This article provides answers to some of the most common questions about how to run Azure HDInsight.
To review the HDInsight clusters types, and the provisioning methods, see Set up clusters in HDInsight with Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, and more.
To learn more about deleting a cluster when it's no longer in use, see Delete a HDInsight cluster.
Try to leave at least 30 to 60 minutes between create and delete operations. Otherwise the operation may fail with the following error message:
Conflict (HTTP Status Code: 409) error when attempting to delete a cluster immediately after creation of a cluster. If you encounter this error, wait until the newly created cluster is in operational state before attempting to delete it.
The appropriate number of cores and other configuration options depend on various factors.
For more information, see Capacity planning for HDInsight clusters.
- Recommend setting up HDInsight clusters with a Custom Ambari DB to improve the cluster scalability.
- Use Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 to create HDInsight clusters to take advantage of higher bandwidth and other performance characteristics of Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2.
- Headnodes should be sufficiently large to accommodate multiple master services running on these nodes.
- Some specific workloads such as Interactive Query will also need larger Zookeeper nodes. Please consider minimum of eight core VMs.
- In the case of Hive and Spark, use External Hive metastore.
Yes. To install more components or customize cluster configuration, use:
Scripts during or after creation. Scripts are invoked via script action. Script action is a configuration option you can use from the Azure portal, HDInsight Windows PowerShell cmdlets, or the HDInsight .NET SDK. This configuration option can be used from the Azure portal, HDInsight Windows PowerShell cmdlets, or the HDInsight .NET SDK.
HDInsight Application Platform to install applications.
For a list of supported components, see What are the Apache Hadoop components and versions available with HDInsight?
If you upgrade built-in components or applications that are preinstalled on your cluster, the resulting configuration won't be supported by Microsoft. These system configurations haven't been tested by Microsoft. Try to use a different version of the HDInsight cluster that may already have the upgraded version of the component preinstalled.
For example, upgrading Hive as an individual component isn't supported. HDInsight is a managed service, and many services are integrated with Ambari server and tested. Upgrading a Hive on its own causes the indexed binaries of other components to change, and will cause component integration issues on your cluster.
No, it's not possible to run Apache Kafka and Apache Spark on the same HDInsight cluster. Create separate clusters for Kafka and Spark to avoid resource contention issues.
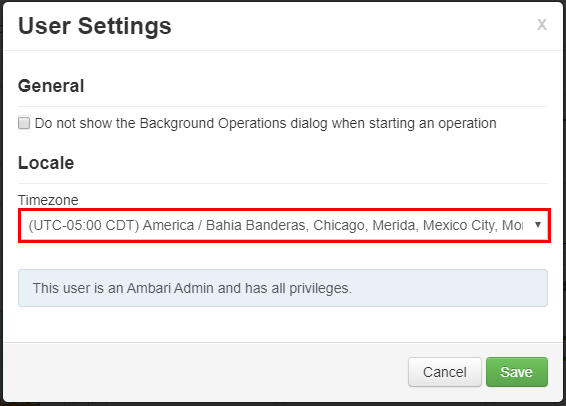
Open the Ambari Web UI at
https://CLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net, where CLUSTERNAME is the name of your cluster.In the upper-right corner, select admin | Settings.
In the User Settings window, select the new timezone from the Timezone drop down, and then select Save.
To migrate from SQL Server to Azure SQL Database, see Tutorial: Migrate SQL Server to a single database or pooled database in Azure SQL Database offline using DMS.
It depends on the type of metastore that your cluster is configured to use.
For a default metastore: The default metastore is part of the cluster lifecycle. When you delete a cluster, the corresponding metastore and metadata are also deleted.
For a custom metastore: The lifecycle of the metastore isn't tied to a cluster's lifecycle. So, you can create and delete clusters without losing metadata. Metadata such as your Hive schemas persists even after you delete and re-create the HDInsight cluster.
For more information, see Use external metadata stores in Azure HDInsight.
No, the policy definition is in the Ranger database, so migrating the Ranger database migrates its policy.
Can you migrate a Hive metastore from an Enterprise Security Package (ESP) cluster to a non-ESP cluster, and the other way around?
Yes, you can migrate a Hive metastore from an ESP to a non-ESP cluster.
A Hive metastore is used to store the metadata for data sources that are used by the Hive server. The size requirements depend partly on the number and complexity of your Hive data sources. These items can't be estimated up front. As outlined in Hive metastore guidelines, you can start with a S2 tier. The tier provides 50 DTU and 250 GB of storage, and if you see a bottleneck, scale up the database.
No, Microsoft supports only Azure SQL Database as an external custom metastore.
Yes, you can share custom metastore across multiple clusters as long as they're using the same version of HDInsight.
If you block ports 22 and port 23, you won't have SSH access to the cluster. These ports aren't used by HDInsight service.
For more information, see the following documents:
Yes, you can deploy more virtual machine within the same subnet as a HDInsight cluster. The following configurations are possible:
Edge nodes: You can add another edge node to the cluster, as described in Use empty edge nodes on Apache Hadoop clusters in HDInsight.
Standalone nodes: You can add a standalone virtual machine to the same subnet and access the cluster from that virtual machine by using the private end point
https://<CLUSTERNAME>-int.azurehdinsight.net. For more information, see Control network traffic.
No, storing data on a local disk isn't a good idea. If the node fails, all data stored locally will be lost. We recommend storing data in Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 or Azure Blob storage, or by mounting an Azure Files share for storing the data.
No, you can't. The virtual network should be specified at the time of provisioning. If no virtual network is specified during provisioning, the deployment creates an internal network that isn't accessible from outside. For more information, see Add HDInsight to an existing virtual network.
For information on malware protection, see Microsoft Antimalware for Azure Cloud Services and Virtual Machines.
Create a Kerberos keytab for your domain username. You can later use this keytab to authenticate to remote domain-joined clusters without entering a password. The domain name is uppercase:
ktutil
ktutil: addent -password -p <username>@<DOMAIN.COM> -k 1 -e aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96
Password for <username>@<DOMAIN.COM>: <password>
ktutil: wkt <username>.keytab
ktutil: q
If your TenantName & DomainName are different (example TenantName – bob@CONTOSO.ONMICROSOFT.COM & DomainName – bob@CONTOSOMicrosoft.ONMICROSOFT.COM), you need to add a SALT value using the -s option.
- Use an interactive Kerberos sign-in to determine the proper salt value for the keytab. Interactive Kerberos sign-in uses the highest encryption by default. Tracing should be enabled to observe the salt. Below is a sample Kerberos sign-in:
$ KRB5_TRAACE=/dev/stdout kinit <username> -V
- Look through the output for the salt "......." line.
- Use this salt value when creating the keytab.
ktutil
ktutil: addent -password -p <username>@<DOMAIN.COM> -k 1 -e aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96 -s <SALTvalue>
Password for <username>@<DOMAIN.COM>: <password>
ktutil: wkt <username>.keytab
ktutil: q
Enable Microsoft Entra Domain Services before you can create a HDInsight cluster with ESP. Open-source Hadoop relies on Kerberos for Authentication (as opposed to OAuth).
To join VMs to a domain, you must have a domain controller. Microsoft Entra Domain Services is the managed domain controller, and is considered an extension of Microsoft Entra ID. Microsoft Entra Domain Services provides all the Kerberos requirements to build a secure Hadoop cluster in a managed way. HDInsight as a managed service integrates with Microsoft Entra Domain Services to provide security.
Can I use a self-signed certificate in a Microsoft Entra Domain Services secure LDAP setup and provision an ESP cluster?
Using a certificate issued by a certificate authority is recommended. But using a self-signed certificate is also supported on ESP. For more information, see:
No, DAS is not supported on ESP clusters.
For auditing requirements, Microsoft recommends enabling Azure Monitor logs as described in Use Azure Monitor logs to monitor HDInsight clusters.
Clamscan is the antivirus software that runs on the HDInsight cluster and is used by Azure security (azsecd) to protect your clusters from virus attacks. Microsoft strongly recommends that users refrain from making any changes to the default Clamscan configuration.
This process doesn't interfere with or take any cycles away from other processes. It will always yield to other process. CPU spikes from Clamscan should be seen only when the system is idle.
In scenarios in which you must control the schedule, you can use the following steps:
Disable automatic execution using the following command:
sudo
usr/local/bin/azsecd config -s clamav -d Disabledsudo service azsecd restartAdd a Cron job that runs the following command as root:
/usr/local/bin/azsecd manual -s clamav
For more information about how to set up and run a cron job, see How do I set up a Cron job?
LLAP is enabled for security reasons (Apache Ranger), not performance. Use larger node VMs to accommodate for the resource usage of LLAP (for example, minimum D13V2).
There are two ways to achieve this goal:
1- You can recreate the cluster and add the additional group at the time of cluster creation. If you're using scoped synchronization in Microsoft Entra Domain Services, make sure group B is included in the scoped synchronization.
2- Add the group as a nested sub group of the previous group that was used to create the ESP cluster. For example, if you've created an ESP cluster with group A, you can later on add group B as a nested subgroup of A and after approximately one hour it will be synced and available in the cluster automatically.
Can I add an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 to an existing HDInsight cluster as an additional storage account?
No, it's currently not possible to add an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 storage account to a cluster that has blob storage as its primary storage. For more information, see Compare storage options.
You can find your settings in Data Lake Storage Gen1 access under your cluster properties in the Azure portal. For more information, see Verify cluster setup.
Do one of the following actions:
Find the size of the /user/hive/.Trash/ folder on the HDInsight cluster, using the following command line:
hdfs dfs -du -h /user/hive/.Trash/
To audit blob storage accounts, configure monitoring using the procedure at Monitor a storage account in the Azure portal. An HDFS-audit log provides only auditing information for the local HDFS filesystem only (hdfs://mycluster). It doesn't include operations that are done on remote storage.
Run a script similar to the following shell script on your head node:
for i in cat filenames.txt
do
hadoop fs -get $i <local destination>
done
Note
The file filenames.txt will have the absolute path of the files in the blob containers.
Currently, no Ranger plugin exists for blob storage and Azure Data Lake Storage Gen1 or Gen2. For ESP clusters, you should use Azure Data Lake Storage. You can at least set fine-grain permissions manually at the file system level using HDFS tools. Also, when using Azure Data Lake Storage, ESP clusters will do some of the file system access control using Microsoft Entra ID at the cluster level.
You can assign data access policies to your users' security groups by using the Azure Storage Explorer. For more information, see:
No. You can't increase the disk size of any worker node. So the only way to increase disk size is to drop the cluster and recreate it with larger worker VMs. Don't use HDFS for storing any of your HDInsight data, because the data is deleted if you delete your cluster. Instead, store your data in Azure. Scaling up the cluster can also add additional capacity to your HDInsight cluster.
After you create an edge node, you can connect to it by using SSH on port 22. You can find the name of the edge node from the cluster portal. The names usually end with -ed.
You use persisted scripts to customize new worker nodes added to the cluster through scaling operations. Persisted scripts don't apply to edge nodes.
You can use the following REST endpoints to pull the necessary information in JSON format. Use basic authentication headers to make the requests.
Tez Query View: https://<cluster name>.azurehdinsight.net/ws/v1/timeline/HIVE_QUERY_ID/Tez Dag View: https://<cluster name>.azurehdinsight.net/ws/v1/timeline/TEZ_DAG_ID/
To negotiate proper authentication tokens with your Microsoft Entra user, go through the gateway by using the following format:
- https://
<cluster dnsname>.azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/testclusterdem/stack_versions/1/repository_versions/1
If you call the Curl command in the same virtual network or a peered virtual network, the command is:
curl -u <cluster login username> -sS -G
http://<headnodehost>:8080/api/v1/clusters/<ClusterName>/services/YARN/components/NODEMANAGER?fields=metrics/cpu
If you call the command from outside the virtual network or from a non-peered virtual network, the command format is:
For a non-ESP cluster:
curl -u <cluster login username> -sS -G https://<ClusterName>.azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/<ClusterName>/services/YARN/components/NODEMANAGER?fields=metrics/cpuFor an ESP cluster:
curl -u <cluster login username>-sS -G https://<ClusterName>.azurehdinsight.net/api/v1/clusters/<ClusterName>/services/YARN/components/NODEMANAGER?fields=metrics/cpu
Note
Curl prompts you for a password. You must enter a valid password for the cluster sign-in username.
For more information about pricing and FAQ related to billing, see the Azure HDInsight Pricing page.
HDInsight cluster billing starts once a cluster is created and stops when the cluster is deleted. Billing is pro-rated per minute.
For information about how to cancel your subscription, see Cancel your Azure subscription.
For information about your subscription after it's canceled, see What happens after I cancel my subscription?
Why does the Hive version appear as 1.2.1000 instead of 2.1 in the Ambari UI even though I'm running a HDInsight 3.6 cluster?
Although only 1.2 appears in the Ambari UI, HDInsight 3.6 contains both Hive 1.2 and Hive 2.1.
For information about integration capabilities of stream processing, see Choosing a stream processing technology in Azure.
Is there a way to dynamically kill the head node of the cluster when the cluster is idle for a specific period?
You can't do this action with HDInsight clusters. You can use Azure Data Factory for these scenarios.
For compliance information, see the Microsoft Trust Center.