Manage indexing policies in Azure Cosmos DB
In Azure Cosmos DB, data is indexed following indexing policies that are defined for each container. The default indexing policy for newly created containers enforces range indexes for any string or number. You can override this policy with your own custom indexing policy.
Note
The method of updating indexing policies described in this article only applies to Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL. Learn about indexing in Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB and Secondary indexing in Azure Cosmos DB for Apache Cassandra.
Here are some examples of indexing policies shown in their JSON format. They're exposed on the Azure portal in JSON format. The same parameters can be set through the Azure CLI or any SDK.
{
"indexingMode": "consistent",
"includedPaths": [
{
"path": "/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths": [
{
"path": "/path/to/single/excluded/property/?"
},
{
"path": "/path/to/root/of/multiple/excluded/properties/*"
}
]
}
{
"indexingMode": "consistent",
"includedPaths": [
{
"path": "/path/to/included/property/?"
},
{
"path": "/path/to/root/of/multiple/included/properties/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths": [
{
"path": "/*"
}
]
}
Note
We generally recommend that you use an opt-out indexing policy. Azure Cosmos DB proactively indexes any new property that might be added to your data model.
{
"indexingMode": "consistent",
"automatic": true,
"includedPaths": [
{
"path": "/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths": [
{
"path": "/_etag/?"
}
],
"spatialIndexes": [
{
"path": "/path/to/geojson/property/?",
"types": [
"Point",
"Polygon",
"MultiPolygon",
"LineString"
]
}
]
}
In addition to including or excluding paths for individual properties, you can also specify a vector index. In general, vector indexes should be specified whenever the VectorDistance system function is used to measure similarity between a query vector and a vector property.
Note
Before proceeding, you must enable the Azure Cosmos DB NoSQL Vector Indexing and Search.
Important
A vector indexing policy must be on the same path defined in the container's vector policy. Learn more about container vector policies.
{
"indexingMode": "consistent",
"automatic": true,
"includedPaths": [
{
"path": "/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths": [
{
"path": "/_etag/?"
},
{
"path": "/vector/*"
}
],
"vectorIndexes": [
{
"path": "/vector",
"type": "quantizedFlat"
}
]
}
Important
The vector path added to the "excludedPaths" section of the indexing policy to ensure optimized performance for insertion. Not adding the vector path to "excludedPaths" will result in higher RU charge and latency for vector insertions.
Important
Currently, vector policies and vector indexes are immutable after creation. To make changes, please create a new collection.
You can define the following types of vector index policies:
| Type | Description | Max dimensions |
|---|---|---|
flat |
Stores vectors on the same index as other indexed properties. | 505 |
quantizedFlat |
Quantizes (compresses) vectors before storing on the index. This can improve latency and throughput at the cost of a small amount of accuracy. | 4096 |
diskANN |
Creates an index based on DiskANN for fast and efficient approximate search. | 4096 |
The flat and quantizedFlat index types leverage Azure Cosmos DB's index to store and read each vector when performing a vector search. Vector searches with a flat index are brute-force searches and produce 100% accuracy. However, there is a limitation of 505 dimensions for vectors on a flat index.
The quantizedFlat index stores quantized or compressed vectors on the index. Vector searches with quantizedFlat index are also brute-force searches, however their accuracy might be slightly less than 100% since the vectors are quantized before adding to the index. However, vector searches with quantized flat should have lower latency, higher throughput, and lower RU cost than vector searches on a flat index. This is a good option for scenarios where you are using query filters to narrow down the vector search to a relatively small set of vectors.
The diskANN index is a separate index defined specifically for vectors leveraging DiskANN, a suite of highly performant vector indexing algorithms developed by Microsoft Research. DiskANN indexes can offer some of the lowest latency, highest query-per-second (QPS), and lowest RU cost queries at high accuracy. However, since DiskANN is an approximate nearest neighbors (ANN) index, the accuracy may be lower than quantizedFlat or flat.
The diskANN and quantizedFlat indexes can take optional index build parameters that can be used to tune the accuracy vs latency trade-off that applies to every Approximate Nearest Neighbors vector index.
quantizationByteSize: Sets the size (in bytes) for product quantization. Min=1, Default=dynamic (system decides), Max=512. Setting this larger may result in higher accuracy vector searches at expense of higher RU cost and higher latency. This applies to bothquantizedFlatandDiskANNindex types.indexingSearchListSize: Sets how many vectors to search over during index build construction. Min=10, Default=100, Max=500. Setting this larger may result in higher accuracy vector searches at the expense of longer index build times and higher vector ingest latencies. This applies toDiskANNindexes only.
This example indexing policy defines a tuple index on events.name and events.category
{
"automatic":true,
"indexingMode":"Consistent",
"includedPaths":[
{"path":"/*"},
{"path":"/events/[]/{name,category}/?"}
],
"excludedPaths":[],
"compositeIndexes":[]
}
The above index is used for the below query.
SELECT *
FROM root r
WHERE
EXISTS (SELECT VALUE 1 FROM ev IN r.events
WHERE ev.name = ‘M&M’ AND ev.category = ‘Candy’)
In addition to including or excluding paths for individual properties, you can also specify a composite index. To perform a query that has an ORDER BY clause for multiple properties, a composite index is required on those properties. If the query includes filters along with sorting on multiple properties, you may need more than one composite index.
Composite indexes also have a performance benefit for queries that have multiple filters or both a filter and an ORDER BY clause.
Note
Composite paths have an implicit /? since only the scalar value at that path is indexed. The /* wildcard is not supported in composite paths. You shouldn't specify /? or /* in a composite path. Composite paths are also case-sensitive.
{
"automatic":true,
"indexingMode":"Consistent",
"includedPaths":[
{
"path":"/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths":[],
"compositeIndexes":[
[
{
"path":"/name",
"order":"ascending"
},
{
"path":"/age",
"order":"descending"
}
]
]
}
The composite index on name and age is required for the following queries:
Query #1:
SELECT *
FROM c
ORDER BY c.name ASC, c.age DESC
Query #2:
SELECT *
FROM c
ORDER BY c.name DESC, c.age ASC
This composite index benefits the following queries and optimizes the filters:
Query #3:
SELECT *
FROM c
WHERE c.name = "Tim"
ORDER BY c.name DESC, c.age ASC
Query #4:
SELECT *
FROM c
WHERE c.name = "Tim" AND c.age > 18
You can define multiple composite indexes within the same indexing policy.
{
"automatic":true,
"indexingMode":"Consistent",
"includedPaths":[
{
"path":"/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths":[],
"compositeIndexes":[
[
{
"path":"/name",
"order":"ascending"
},
{
"path":"/age",
"order":"ascending"
}
],
[
{
"path":"/name",
"order":"ascending"
},
{
"path":"/age",
"order":"descending"
}
]
]
}
It's optional to specify the order. If not specified, the order is ascending.
{
"automatic":true,
"indexingMode":"Consistent",
"includedPaths":[
{
"path":"/*"
}
],
"excludedPaths":[],
"compositeIndexes":[
[
{
"path":"/name"
},
{
"path":"/age"
}
]
]
}
You can use this policy where the Time-to-Live (TTL) feature is active but no other indexes are necessary to use Azure Cosmos DB as a pure key-value store.
{
"indexingMode": "consistent",
"includedPaths": [],
"excludedPaths": [{
"path": "/*"
}]
}
This policy turns off indexing. If indexingMode is set to none, you can't set a TTL on the container.
{
"indexingMode": "none"
}
In Azure Cosmos DB, the indexing policy can be updated using any of the following methods:
- From the Azure portal
- Using the Azure CLI
- Using PowerShell
- Using one of the SDKs
An indexing policy update triggers an index transformation. The progress of this transformation can also be tracked from the SDKs.
Note
When you update indexing policy, writes to Azure Cosmos DB are uninterrupted. Learn more about indexing transformations.
Important
Removing an index takes effect immediately, whereas adding a new index takes some time as it requires an indexing transformation. When replacing one index with another (for example, replacing a single property index with a composite-index) make sure to add the new index first and then wait for the index transformation to complete before you remove the previous index from the indexing policy. Otherwise this will negatively affect your ability to query the previous index and may break any active workloads that reference the previous index.
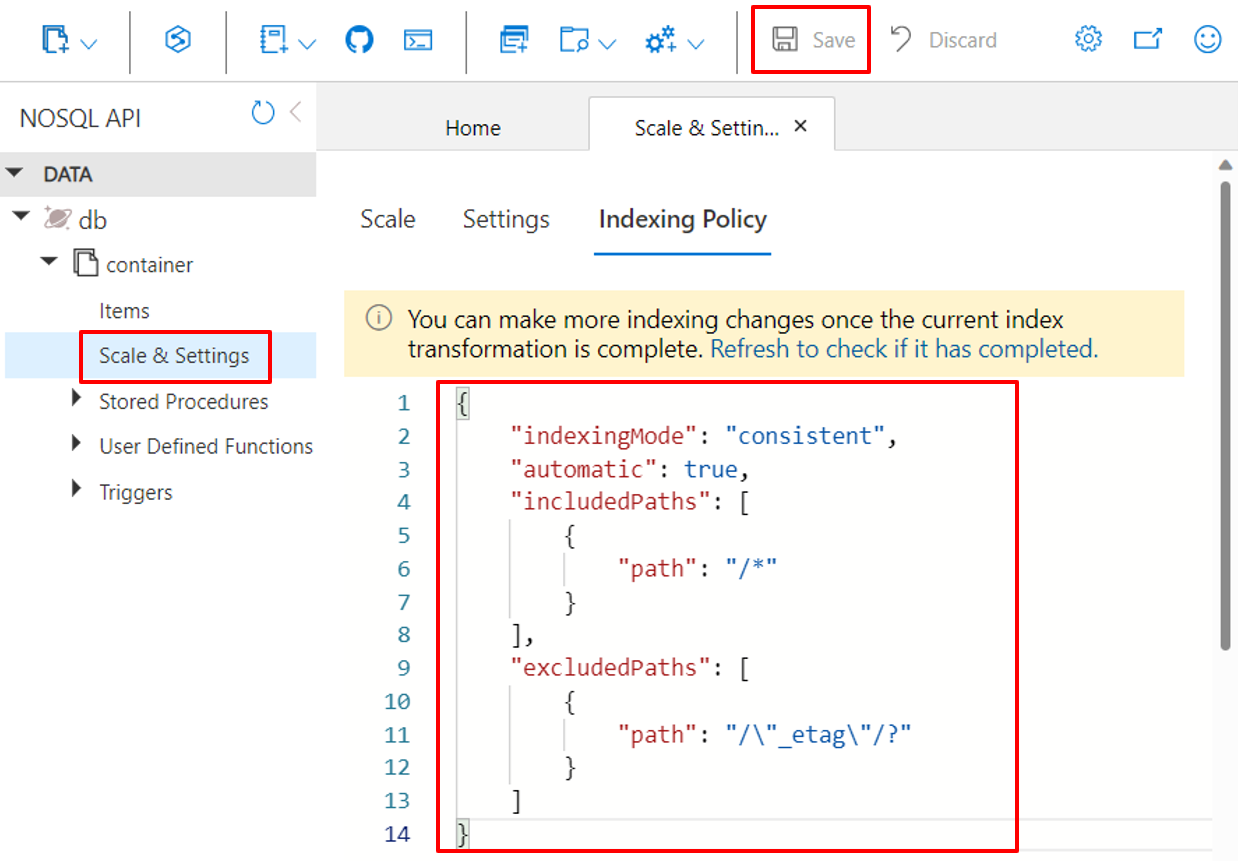
Azure Cosmos DB containers store their indexing policy as a JSON document that the Azure portal lets you directly edit.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
Create a new Azure Cosmos DB account or select an existing account.
Open the Data Explorer pane and select the container that you want to work on.
Select Scale & Settings.
Modify the indexing policy JSON document, as shown in these examples.
Select Save when you're done.
To create a container with a custom indexing policy, see Create a container with a custom index policy using CLI.
To create a container with a custom indexing policy, see Create a container with a custom index policy using PowerShell.
The ContainerProperties object from the .NET SDK v3 exposes an IndexingPolicy property that lets you change the IndexingMode and add or remove IncludedPaths and ExcludedPaths. For more information, see Quickstart: Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL client library for .NET.
// Retrieve the container's details
ContainerResponse containerResponse = await client.GetContainer("database", "container").ReadContainerAsync();
// Set the indexing mode to consistent
containerResponse.Resource.IndexingPolicy.IndexingMode = IndexingMode.Consistent;
// Add an included path
containerResponse.Resource.IndexingPolicy.IncludedPaths.Add(new IncludedPath { Path = "/*" });
// Add an excluded path
containerResponse.Resource.IndexingPolicy.ExcludedPaths.Add(new ExcludedPath { Path = "/name/*" });
// Add a spatial index
SpatialPath spatialPath = new SpatialPath
{
Path = "/locations/*"
};
spatialPath.SpatialTypes.Add(SpatialType.Point);
containerResponse.Resource.IndexingPolicy.SpatialIndexes.Add(spatialPath);
// Add a composite index
containerResponse.Resource.IndexingPolicy.CompositeIndexes.Add(new Collection<CompositePath> { new CompositePath() { Path = "/name", Order = CompositePathSortOrder.Ascending }, new CompositePath() { Path = "/age", Order = CompositePathSortOrder.Descending } });
// Update container with changes
await client.GetContainer("database", "container").ReplaceContainerAsync(containerResponse.Resource);
To track the index transformation progress, pass a RequestOptions object that sets the PopulateQuotaInfo property to true. Retrieve the value from the x-ms-documentdb-collection-index-transformation-progress response header.
// retrieve the container's details
ContainerResponse containerResponse = await client.GetContainer("database", "container").ReadContainerAsync(new ContainerRequestOptions { PopulateQuotaInfo = true });
// retrieve the index transformation progress from the result
long indexTransformationProgress = long.Parse(containerResponse.Headers["x-ms-documentdb-collection-index-transformation-progress"]);
The SDK V3 fluent API lets you write this definition in a concise and efficient way when defining a custom indexing policy while creating a new container:
await client.GetDatabase("database").DefineContainer(name: "container", partitionKeyPath: "/myPartitionKey")
.WithIndexingPolicy()
.WithIncludedPaths()
.Path("/*")
.Attach()
.WithExcludedPaths()
.Path("/name/*")
.Attach()
.WithSpatialIndex()
.Path("/locations/*", SpatialType.Point)
.Attach()
.WithCompositeIndex()
.Path("/name", CompositePathSortOrder.Ascending)
.Path("/age", CompositePathSortOrder.Descending)
.Attach()
.Attach()
.CreateIfNotExistsAsync();
The DocumentCollection object from the Java SDK exposes the getIndexingPolicy() and setIndexingPolicy() methods. The IndexingPolicy object they manipulate lets you change the indexing mode and add or remove included and excluded paths. For more information, see Quickstart: Build a Java app to manage Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL data.
// Retrieve the container's details
Observable<ResourceResponse<DocumentCollection>> containerResponse = client.readCollection(String.format("/dbs/%s/colls/%s", "database", "container"), null);
containerResponse.subscribe(result -> {
DocumentCollection container = result.getResource();
IndexingPolicy indexingPolicy = container.getIndexingPolicy();
// Set the indexing mode to consistent
indexingPolicy.setIndexingMode(IndexingMode.Consistent);
// Add an included path
Collection<IncludedPath> includedPaths = new ArrayList<>();
IncludedPath includedPath = new IncludedPath();
includedPath.setPath("/*");
includedPaths.add(includedPath);
indexingPolicy.setIncludedPaths(includedPaths);
// Add an excluded path
Collection<ExcludedPath> excludedPaths = new ArrayList<>();
ExcludedPath excludedPath = new ExcludedPath();
excludedPath.setPath("/name/*");
excludedPaths.add(excludedPath);
indexingPolicy.setExcludedPaths(excludedPaths);
// Add a spatial index
Collection<SpatialSpec> spatialIndexes = new ArrayList<SpatialSpec>();
Collection<SpatialType> collectionOfSpatialTypes = new ArrayList<SpatialType>();
SpatialSpec spec = new SpatialSpec();
spec.setPath("/locations/*");
collectionOfSpatialTypes.add(SpatialType.Point);
spec.setSpatialTypes(collectionOfSpatialTypes);
spatialIndexes.add(spec);
indexingPolicy.setSpatialIndexes(spatialIndexes);
// Add a composite index
Collection<ArrayList<CompositePath>> compositeIndexes = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<CompositePath> compositePaths = new ArrayList<>();
CompositePath nameCompositePath = new CompositePath();
nameCompositePath.setPath("/name");
nameCompositePath.setOrder(CompositePathSortOrder.Ascending);
CompositePath ageCompositePath = new CompositePath();
ageCompositePath.setPath("/age");
ageCompositePath.setOrder(CompositePathSortOrder.Descending);
compositePaths.add(ageCompositePath);
compositePaths.add(nameCompositePath);
compositeIndexes.add(compositePaths);
indexingPolicy.setCompositeIndexes(compositeIndexes);
// Update the container with changes
client.replaceCollection(container, null);
});
To track the index transformation progress on a container, pass a RequestOptions object that requests the quota info to be populated. Retrieve the value from the x-ms-documentdb-collection-index-transformation-progress response header.
// set the RequestOptions object
RequestOptions requestOptions = new RequestOptions();
requestOptions.setPopulateQuotaInfo(true);
// retrieve the container's details
Observable<ResourceResponse<DocumentCollection>> containerResponse = client.readCollection(String.format("/dbs/%s/colls/%s", "database", "container"), requestOptions);
containerResponse.subscribe(result -> {
// retrieve the index transformation progress from the response headers
String indexTransformationProgress = result.getResponseHeaders().get("x-ms-documentdb-collection-index-transformation-progress");
});
The ContainerDefinition interface from Node.js SDK exposes an indexingPolicy property that lets you change the indexingMode and add or remove includedPaths and excludedPaths. For more information, see Quickstart - Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL client library for Node.js.
Retrieve the container's details:
const containerResponse = await client.database('database').container('container').read();
Set the indexing mode to consistent:
containerResponse.body.indexingPolicy.indexingMode = "consistent";
Add included path including a spatial index:
containerResponse.body.indexingPolicy.includedPaths.push({
includedPaths: [
{
path: "/age/*",
indexes: [
{
kind: cosmos.DocumentBase.IndexKind.Range,
dataType: cosmos.DocumentBase.DataType.String
},
{
kind: cosmos.DocumentBase.IndexKind.Range,
dataType: cosmos.DocumentBase.DataType.Number
}
]
},
{
path: "/locations/*",
indexes: [
{
kind: cosmos.DocumentBase.IndexKind.Spatial,
dataType: cosmos.DocumentBase.DataType.Point
}
]
}
]
});
Add excluded path:
containerResponse.body.indexingPolicy.excludedPaths.push({ path: '/name/*' });
Update the container with changes:
const replaceResponse = await client.database('database').container('container').replace(containerResponse.body);
To track the index transformation progress on a container, pass a RequestOptions object that sets the populateQuotaInfo property to true. Retrieve the value from the x-ms-documentdb-collection-index-transformation-progress response header.
// retrieve the container's details
const containerResponse = await client.database('database').container('container').read({
populateQuotaInfo: true
});
// retrieve the index transformation progress from the response headers
const indexTransformationProgress = replaceResponse.headers['x-ms-documentdb-collection-index-transformation-progress'];
Add a composite index:
console.log("create container with composite indexes");
const containerDefWithCompositeIndexes = {
id: "containerWithCompositeIndexingPolicy",
indexingPolicy: {
automatic: true,
indexingMode: IndexingMode.consistent,
includedPaths: [
{
path: "/*",
},
],
excludedPaths: [
{
path: '/"systemMetadata"/*',
},
],
compositeIndexes: [
[
{ path: "/field", order: "ascending" },
{ path: "/key", order: "ascending" },
],
],
},
};
const containerWithCompositeIndexes = (
await database.containers.create(containerDefWithCompositeIndexes)
).container;
When you use the Python SDK V3, the container configuration is managed as a dictionary. From this dictionary, you can access the indexing policy and all its attributes. For more information, see Quickstart: Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL client library for Python.
Retrieve the container's details:
containerPath = 'dbs/database/colls/collection'
container = client.ReadContainer(containerPath)
Set the indexing mode to consistent:
container['indexingPolicy']['indexingMode'] = 'consistent'
Define an indexing policy with an included path and a spatial index:
container["indexingPolicy"] = {
"indexingMode":"consistent",
"spatialIndexes":[
{"path":"/location/*","types":["Point"]}
],
"includedPaths":[{"path":"/age/*","indexes":[]}],
"excludedPaths":[{"path":"/*"}]
}
Define an indexing policy with an excluded path:
container["indexingPolicy"] = {
"indexingMode":"consistent",
"includedPaths":[{"path":"/*","indexes":[]}],
"excludedPaths":[{"path":"/name/*"}]
}
Add a composite index:
container['indexingPolicy']['compositeIndexes'] = [
[
{
"path": "/name",
"order": "ascending"
},
{
"path": "/age",
"order": "descending"
}
]
]
Update the container with changes:
response = client.ReplaceContainer(containerPath, container)