Training
Module
Configure network security groups - Training
Learn how to implement network security groups, and ensure network security group rules are correctly applied.
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
When you use security rules in network security groups (NSGs), you can filter the type of network traffic that flows in and out of virtual network subnets and network interfaces. To learn more about NSGs, see Network security group overview. Next, complete the Filter network traffic tutorial to gain some experience with NSGs.
If you don't have an Azure account with an active subscription, create one for free. Complete one of these tasks before you start the remainder of this article:
Portal users: Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure account.
PowerShell users: Either run the commands in Azure Cloud Shell or run PowerShell locally from your computer. Cloud Shell is a free interactive shell that you can use to run the steps in this article. It has common Azure tools that are preinstalled and configured to use with your account. On the Cloud Shell browser tab, find the Select environment dropdown list. Then select PowerShell if it isn't already selected.
If you're running PowerShell locally, use Azure PowerShell module version 1.0.0 or later. Run Get-Module -ListAvailable Az.Network to find the installed version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install Azure PowerShell module. Run Connect-AzAccount to sign in to Azure.
Azure CLI users: Either run the commands in Cloud Shell or run the Azure CLI locally from your computer. Cloud Shell is a free interactive shell that you can use to run the steps in this article. It has common Azure tools that are preinstalled and configured to use with your account. On the Cloud Shell browser tab, find the Select environment dropdown list. Then select Bash if it isn't already selected.
If you're running the Azure CLI locally, use Azure CLI version 2.0.28 or later. Run az --version to find the installed version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install the Azure CLI. Run az login to sign in to Azure.
Assign the Network Contributor role or a custom role with the appropriate permissions.
You can create, view all, view details of, change, and delete an NSG. You can also associate or dissociate an NSG from a network interface or a subnet.
The number of NSGs that you can create for each Azure region and subscription is limited. To learn more, see Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Select Network security groups in the search results.
Select + Create.
On the Create network security group page, under the Basics tab, enter or select the following values:
| Setting | Action |
|---|---|
| Project details | |
| Subscription | Select your Azure subscription. |
| Resource group | Select an existing resource group, or create a new one by selecting Create new. This example uses the myResourceGroup resource group. |
| Instance details | |
| Network security group name | Enter a name for the NSG that you're creating. |
| Region | Select the region that you want. |
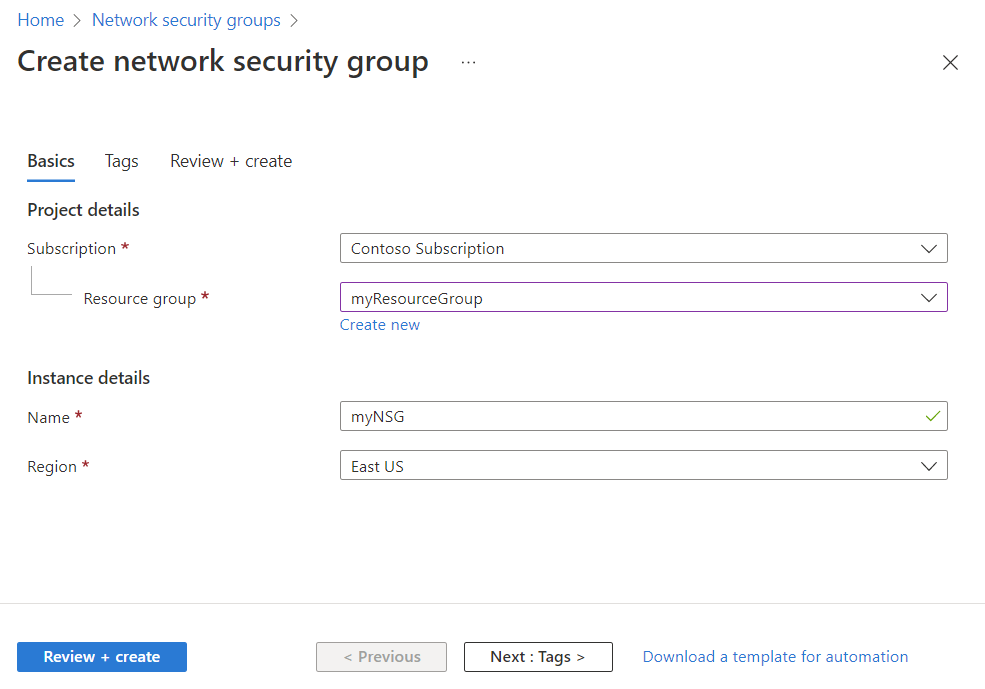
Select Review + create.
After you see the Validation passed message, select Create.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Select Network security groups in the search results to see the list of NSGs in your subscription.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group and select Network security groups in the search results.
Select the name of your NSG.
To learn more about the common Azure settings that are listed, see the following articles:
The most common changes to an NSG are:
For more information about the association and dissociation of an NSG, see Associate or dissociate a network security group.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
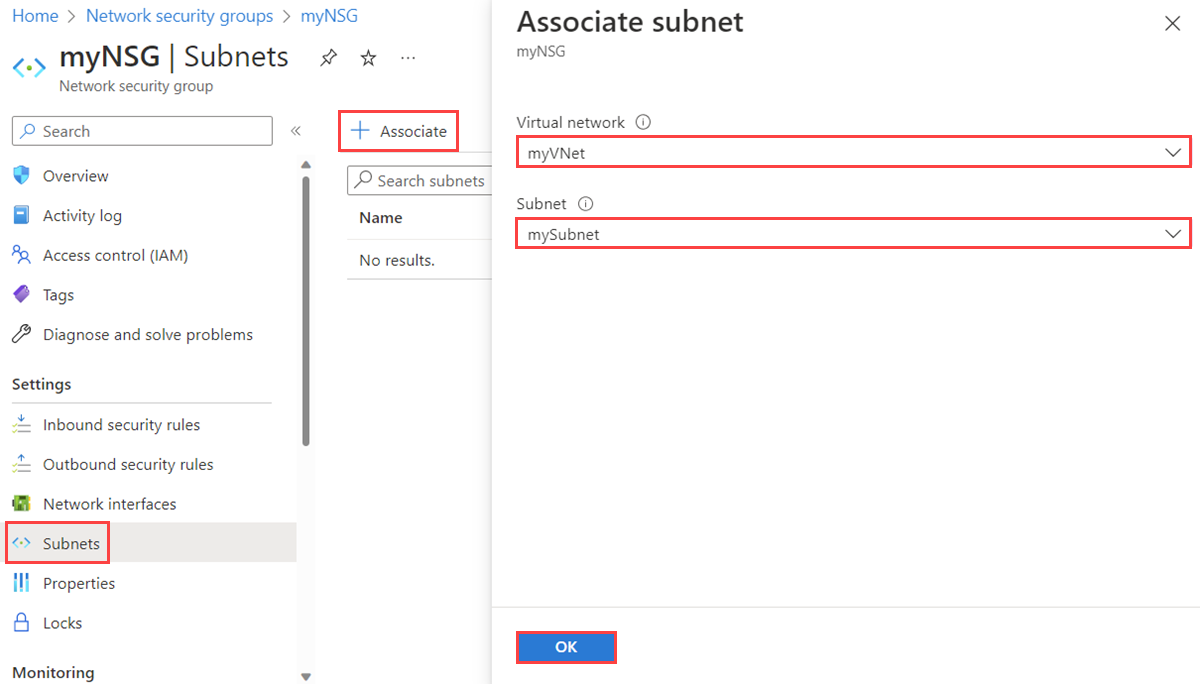
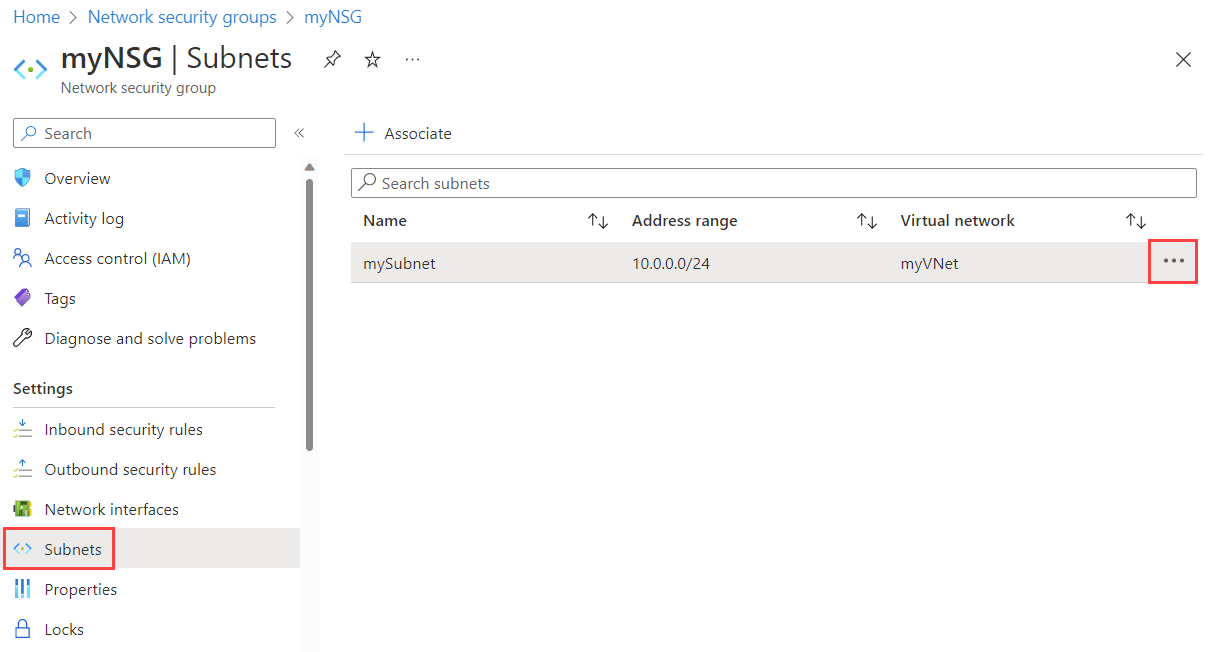
Select the name of your NSG, and then select Subnets.
To associate an NSG to the subnet, select + Associate. Then select your virtual network and the subnet to which you want to associate the NSG. Select OK.
To dissociate an NSG from the subnet, select the three dots next to the subnet from which you want to dissociate the NSG, and then select Dissociate. Select Yes.
If an NSG is associated to any subnets or network interfaces, it can't be deleted. Dissociate an NSG from all subnets and network interfaces before you attempt to delete it.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
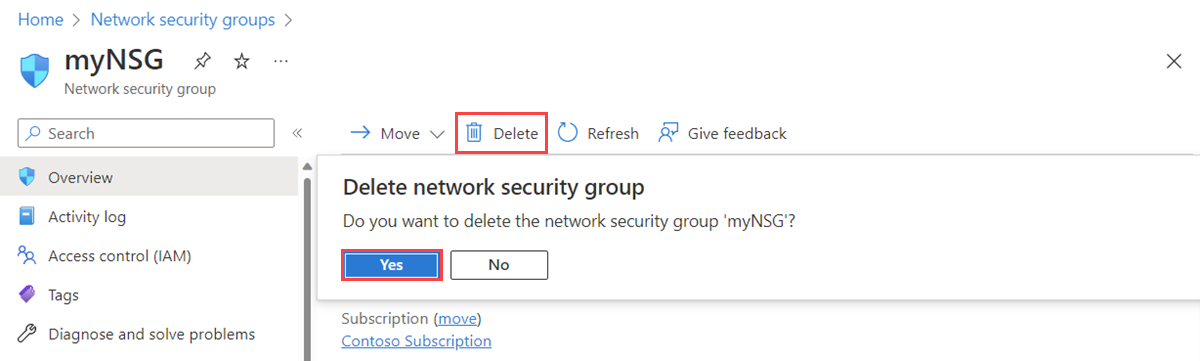
Select the NSG that you want to delete.
Select Delete, and then select Yes in the confirmation dialog box.
An NSG contains zero or more security rules. You can create, view all, view details of, change, and delete a security rule.
The number of rules per NSG that you can create for each Azure location and subscription is limited. To learn more, see Azure subscription and service limits, quotas, and constraints.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
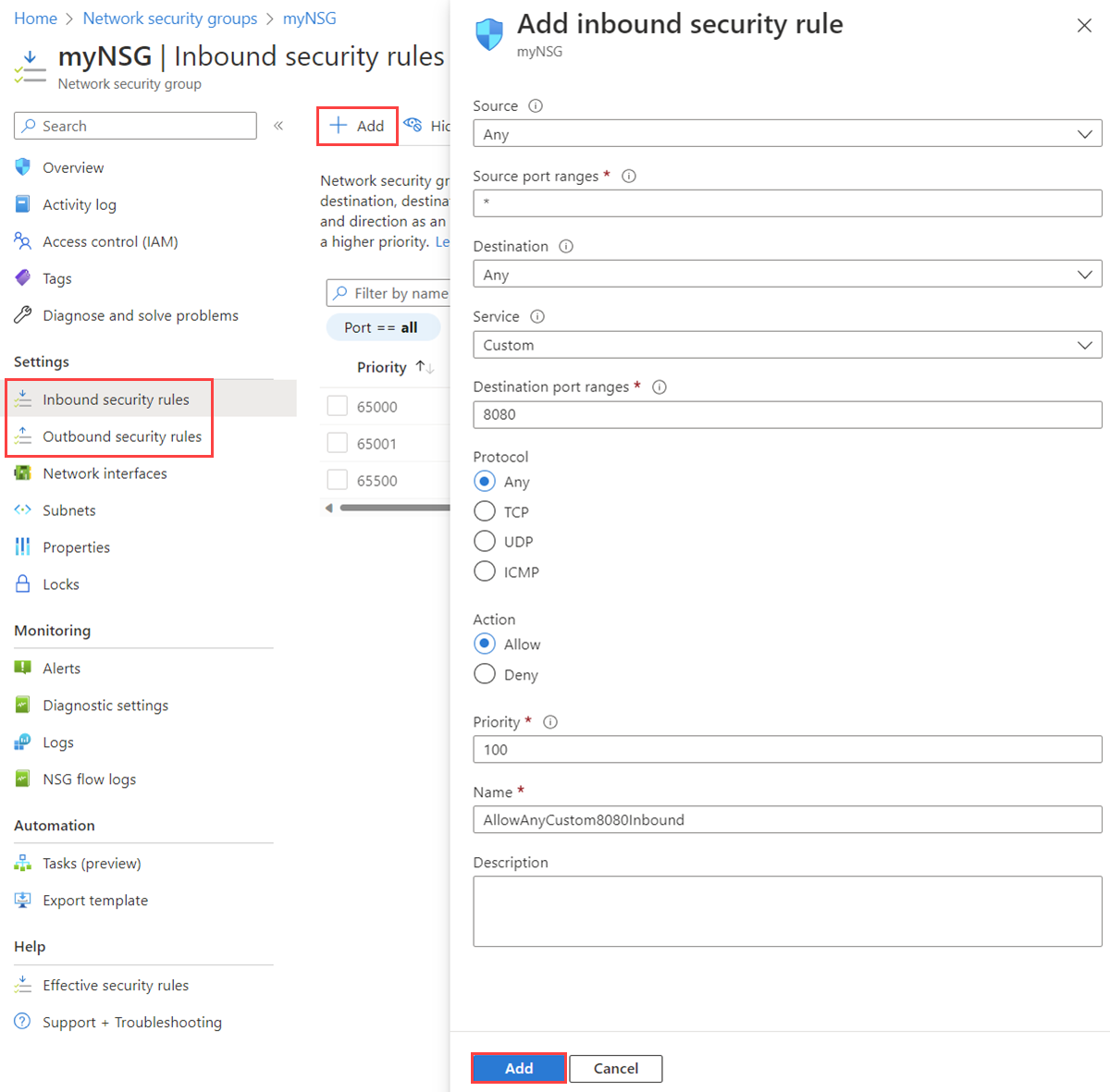
Select the name of the NSG to which you want to add a security rule.
Select Inbound security rules or Outbound security rules.
Several existing rules are listed, including some that you might not have added. When you create an NSG, several default security rules are created in it. To learn more, see Default security rules. You can't delete default security rules, but you can override them with rules that have a higher priority.
Select + Add. Select or add values for the following settings, and then select Add.
| Setting | Value | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Source | One of:
|
If you select IP Addresses, you must also specify Source IP addresses/CIDR ranges. If you select Service Tag, you must also select a Source service tag. If you select Application security group, you must also select an existing application security group. If you select Application security group for both Source and Destination, the network interfaces within both application security groups must be in the same virtual network. Learn how to create an application security group. |
| Source IP addresses/CIDR ranges | A comma-delimited list of IP addresses and Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR) ranges | This setting appears if you set Source to IP Addresses. You must specify a single value or comma-separated list of multiple values. An example of multiple values is If the IP address that you specify is assigned to an Azure VM, specify its private IP address, not its public IP address. Azure processes security rules after it translates the public IP address to a private IP address for inbound security rules, but before it translates a private IP address to a public IP address for outbound rules. To learn more about IP addresses in Azure, see Public IP addresses and Private IP addresses. |
| Source service tag | A service tag from the dropdown list | This setting appears if you set Source to Service Tag for a security rule. A service tag is a predefined identifier for a category of IP addresses. To learn more about available service tags, and what each tag represents, see Service tags. |
| Source application security group | An existing application security group | This setting appears if you set Source to Application security group. Select an application security group that exists in the same region as the network interface. Learn how to create an application security group. |
| Source port ranges | One of:
|
This setting specifies the ports on which the rule allows or denies traffic. The number of ports that you can specify is limited. For more information, see Azure limits. |
| Destination | One of:
|
If you select IP Addresses, you must also specify Destination IP addresses/CIDR ranges. If you select Service Tag, you must also select a Destination service tag. If you select Application security group, you must also select an existing application security group. If you select Application security group for both Source and Destination, the network interfaces within both application security groups must be in the same virtual network. Learn how to create an application security group. |
| Destination IP addresses/CIDR ranges | A comma-delimited list of IP addresses and CIDR ranges | This setting appears if you change Destination to IP Addresses. You can specify single or multiple addresses or ranges like you can do with Source and Source IP addresses/CIDR ranges. The number that you can specify is limited. For more information, see Azure limits. If the IP address that you specify is assigned to an Azure VM, ensure that you specify its private IP, not its public IP address. Azure processes security rules after it translates the public IP address to a private IP address for inbound security rules, but before Azure translates a private IP address to a public IP address for outbound rules. To learn more about IP addresses in Azure, see Public IP addresses and Private IP addresses. |
| Destination service tag | A service tag from the dropdown list | This setting appears if you set Destination to Service Tag for a security rule. A service tag is a predefined identifier for a category of IP addresses. To learn more about available service tags, and what each tag represents, see Service tags. |
| Destination application security group | An existing application security group | This setting appears if you set Destination to Application security group. Select an application security group that exists in the same region as the network interface. Learn how to create an application security group. |
| Service | A destination protocol from the dropdown list | This setting specifies the destination protocol and port range for the security rule. You can select a predefined service, like RDP, or select Custom and provide the port range in Destination port ranges. |
| Destination port ranges | One of:
|
As with Source port ranges, you can specify single or multiple ports and ranges. The number that you can specify is limited. For more information, see Azure limits. |
| Protocol | Any, TCP, UDP, or ICMP | You can restrict the rule to the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), User Datagram Protocol (UDP), or Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP). The default is for the rule to apply to all protocols (Any). |
| Action | Allow or Deny | This setting specifies whether this rule allows or denies access for the supplied source and destination configuration. |
| Priority | A value between 100 and 4,096 that's unique for all security rules within the NSG | Azure processes security rules in priority order. The lower the number, the higher the priority. We recommend that you leave a gap between priority numbers when you create rules, such as 100, 200, and 300. Leaving gaps makes it easier to add rules in the future so that you can give them higher or lower priority than existing rules. |
| Name | A unique name for the rule within the NSG | The name can be up to 80 characters. It must begin with a letter or number, and it must end with a letter, number, or underscore. The name can contain only letters, numbers, underscores, periods, or hyphens. |
| Description | A text description | You can optionally specify a text description for the security rule. The description can't be longer than 140 characters. |
An NSG contains zero or more rules. To learn more about the list of information when you view the rules, see Security rules.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
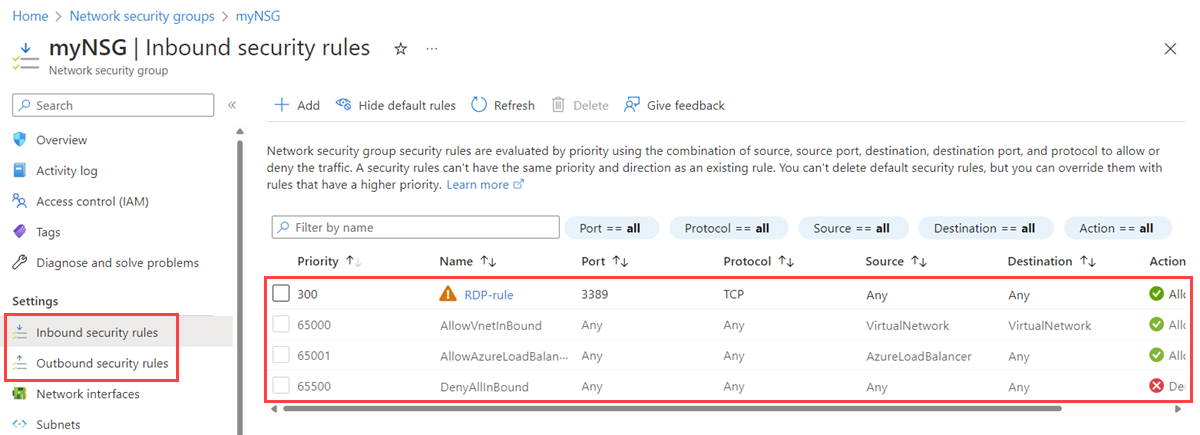
Select the name of the NSG for which you want to view the rules.
Select Inbound security rules or Outbound security rules.
The list contains any rules that you created and the default security rules of your NSG.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
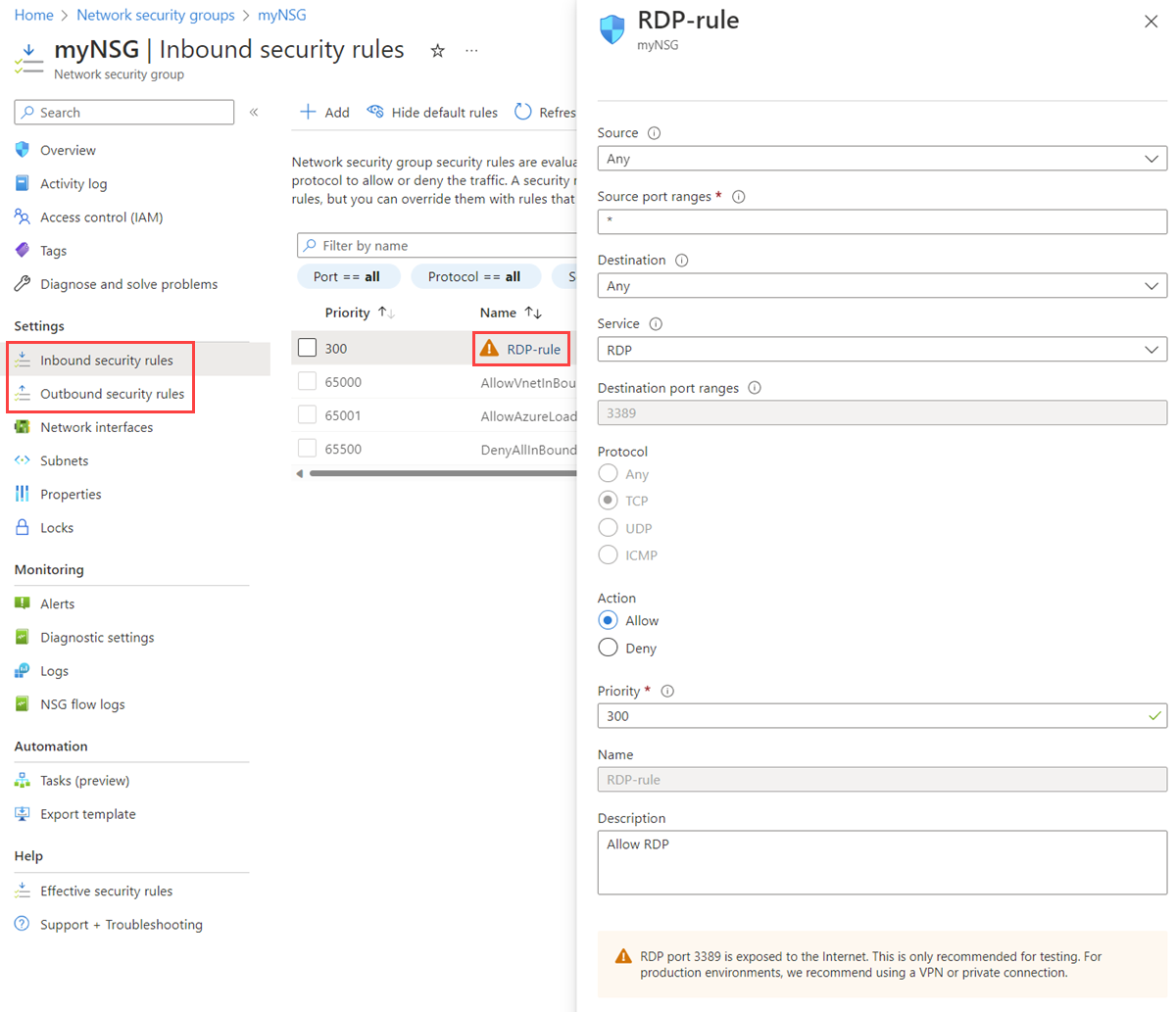
Select the name of the NSG for which you want to view the rules.
Select Inbound security rules or Outbound security rules.
Select the rule for which you want to view details. For an explanation of all settings, see Security rule settings.
Note
This procedure applies only to a custom security rule. It doesn't work if you choose a default security rule.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
Select the name of the NSG for which you want to view the rules.
Select Inbound security rules or Outbound security rules.
Select the rule that you want to change.
Change the settings as needed, and then select Save. For an explanation of all settings, see Security rule settings.
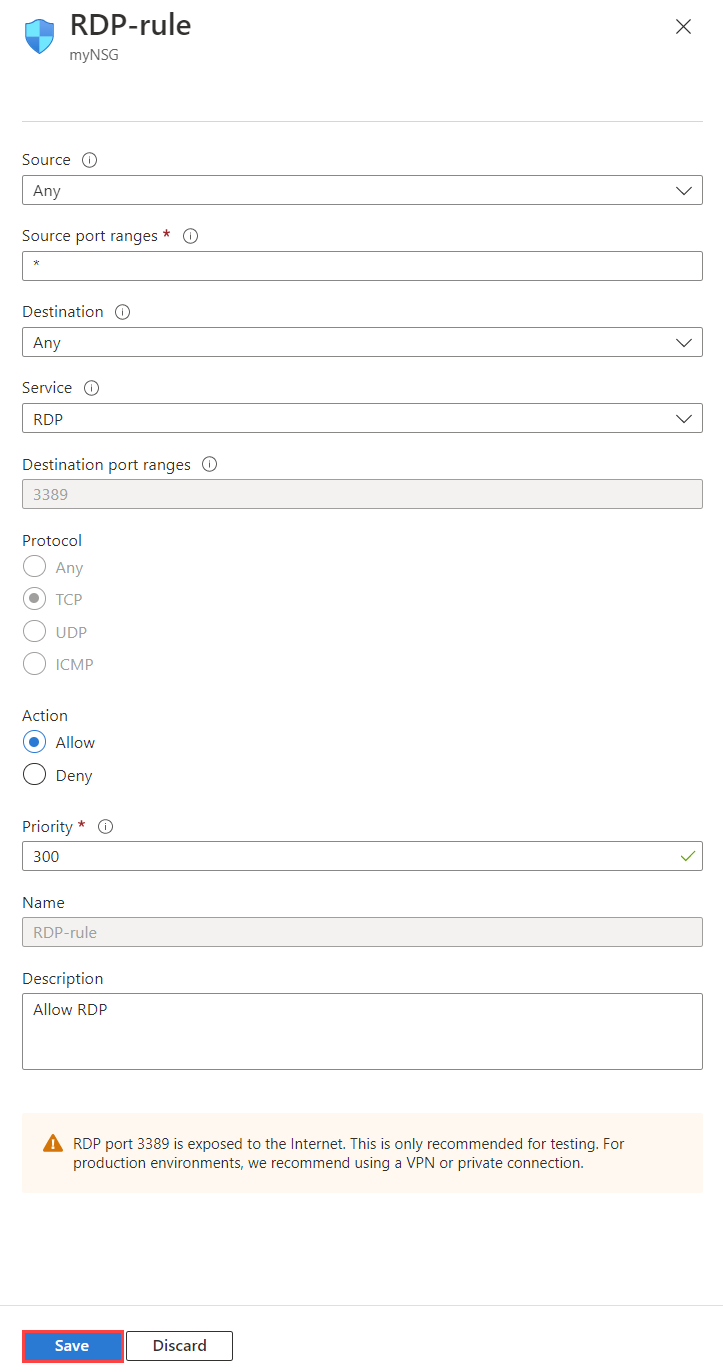
Note
This procedure applies only to a custom security rule. You aren't allowed to change a default security rule.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Network security group. Then select Network security groups in the search results.
Select the name of the NSG for which you want to view the rules.
Select Inbound security rules or Outbound security rules.
Select the rules that you want to delete.
Select Delete, and then select Yes.
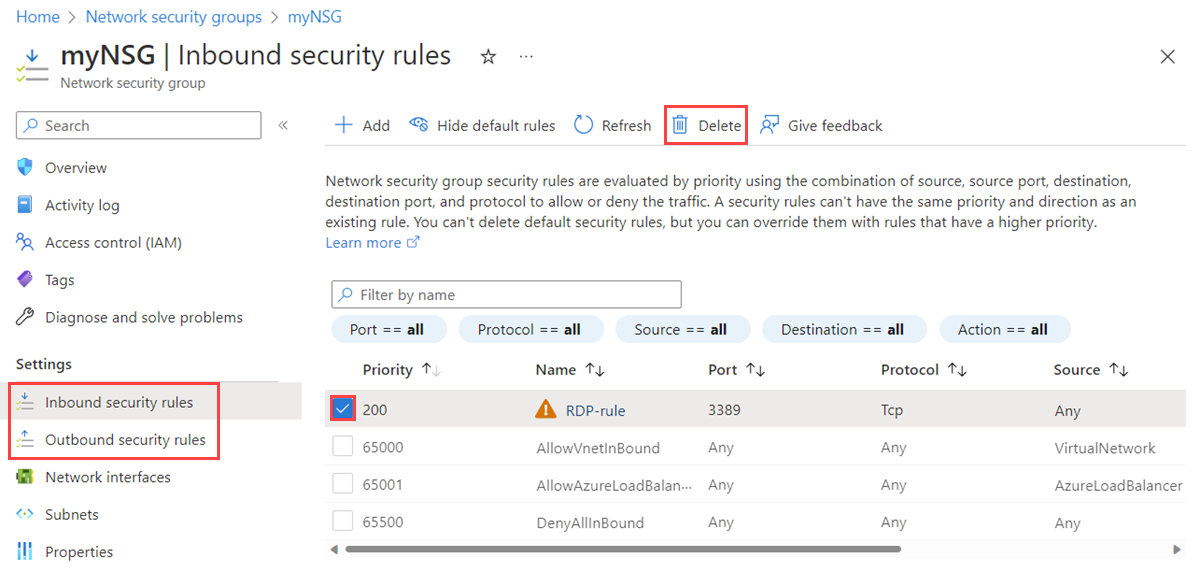
Note
This procedure applies only to a custom security rule. You aren't allowed to delete a default security rule.
An application security group contains zero or more network interfaces. To learn more, see Application security groups. All network interfaces in an application security group must exist in the same virtual network. To learn how to add a network interface to an application security group, see Add a network interface to an application security group.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Application security group. Then select Application security groups in the search results.
Select + Create.
On the Create an application security group page, under the Basics tab, enter or select the following values:
| Setting | Action |
|---|---|
| Project details | |
| Subscription | Select your Azure subscription. |
| Resource group | Select an existing resource group, or create a new one by selecting Create new. This example uses the myResourceGroup resource group. |
| Instance details | |
| Name | Enter a name for the application security group that you're creating. |
| Region | Select the region in which you want to create the application security group. |
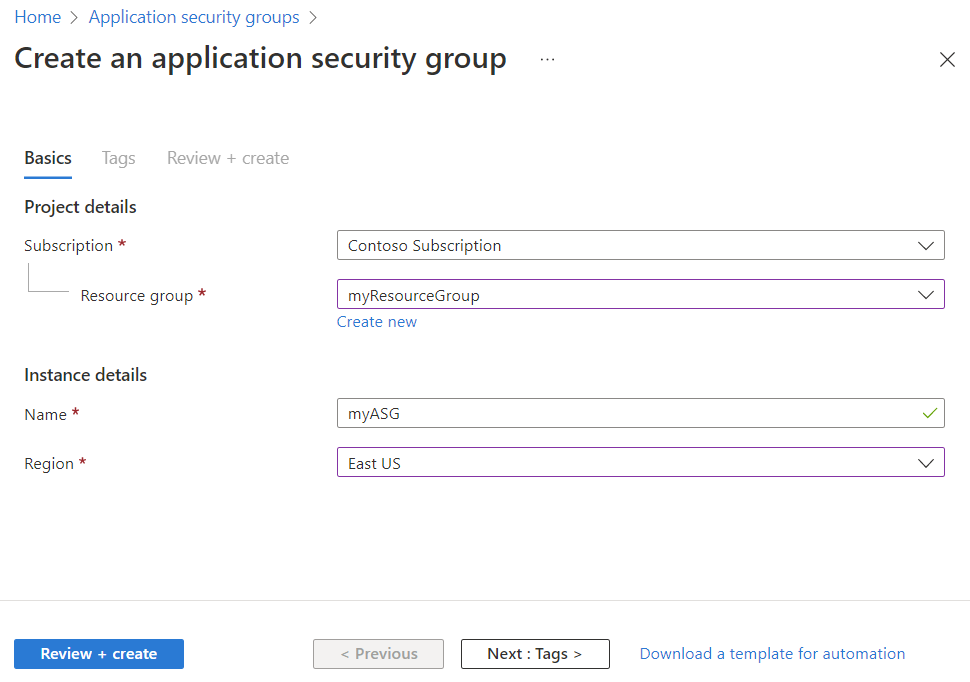
Select Review + create.
After you see the Validation passed message, select Create.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Application security group. Then select Application security groups in the search results. A list of your application security groups appears in the Azure portal.

In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Application security group. Then select Application security groups in the search results.
Select the application security group for which you want to view the details.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Application security group. Then select Application security groups in the search results.
Select the application security group that you want to change:
Select move next to Resource group or Subscription to change the resource group or subscription, respectively.
Select edit next to Tags to add or remove tags. To learn more, see Use tags to organize your Azure resources and management hierarchy.
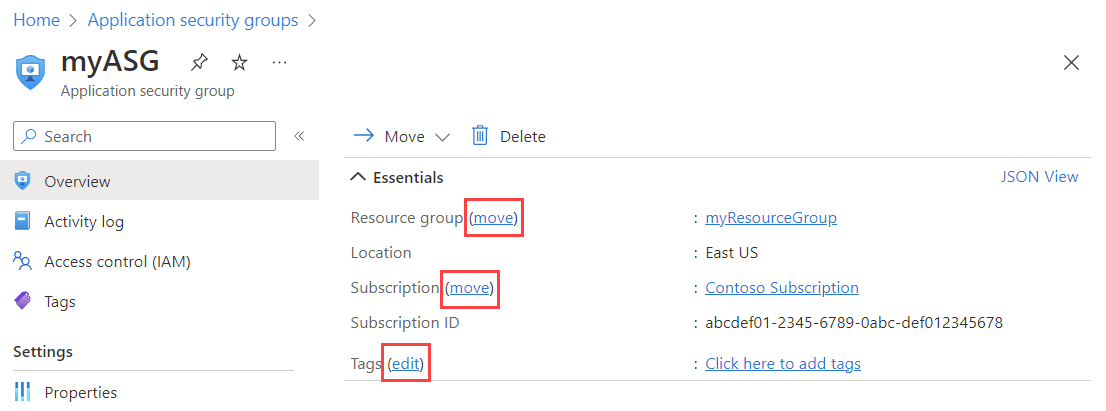
Note
You can't change the location of an application security group.
Select Access control (IAM) to assign or remove permissions to the application security group.
You can't delete an application security group if it contains any network interfaces. To remove all network interfaces from the application security group, either change the network interface settings or delete the network interfaces. To learn more, see Add or remove from application security groups or Delete a network interface.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Application security group. Then select Application security groups in the search results.
Select the application security group that you want to delete.
Select Delete, and then select Yes to delete the application security group.
To manage NSGs, security rules, and application security groups, your account must be assigned to the Network Contributor role. You can also use a custom role with the appropriate permissions assigned, as listed in the following tables.
Note
You might not see the full list of service tags if the Network Contributor role was assigned at a resource group level. To view the full list, you can assign this role at a subscription scope instead. If you can only allow the Network Contributor role for the resource group, you can then also create a custom role for the permissions Microsoft.Network/locations/serviceTags/read and Microsoft.Network/locations/serviceTagDetails/read. Assign them at a subscription scope along with the Network Contributor role at the resource group scope.
| Action | Name |
|---|---|
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/read |
Get an NSG. |
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/write |
Create or update an NSG. |
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/delete |
Delete an NSG. |
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/join/action |
Associate an NSG to a subnet or network interface. |
Note
To perform write operations on an NSG, the subscription account must have at least read permissions for the resource group along with Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/write permission.
| Action | Name |
|---|---|
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/securityRules/read |
Get a rule. |
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/securityRules/write |
Create or update a rule. |
Microsoft.Network/networkSecurityGroups/securityRules/delete |
Delete a rule. |
| Action | Name |
|---|---|
Microsoft.Network/applicationSecurityGroups/joinIpConfiguration/action |
Join an IP configuration to an application security group. |
Microsoft.Network/applicationSecurityGroups/joinNetworkSecurityRule/action |
Join a security rule to an application security group. |
Microsoft.Network/applicationSecurityGroups/read |
Get an application security group. |
Microsoft.Network/applicationSecurityGroups/write |
Create or update an application security group. |
Microsoft.Network/applicationSecurityGroups/delete |
Delete an application security group. |
Training
Module
Configure network security groups - Training
Learn how to implement network security groups, and ensure network security group rules are correctly applied.
Documentation
Azure network security groups overview
Learn about network security groups. Network security groups help you filter network traffic between Azure resources.
Network security group - how it works
Learn how network security groups help you filter network traffic between Azure resources.
Tutorial: Filter network traffic with a network security group (NSG)
In this tutorial, you learn how to filter network traffic to a subnet with a network security group (NSG).