Connected Machine agent prerequisites
This article outlines the technical prerequisites, supported environments, and specifications required for successfully onboarding physical and virtual servers to Azure Arc-enabled servers. It serves as a reference for administrators and engineers planning to implement Azure Arc in their environments. Some onboarding methods may have more requirements.
Azure Arc-enabled servers support the installation of the Connected Machine agent on physical servers and virtual machines hosted outside of Azure, including on platforms like:
- VMware (including Azure VMware Solution)
- Azure Local
- Other cloud environments
Note
You shouldn't install Azure Arc on virtual machines hosted in Azure, Azure Stack Hub, or Azure Stack Edge, as they already have similar capabilities. You can, however, use an Azure VM to simulate an on-premises environment for testing purposes, only.
Take extra care when using Azure Arc on systems that are:
- Cloned
- Restored from backup as a second instance of the server
- Used to create a "golden image" from which other virtual machines are created
If two agents use the same source id, you'll encounter inconsistent behaviors when both agents try to act as one Azure resource. The best practice for these situations is to use an automation tool or script to onboard the server to Azure Arc after its cloned, restored from backup, or created from a golden image. For more information about cloning machines to use as Arc-enabled servers, see Cloning guidelines.
Note
For more information on using Azure Arc-enabled servers in VMware environments, see the VMware FAQ.
Azure Arc supports Windows and Linux operating systems as listed in the table. x86-64 (64-bit) architecture is fully supported, while only some features are supported on Arm64 as noted in the table. The Azure Connected Machine agent doesn't run on 32-bit architectures.
| Operating system | Version | x86-64 | ARM64 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlmaLinux | 8 | ✅ | ✅ | |
| AlmaLinux | 9 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Amazon Linux | 2 | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Amazon Linux | 2023 | ✅ | ✅ | see ARM64 architecture support |
| Azure Linux (CBL-Mariner) | 1.0 | ⚠️ | ❌ | Limited support, see Limited support operating systems |
| Azure Linux (CBL-Mariner) | 2.0 | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Azure Linux (CBL-Mariner) | 3.0 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Azure Local | ||||
| Centos | 7 | ⚠️ | ❌ | Limited support, see Limited support operating systems |
| Centos | 8 | ⚠️ | ❌ | Limited support, see Limited support operating systems |
| Debian | 10 | ⚠️ | ❌ | Limited support, see Limited support operating systems |
| Debian | 11 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Debian | 12 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Oracle Linux | 7 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Oracle Linux | 8 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Oracle Linux | 9 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) | 7 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) | 8 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) | 9 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Rocky Linux | 8 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Rocky Linux | 9 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) | 12 SP3-SP5 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) | 15 | ✅ | ✅ | see ARM64 architecture support |
| Ubuntu | 16.04 | ⚠️ | ❌ | Limited support, see Limited support operating systems |
| Ubuntu | 18.04 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Ubuntu | 20.04 | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Ubuntu | 22.04 | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Ubuntu | 24.04 | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Windows Client | 10 | ✅ | ❌ | see client operating system guidance |
| Windows Client | 11 | ✅ | ❌ | see client operating system guidance |
| Windows IoT Enterprise | 10 (22H2) | ✅ | ❌ | see client operating system guidance |
| Windows IoT Enterprise | 11 | ✅ | ❌ | see client operating system guidance |
| Windows IoT Enterprise LTSC | 10 (2021) | ✅ | ❌ | see client operating system guidance |
| Windows IoT Enterprise LTSC | 11 (2024) | ✅ | ❌ | see client operating system guidance |
| Windows Server | 2008 R2 SP1 | ⚠️ | ❌ | Limited support, see Limited support operating systems |
| Windows Server | 2012 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Windows Server | 2012 R2 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Windows Server | 2016 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Windows Server | 2019 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Windows Server | 2022 | ✅ | ❌ | |
| Windows Server | 2025 | ✅ | ❌ |
For Windows Server, both Desktop and Server Core experiences are supported. Azure Editions are supported on Azure Local.
The Azure Connected Machine agent isn't tested on operating systems hardened by the Center for Information Security (CIS) Benchmark.
Not all features, virtual machine extensions, and services are supported on Arm64 at this point. For full details on Arm64 compatibility or to check if other services are supported, refer to the documentation for the service you wish to use. The following are a few features known to be supported on Arm64:
- RunCommand
- CustomScriptExtension
- Azure Monitor Agent
Note
Machine configuration is not compatible with Arm64 at this time.
The following operating system versions have limited support. In each case, newer agent versions won't support these operating systems. The last agent version that supports the operating system is listed, and newer agent releases won't be made available for that system. The listed version is supported until the End of Arc Support Date. If critical security issues are identified that affect these agent versions, the fixes can be backported to the last supported version but new functionality or other bug fixes won't be.
| Operating system | Last supported agent version | End of Arc Support Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 | 1.39 Download | 03/31/2025 | Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 reached End of Support in January 2020. See End of support for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. |
| CentOS 7 | 1.44 | 07/15/2025 | |
| CentOS 8 | 1.44 | 07/15/2025 | |
| Debian 10 | 1.44 | 07/15/2025 | |
| Ubuntu 16.04 | 1.44 | 07/15/2025 | |
| Azure Linux (CBL-Mariner) 1.0 | 1.44 | 07/15/2025 |
To connect a new server running a Limited Support operating system to Azure Arc, you will need to make some adjustments to the onboarding script.
For Windows, modify the installation script to specify the version required, using the -AltDownload parameter.
Instead of
# Install the hybrid agent
& "$env:TEMP\install_windows_azcmagent.ps1";
Use
# Install the hybrid agent
& "$env:TEMP\install_windows_azcmagent.ps1" -AltDownload https://aka.ms/AzureConnectedMachineAgent-1.39;
For Linux, the relevant package repository will only contain releases that are applicable, so no special considerations are required.
The Azure Arc service and Azure Connected Machine Agent are supported on Windows 10 and 11 client operating systems only when using those computers in a server-like environment. That is, the computer should always be:
- Connected to the internet
- Connected to a power source
- Powered on
For example, a computer running Windows 11 that's responsible for digital signage, point-of-sale solutions, and general back office management tasks is a good candidate for Azure Arc. End-user productivity machines, such as a laptop, which may go offline for long periods of time, shouldn't use Azure Arc and instead should consider Microsoft Intune or Microsoft Configuration Manager.
Microsoft doesn't recommend running Azure Arc on short-lived (ephemeral) servers or virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) VMs. Azure Arc is designed for long-term management of servers and isn't optimized for scenarios where you are regularly creating and deleting servers. For example, Azure Arc doesn't know if the agent is offline due to planned system maintenance or if the VM was deleted, so it won't automatically clean up server resources that stopped sending heartbeats. As a result, you could encounter a conflict if you re-create the VM with the same name and there's an existing Azure Arc resource with the same name.
Azure Virtual Desktop on Azure Local doesn't use short-lived VMs and supports running Azure Arc in the desktop VMs.
This section details the software requirements for the Azure Connected Machine agent.
Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 requires PowerShell 4.0 or later. Microsoft recommends running the latest version, Windows Management Framework 5.1.
- systemd
- wget (to download the installation script)
- openssl
- gnupg (Debian-based systems, only)
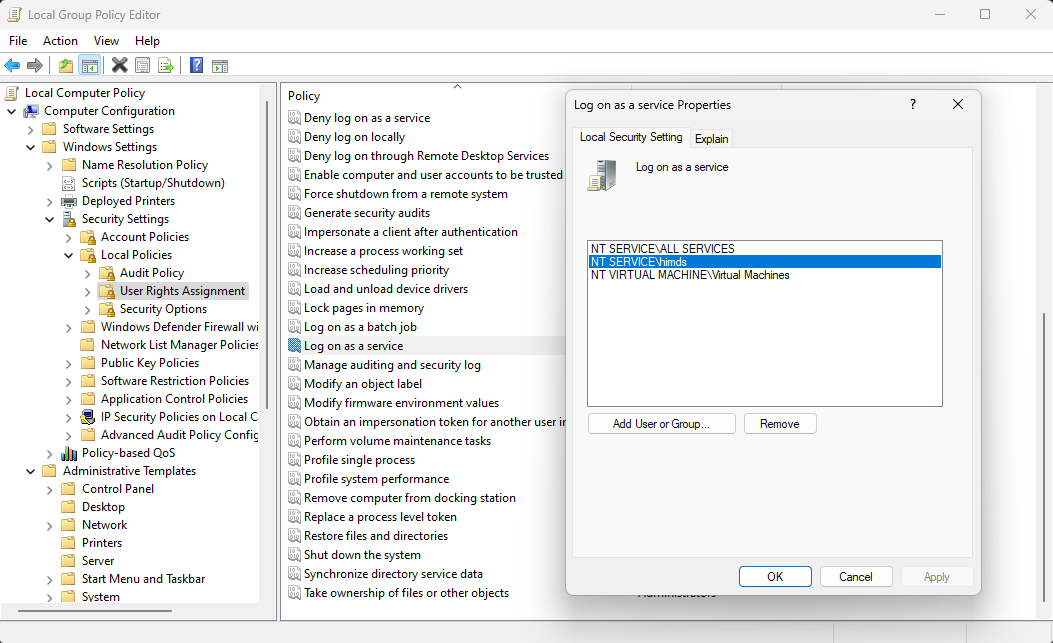
The Azure Hybrid Instance Metadata Service runs under a low-privileged virtual account, NT SERVICE\himds. This account needs the "log on as a service" right in Windows to run. In most cases, there's nothing you need to do because this right is granted to virtual accounts by default. However, if your organization uses Group Policy to customize this setting, you'll need to add NT SERVICE\himds to the list of accounts allowed to log on as a service.
You can check the current policy on your machine by opening the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) from the Start menu and navigating to the following policy item:
Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment > Log on as a service
Check if any of NT SERVICE\ALL SERVICES, NT SERVICE\himds, or S-1-5-80-4215458991-2034252225-2287069555-1155419622-2701885083 (the static security identifier for NT SERVICE\himds) are in the list. If none are in the list, you'll need to work with your Group Policy administrator to add NT SERVICE\himds to any policies that configure user rights assignments on your servers. The Group Policy administrator needs to make the change on a computer with the Azure Connected Machine agent installed so the object picker resolves the identity correctly. The agent doesn't need to be configured or connected to Azure to make this change.
You'll need the following Azure built-in roles for different aspects of managing connected machines:
- To onboard machines, you must have the Azure Connected Machine Onboarding or Contributor role for the resource group where you're managing the servers.
- To read, modify, and delete a machine, you must have the Azure Connected Machine Resource Administrator role for the resource group.
- To select a resource group from the drop-down list when using the Generate script method, you'll also need the Reader role for that resource group (or another role that includes Reader access).
- When associating a Private Link Scope with an Arc Server, you must have Microsoft.HybridCompute/privateLinkScopes/read permission on the Private Link Scope Resource.
The following Azure resource providers must be registered in your subscription to use Azure Arc-enabled servers. :
- Microsoft.HybridCompute
- Microsoft.GuestConfiguration
- Microsoft.HybridConnectivity
- Microsoft.AzureArcData (if you plan to Arc-enable SQL Servers)
- Microsoft.Compute (for Azure Update Manager and automatic extension upgrades)
You can register the resource providers using the following commands:
Azure PowerShell:
Connect-AzAccount
Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId [subscription you want to onboard]
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.HybridCompute
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.GuestConfiguration
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.HybridConnectivity
Register-AzResourceProvider -ProviderNamespace Microsoft.AzureArcData
Azure CLI:
az account set --subscription "{Your Subscription Name}"
az provider register --namespace 'Microsoft.HybridCompute'
az provider register --namespace 'Microsoft.GuestConfiguration'
az provider register --namespace 'Microsoft.HybridConnectivity'
az provider register --namespace 'Microsoft.AzureArcData'
You can also register the resource providers in the Azure portal.
- Review the networking requirements for deploying Azure Arc-enabled servers.
- Before you deploy the Azure Connected Machine agent and integrate with other Azure management and monitoring services, review the Planning and deployment guide.* To resolve problems, review the agent connection issues troubleshooting guide.