllRefreshToken PowerShell cmdlet.
Note
Starting July 29, 2024, new tenants may not have the 14-day grace period for users to register for MFA. We are making this change to help reduce the risk of account compromise during the 14-day window, as MFA can block over 99.2% of identity-based attacks.
All users have 14 days to register using the Microsoft Authenticator app or any app supporting OATH TOTP. After the 14 days pass, the user can't sign in until registration is completed. A user's 14-day period begins after their first successful interactive sign-in after enabling security defaults.
When users sign in and are prompted to perform multifactor authentication, they see a screen providing them with a number to enter in the Microsoft Authenticator app. This measure helps prevent users from falling for MFA fatigue attacks.
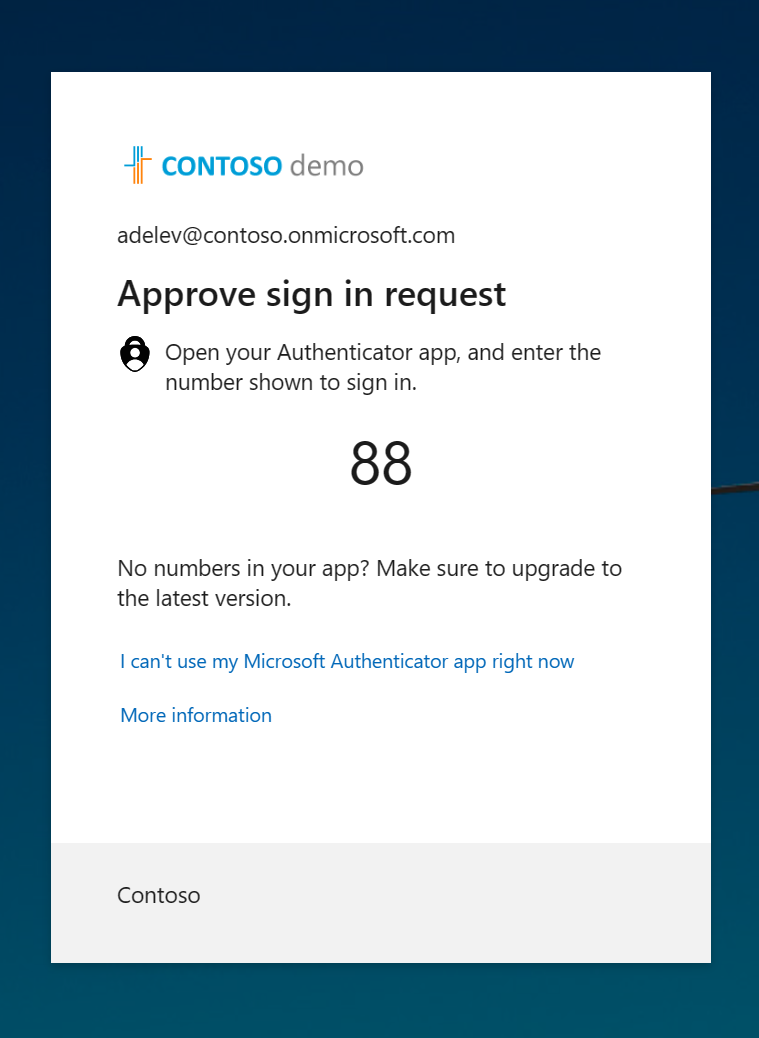
Administrators have increased access to your environment. Because of the power these highly privileged accounts have, you should treat them with special care. One common method to improve the protection of privileged accounts is to require a stronger form of account verification for sign-in, like requiring multifactor authentication.
Tip
Recommendations for your admins:
- Ensure all your admins sign in after enabling security defaults so that they can register for authentication methods.
- Have separate accounts for administration and standard productivity tasks to significantly reduce the number of times your admins are prompted for MFA.
After registration is finished, the following administrator roles will be required to do multifactor authentication every time they sign in:
- Global Administrator
- Application Administrator
- Authentication Administrator
- Billing Administrator
- Cloud Application Administrator
- Conditional Access Administrator
- Exchange Administrator
- Helpdesk Administrator
- Password Administrator
- Privileged Authentication Administrator
- Privileged Role Administrator
- Security Administrator
- SharePoint Administrator
- User Administrator
- Authentication Policy Administrator
- Identity Governance Administrator
We tend to think that administrator accounts are the only accounts that need extra layers of authentication. Administrators have broad access to sensitive information and can make changes to subscription-wide settings. But attackers frequently target end users.
After these attackers gain access, they can request access to privileged information for the original account holder. They can even download the entire directory to do a phishing attack on your whole organization.
One common method to improve protection for all users is to require a stronger form of account verification, such as multifactor authentication, for everyone. After users complete registration, they'll be prompted for another authentication whenever necessary. Microsoft decides when a user is prompted for multifactor authentication, based on factors such as location, device, role, and task. This functionality protects all registered applications, including SaaS applications.
Note
In case of B2B direct connect users, any multifactor authentication requirement from security defaults enabled in resource tenant will need to be satisfied, including multifactor authentication registration by the direct connect user in their home tenant.
To give your users easy access to your cloud apps, we support various authentication protocols, including legacy authentication. Legacy authentication is a term that refers to an authentication request made by:
- Clients that don't use modern authentication (for example, an Office 2010 client)
- Any client that uses older mail protocols such as IMAP, SMTP, or POP3
Today, most compromising sign-in attempts come from legacy authentication. Legacy authentication doesn't support multifactor authentication. Even if you have a multifactor authentication policy enabled on your directory, an attacker can authenticate by using an older protocol and bypass multifactor authentication.
After security defaults are enabled in your tenant, all authentication requests made by an older protocol will be blocked. Security defaults blocks Exchange Active Sync basic authentication.
Warning
Before you enable security defaults, make sure your administrators aren't using older authentication protocols. For more information, see How to move away from legacy authentication.
Organizations use various Azure services managed through the Azure Resource Manager API, including:
- Azure portal
- Microsoft Entra admin center
- Azure PowerShell
- Azure CLI
Using Azure Resource Manager to manage your services is a highly privileged action. Azure Resource Manager can alter tenant-wide configurations, such as service settings and subscription billing. Single-factor authentication is vulnerable to various attacks like phishing and password spray.
It's important to verify the identity of users who want to access Azure Resource Manager and update configurations. You verify their identity by requiring more authentication before you allow access.
After you enable security defaults in your tenant, any user accessing the following services must complete multifactor authentication:
- Azure portal
- Microsoft Entra admin center
- Azure PowerShell
- Azure CLI
This policy applies to all users who are accessing Azure Resource Manager services, whether they're an administrator or a user. This policy applies to Azure Resource Manager APIs such as accessing your subscription, VMs, storage accounts, and so on. This policy doesn't include Microsoft Entra ID or Microsoft Graph.
Note
Pre-2017 Exchange Online tenants have modern authentication disabled by default. In order to avoid the possibility of a login loop while authenticating through these tenants, you must enable modern authentication.
Note
The Microsoft Entra Connect synchronization account is excluded from security defaults and will not be prompted to register for or perform multifactor authentication. Organizations should not be using this account for other purposes.
It's critical to inform users about upcoming changes, registration requirements, and any necessary user actions. We provide communication templates and user documentation to prepare your users for the new experience and help to ensure a successful rollout. Send users to https://myprofile.microsoft.com to register by selecting the Security Info link on that page.
Security defaults users are required to register for and use multifactor authentication using the Microsoft Authenticator app using notifications. Users might use verification codes from the Microsoft Authenticator app but can only register using the notification option. Users can also use any third party application using OATH TOTP to generate codes.
Warning
Do not disable methods for your organization if you are using security defaults. Disabling methods may lead to locking yourself out of your tenant. Leave all Methods available to users enabled in the MFA service settings portal.
Any B2B guest users or B2B direct connect users that access your directory are treated the same as your organization's users.
If your organization is a previous user of per-user based multifactor authentication, don't be alarmed to not see users in an Enabled or Enforced status if you look at the multifactor authentication status page. Disabled is the appropriate status for users who are using security defaults or Conditional Access based multifactor authentication.
Organizations that choose to implement Conditional Access policies that replace security defaults must disable security defaults.
To disable security defaults in your directory:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a Security Administrator.
- Browse to Identity > Overview > Properties.
- Select Manage security defaults.
- Set Security defaults to Disabled (not recommended).
- Select Save.
While security defaults are a good baseline to start your security posture from, they don't allow for the customization that many organizations require. Conditional Access policies provide a full range of customization that more complex organizations require.
| Security defaults | Conditional Access | |
|---|---|---|
| Required licenses | None | At least Microsoft Entra ID P1 |
| Customization | No customization (on or off) | Fully customizable |
| Enabled by | Microsoft or administrator | Administrator |
| Complexity | Simple to use | Fully customizable based on your requirements |
Recommended steps when moving from security defaults
Organizations who would like to test out the features of Conditional Access can sign up for a free trial to get started.
After administrators disable security defaults, organizations should immediately enable Conditional Access policies to protect their organization. These policies should include at least those policies in the secure foundations category of Conditional Access templates. Organizations with Microsoft Entra ID P2 licenses that include Microsoft Entra ID Protection can expand on this list to include user and sign in risk-based policies to further strengthen their posture.
Microsoft recommends that organizations have two cloud-only emergency access accounts permanently assigned the Global Administrator role. These accounts are highly privileged and aren't assigned to specific individuals. The accounts are limited to emergency or "break glass" scenarios where normal accounts can't be used or all other administrators are accidentally locked out. These accounts should be created following the emergency access account recommendations.
- Blog: Introducing security defaults
- More information about licensing can be found on the Microsoft Entra pricing page.