Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Container Apps allows you to expose your container app to the public web, your virtual network (VNET), and other container apps within your environment by enabling ingress. Ingress settings are enforced through a set of rules that control the routing of external and internal traffic to your container app. When you enable ingress, you don't need to create an Azure Load Balancer, public IP address, or any other Azure resources to enable incoming HTTP requests or TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) traffic.
Ingress supports:
- External and internal ingress
- HTTP and TCP ingress types
- Domain names
- IP restrictions
- Authentication
- Traffic splitting between revisions
- Session affinity
Example ingress configuration showing ingress split between two revisions:
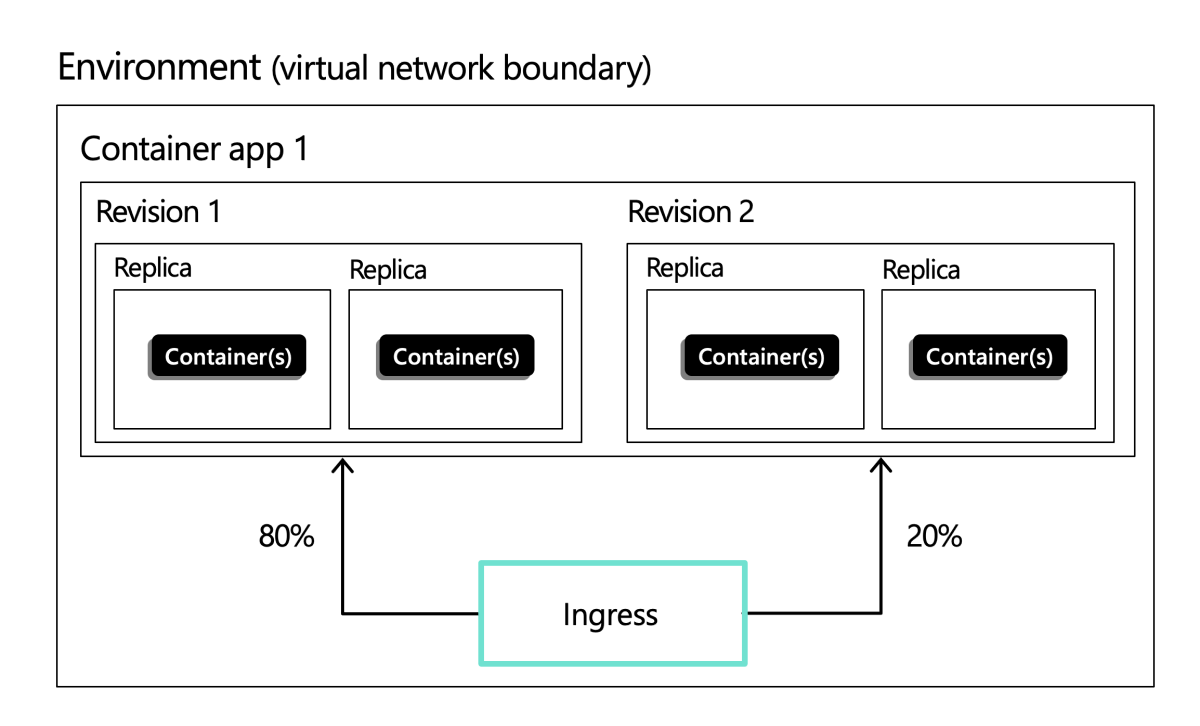
For configuration details, see Configure ingress.
External and internal ingress
When you enable ingress, you can choose between two types of ingress:
- External: Accepts traffic from both the public internet and your container app's internal environment.
- Internal: Allows only internal access from within your container app's environment.
Each container app within an environment can be configured with different ingress settings. For example, in a scenario with multiple microservice apps, to increase security you might have a single container app that receives public requests and passes the requests to a background service. In this scenario, you would configure the public-facing container app with external ingress and the internal-facing container app with internal ingress.
Protocol types
Container Apps supports two protocols for ingress: HTTP and TCP.
HTTP
With HTTP ingress enabled, your container app has:
- Support for TLS (Transport Layer Security) termination
- Support for HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2
- Support for WebSocket and gRPC
- HTTPS endpoints that always use TLS 1.2 or 1.3, terminated at the ingress point
- Endpoints that expose ports 80 (for HTTP) and 443 (for HTTPS)
- By default, HTTP requests to port 80 are automatically redirected to HTTPS on 443
- A fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
- Request time out is 240 seconds
HTTP headers
HTTP ingress adds headers to pass metadata about the client request to your container app. For example, the X-Forwarded-Proto header is used to identify the protocol that the client used to connect with the Container Apps service. The following table lists the HTTP headers that are relevant to ingress in Container Apps:
| Header | Description | Values |
|---|---|---|
X-Forwarded-Proto |
Protocol used by the client to connect with the Container Apps service. | http or https. This value is overwritten if sent by the client. |
X-Forwarded-For |
The IP addresses of the client and/or intermediate proxies that sent the request. | IP addresses of the senders. If specified in initial request, it is appended to. Only the rightmost IP is provided by Azure Container Apps. Any other values must be validated by the user to prevent IP spoofing. |
X-Forwarded-Client-Cert |
The client certificate if clientCertificateMode is set. |
Semicolon separated list of Hash, Cert, and Chain. For example: Hash=....;Cert="...";Chain="...";. This value is overwritten if sent by the client. |
TCP
Container Apps supports TCP-based protocols other than HTTP or HTTPS. For example, you can use TCP ingress to expose a container app that uses the Redis protocol.
Note
External TCP ingress is only supported for Container Apps environments that use a virtual network.
With TCP ingress enabled, your container app:
- Is accessible to other container apps in the same environment via its name (defined by the
nameproperty in the Container Apps resource) and exposed port number. - Is accessible externally via its fully qualified domain name (FQDN) and exposed port number if the ingress is set to
external.
Additional TCP ports
In addition to the main HTTP/TCP port for your container apps, you might expose additional TCP ports to enable applications that accept TCP connections on multiple ports.
Note
To use this feature, you must have the container apps CLI extension. Run az extension add -n containerapp in order to install the latest version of the container apps CLI extension.
The following apply to additional TCP ports:
More TCP ports can only be external if the app itself is set as external and the container app is using a virtual network.
Any externally exposed extra TCP ports must be unique across the entire Container Apps environment. This includes all external extra TCP ports, external main TCP ports, and 80/443 ports used by built-in HTTP ingress. If the extra ports are internal, you can share the same port across multiple apps.
If an exposed port isn't provided, the exposed port defaults to match the target port.
Each target port must be unique, and the same target port can't be exposed on different exposed ports.
There's a maximum of five additional ports per app. If additional ports are required, open a support request.
Only the main ingress port supports built-in HTTP features such as CORS and session affinity. When running HTTP on top of the extra TCP ports, these built-in features aren't supported.
Port number
36985is a reserved for internal health checks and isn't available to TCP applications or extra exposed ports on HTTP applications.
For more information on how to enable extra ports, see Configure ingress for your app.
Domain names
You can access your app in the following ways:
The default fully qualified domain name (FQDN): Each app in a Container Apps environment is automatically assigned an FQDN based on the environment's DNS (Domain Name System) suffix. This suffix is determined by the
CONTAINER_APP_ENV_DNS_SUFFIXenvironment variable. To customize an environment's DNS suffix, see Custom environment DNS Suffix.A custom domain name: You can configure a custom DNS domain for your Container Apps environment. For more information, see Custom domain names and certificates.
The app name: You can use the app name for communication between apps in the same environment.
To get the FQDN for your app, see Location.
IP restrictions
Container Apps supports IP restrictions for ingress. You can create rules to either configure IP addresses that are allowed or denied access to your container app. For more information, see Configure IP restrictions.
Authentication
Azure Container Apps provides built-in authentication and authorization features to secure your external ingress-enabled container app. For more information, see Authentication and authorization in Azure Container Apps.
You can configure your app to support client certificates (mTLS) for authentication and traffic encryption. For more information, see Configure client certificates.
For details on how to use peer-to-peer environment level network encryption, see networking configuration.
Traffic splitting
Containers Apps allows you to split incoming traffic between active revisions. When you define a splitting rule, you assign the percentage of inbound traffic to go to different revisions. For more information, see Traffic splitting.
Session affinity
Session affinity, also known as sticky sessions, is a feature that allows you to route all HTTP requests from a client to the same container app replica. This feature is useful for stateful applications that require a consistent connection to the same replica. For more information, see Session affinity.
Cross origin resource sharing (CORS)
By default, any requests made through the browser from a page to a domain that doesn't match the page's origin domain are blocked. To avoid this restriction for services deployed to Container Apps, you can enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS).
For more information, see Configure CORS in Azure Container Apps.