Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Azure Data Explorer offers ingestion from Event Hubs, a big data streaming platform and event ingestion service. Event Hubs can process millions of events per second in near real time.
In this article, you connect to an event hub and ingest data into Azure Data Explorer. For an overview on ingesting from Event Hubs, see Azure Event Hubs data connection.
To learn how to create the connection using the Kusto software developer kits (SDKs), see Create an Event Hubs data connection with SDKs.
For code samples based on previous SDK versions, see the archived article.
Warning
The Get Data Wizard doesn't support creating a data connection to Event Hubs through private endpoints or managed private endpoints. To create a data connection from the Azure portal, follow the instructions in the Portal - Azure Event Hubs page tab.
Create an event hub data connection
In this section, you establish a connection between the event hub and your Azure Data Explorer table. As long as this connection is in place, data is transmitted from the event hub into your target table. If the event hub is moved to a different resource or subscription, you need to update or recreate the connection.
Prerequisites
- A Microsoft account or a Microsoft Entra user identity. An Azure subscription isn't required.
- An Azure Data Explorer cluster and database. Create a cluster and database.
- Streaming ingestion must be configured on your Azure Data Explorer cluster.
Get data
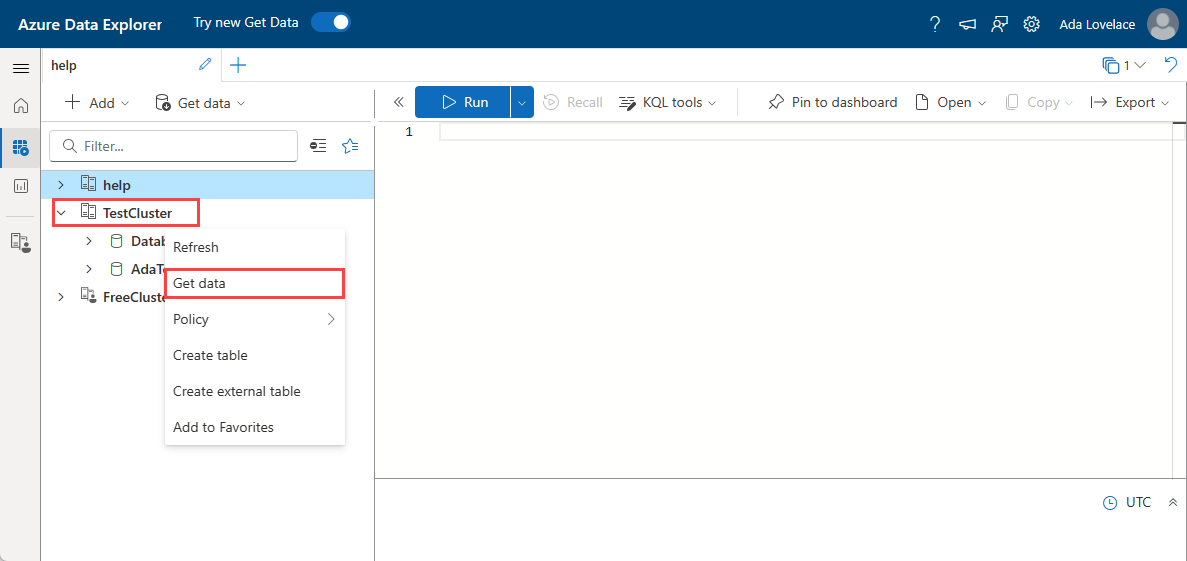
From the left menu, select Query.
Right-click on the database where you want to ingest the data. Select Get data.
Source
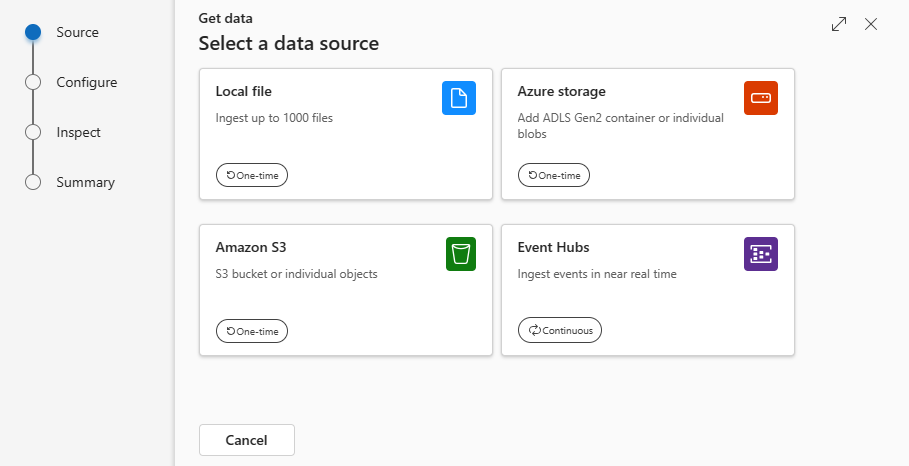
In the Get data window, the Source tab is selected.
Select the data source from the available list. In this example, you're ingesting data from Event Hubs.
Configure
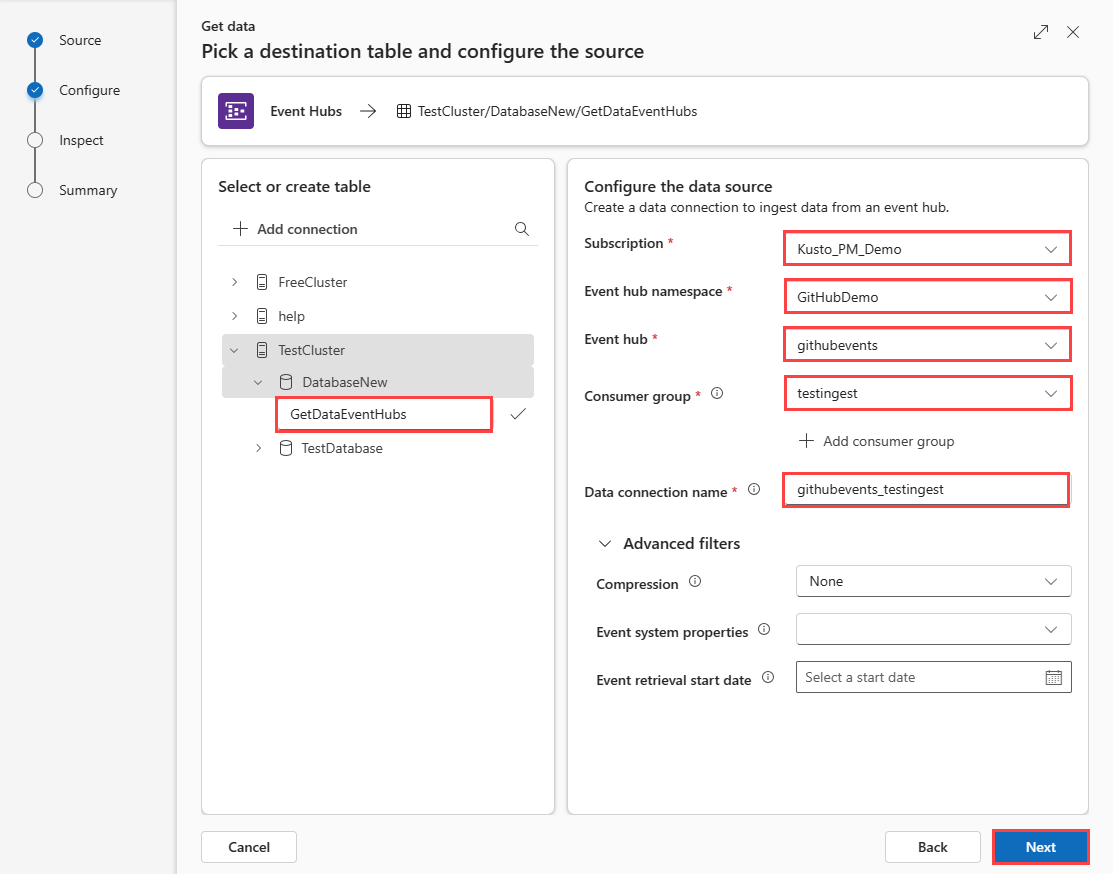
Select a target database and table. If you want to ingest data into a new table, select + New table and enter a table name.
Note
Table names can be up to 1,024 characters including spaces, alphanumeric, hyphens, and underscores. Special characters aren't supported.
Fill in the following fields:
Setting Field description Subscription The subscription ID where the event hub resource is located. Event hub namespace The name that identifies your namespace. Event hub The event hub you wish to Consumer group The consumer group defined in your event Data connection name The name that identifies your data connection. Advanced filters Compression The compression type of the event hub messages payload. Event system properties The event hub system properties. If there are multiple records per event message, the system properties are added to the first one. When adding system properties, create or update table schema and mapping to include the selected properties. Event retrieval start date The data connection retrieves existing Event Hubs events created after the Event retrieval start date. Only events retained by Event Hubs's retention period can be retrieved. If the Event retrieval start date isn't specified, the default time is the time at which the data connection is created. Select Next
Inspect
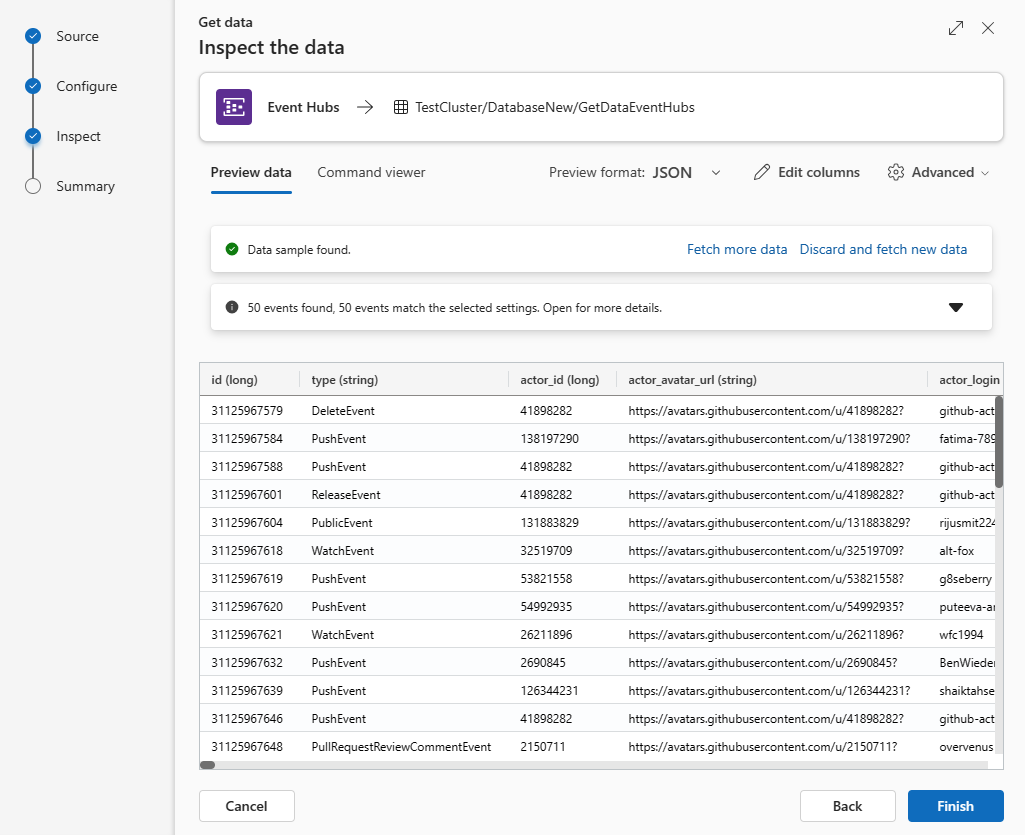
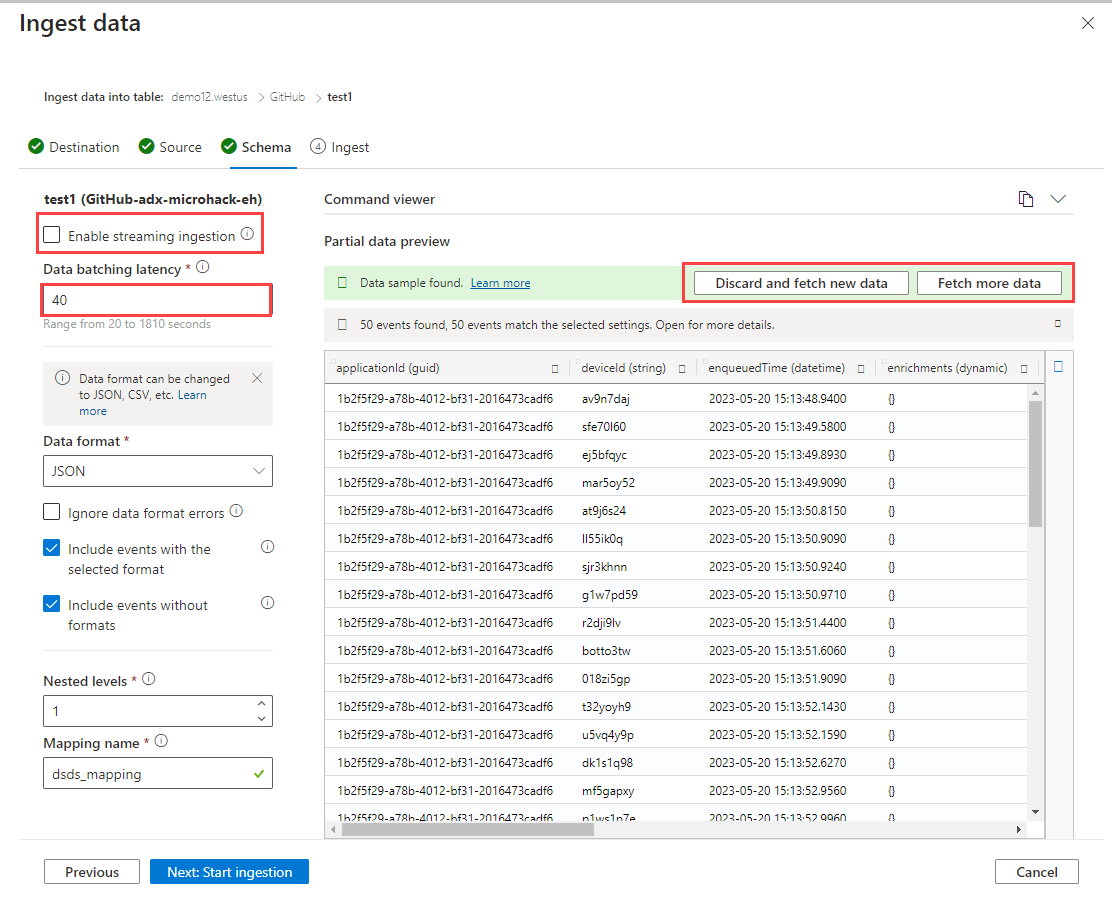
The Inspect tab opens with a preview of the data.
To complete the ingestion process, select Finish.
Optionally:
If the data you see in the preview window isn't complete, you might need more data to create a table with all necessary data fields. Use the following commands to fetch new data from your event hub:
Discard and fetch new data: Discards the data presented and searches for new events.
Fetch more data: Searches for more events in addition to the events already found.
Note
To see a preview of your data, your event hub must be sending events.
Select Command viewer to view and copy the automatic commands generated from your inputs.
Use the Schema definition file dropdown to change the file that the schema is inferred from.
Change the automatically inferred data format by selecting the desired format from the dropdown. See Data formats supported by Azure Data Explorer for ingestion.
Explore Advanced options based on data type.
Edit columns
Note
- For tabular formats (CSV, TSV, PSV), you can't map a column twice. To map to an existing column, first delete the new column.
- You can't change an existing column type. If you try to map to a column having a different format, you may end up with empty columns.
The changes you can make in a table depend on the following parameters:
- Table type is new or existing
- Mapping type is new or existing
| Table type | Mapping type | Available adjustments |
|---|---|---|
| New table | New mapping | Rename column, change data type, change data source, mapping transformation, add column, delete column |
| Existing table | New mapping | Add column (on which you can then change data type, rename, and update) |
| Existing table | Existing mapping | none |
Mapping transformations
Some data format mappings (Parquet, JSON, and Avro) support simple ingest-time transformations. To apply mapping transformations, create or update a column in the Edit columns window.
Mapping transformations can be performed on a column of type string or datetime, with the source having data type int or long. Supported mapping transformations are:
- DateTimeFromUnixSeconds
- DateTimeFromUnixMilliseconds
- DateTimeFromUnixMicroseconds
- DateTimeFromUnixNanoseconds
Advanced options based on data type
Tabular (CSV, TSV, PSV):
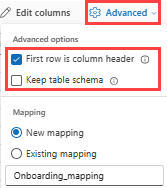
If you're ingesting tabular formats in an existing table, you can select Advanced > Keep current table schema. Tabular data doesn't necessarily include the column names that are used to map source data to the existing columns. When this option is checked, mapping is done by-order, and the table schema remains the same. If this option is unchecked, new columns are created for incoming data, regardless of data structure.
To use the first row as column names, select Advanced > First row is column header.
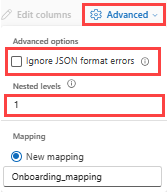
JSON:
To determine column division of JSON data, select Advanced > Nested levels, from 1 to 100.
If you select Advanced > Ignore data format errors, the data is ingested in JSON format. If you leave this check box unselected, the data is ingested in multijson format.
Summary
In the Data preparation window, all three steps are marked with green check marks when data ingestion finishes successfully. You can view the commands that were used for each step, or select a card to query, visualize, or drop the ingested data.
Remove an event hub data connection
Related content
- Check the connection with the Event hub sample message app
- Query data in the Web UI